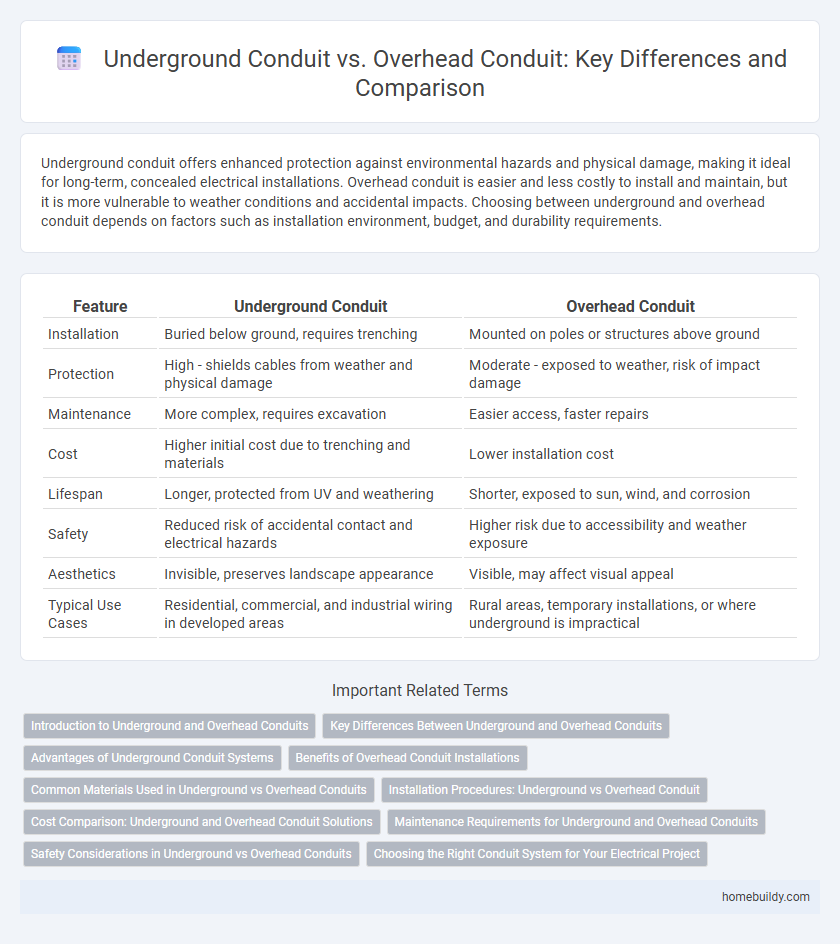
Underground conduit offers enhanced protection against environmental hazards and physical damage, making it ideal for long-term, concealed electrical installations. Overhead conduit is easier and less costly to install and maintain, but it is more vulnerable to weather conditions and accidental impacts. Choosing between underground and overhead conduit depends on factors such as installation environment, budget, and durability requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Underground Conduit | Overhead Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Buried below ground, requires trenching | Mounted on poles or structures above ground |
| Protection | High - shields cables from weather and physical damage | Moderate - exposed to weather, risk of impact damage |
| Maintenance | More complex, requires excavation | Easier access, faster repairs |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to trenching and materials | Lower installation cost |
| Lifespan | Longer, protected from UV and weathering | Shorter, exposed to sun, wind, and corrosion |
| Safety | Reduced risk of accidental contact and electrical hazards | Higher risk due to accessibility and weather exposure |
| Aesthetics | Invisible, preserves landscape appearance | Visible, may affect visual appeal |
| Typical Use Cases | Residential, commercial, and industrial wiring in developed areas | Rural areas, temporary installations, or where underground is impractical |
Introduction to Underground and Overhead Conduits
Underground conduits are designed to protect electrical cables buried beneath the surface, offering enhanced protection against weather, physical damage, and environmental factors. Overhead conduits are installed above ground, typically on poles or building exteriors, providing easy access for maintenance and quick visual inspection. Both types use durable materials such as PVC, metal, or fiberglass, chosen based on installation environment and electrical safety requirements.
Key Differences Between Underground and Overhead Conduits
Underground conduits are installed beneath the surface, offering protection from weather and physical damage, making them suitable for areas prone to harsh environmental conditions. Overhead conduits are mounted above ground on poles or structures, allowing easier access for inspection and maintenance but are more vulnerable to wind, storms, and accidental impacts. Key differences include installation costs, with underground conduits requiring excavation and higher labor expenses, while overhead conduits involve simpler installations but face greater exposure risks.
Advantages of Underground Conduit Systems
Underground conduit systems offer enhanced protection against environmental hazards such as weather, physical damage, and vandalism, ensuring longer lifespan and reliability for electrical wiring. These systems also provide improved aesthetics by eliminating visible cables, which benefits residential and commercial landscapes. Furthermore, underground conduits reduce electromagnetic interference, leading to better signal integrity in sensitive electrical installations.
Benefits of Overhead Conduit Installations
Overhead conduit installations offer superior accessibility for maintenance and repairs, significantly reducing downtime and labor costs. These conduits are less susceptible to water damage and corrosion compared to underground conduits, enhancing their longevity and reliability in diverse weather conditions. Elevated positioning also mitigates risks of accidental physical damage from construction or digging activities common with underground conduit systems.
Common Materials Used in Underground vs Overhead Conduits
Common materials used in underground conduits include PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and HDPE (high-density polyethylene) due to their corrosion resistance and durability in moist, soil environments. Overhead conduits typically utilize rigid metal conduit (RMC) or electrical metallic tubing (EMT) because of their strength and ability to withstand weather exposure and physical impact. Both types prioritize insulation and protection but differ in material selection to suit environmental and mechanical demands.
Installation Procedures: Underground vs Overhead Conduit
Underground conduit installation requires trenching, proper bedding, and sealing to protect cables from moisture and soil pressure, often involving PVC or HDPE pipes for corrosion resistance. Overhead conduit installation involves mounting conduit on poles or building exteriors, requiring secure clamps and weatherproof fittings to withstand wind and temperature variations. Safety protocols differ as underground conduits demand careful excavation to avoid existing utilities, while overhead conduits require fall protection and secure anchoring against environmental exposure.
Cost Comparison: Underground and Overhead Conduit Solutions
Underground conduit installation typically incurs higher initial costs due to excavation, trenching, and waterproofing requirements, while overhead conduit systems are generally more cost-effective with lower labor and material expenses. Maintenance expenses for underground conduits can escalate over time because of potential damage from soil movement and moisture, whereas overhead conduits face increased risks of weather-related wear but offer easier access for repairs. Budget planning for electrical conduit projects should balance upfront installation costs against long-term maintenance and durability factors to determine the most economical solution.
Maintenance Requirements for Underground and Overhead Conduits
Underground conduits require periodic inspection for moisture ingress, corrosion, and physical damage due to soil movement, with maintenance often involving excavation and repair efforts. Overhead conduits demand regular checks for weather-induced wear, UV degradation, and mechanical stress from wind or debris, typically allowing easier visual inspections and quicker repairs. Both types necessitate corrosion-resistant materials and protective coatings to ensure longevity and reduce maintenance frequency.
Safety Considerations in Underground vs Overhead Conduits
Underground conduits offer enhanced protection against physical damage, weather conditions, and electrical hazards, reducing risks of short circuits and fires compared to overhead conduits. Overhead conduits, while easier to inspect and maintain, are more vulnerable to environmental factors such as wind, lightning strikes, and accidental impacts, posing higher safety concerns. Proper installation practices and adherence to NEC (National Electrical Code) guidelines are critical to ensure safety in both underground and overhead conduit systems.
Choosing the Right Conduit System for Your Electrical Project
Selecting the right conduit system hinges on environmental conditions, project requirements, and local regulations. Underground conduit offers superior protection against physical damage and weather, making it ideal for long-lasting installations but requires careful waterproofing and corrosion resistance. Overhead conduit provides easier access for maintenance and lower installation costs, suitable for areas with less risk of impact or environmental exposure.
Underground conduit vs Overhead conduit Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com