EMT conduit is a lightweight, durable metal tubing that provides superior protection against physical damage and is ideal for indoor applications requiring grounding. PVC conduit offers excellent corrosion resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for outdoor and underground installations where moisture exposure is a concern. Both EMT and PVC conduits meet electrical code requirements but differ significantly in material properties, installation procedures, and environmental suitability.
Table of Comparison
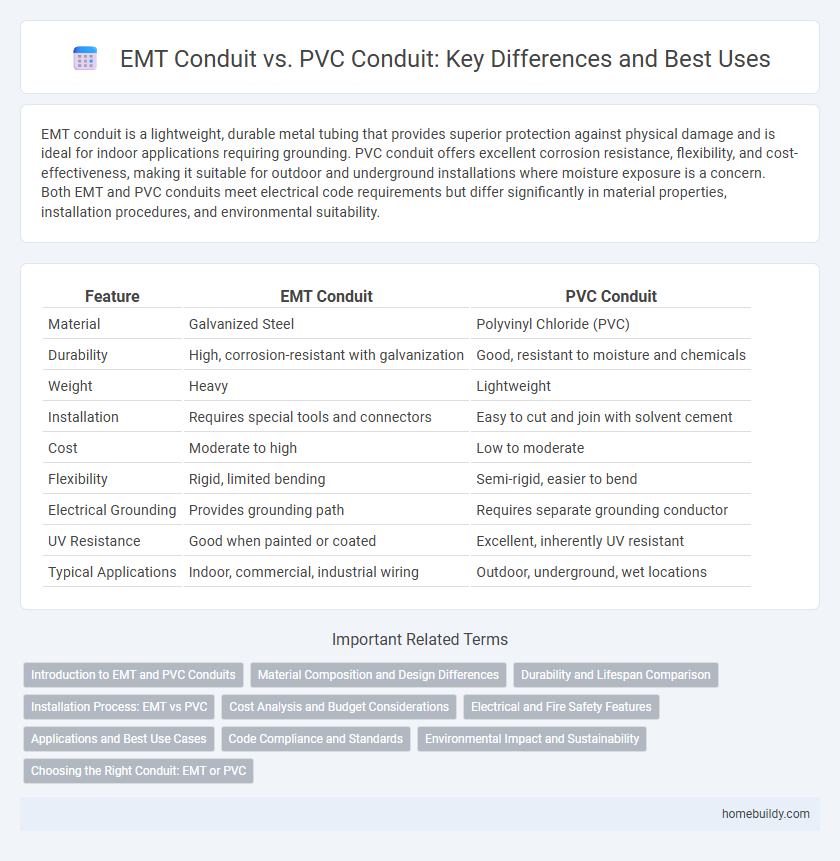
| Feature | EMT Conduit | PVC Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Galvanized Steel | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
| Durability | High, corrosion-resistant with galvanization | Good, resistant to moisture and chemicals |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Installation | Requires special tools and connectors | Easy to cut and join with solvent cement |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Flexibility | Rigid, limited bending | Semi-rigid, easier to bend |
| Electrical Grounding | Provides grounding path | Requires separate grounding conductor |
| UV Resistance | Good when painted or coated | Excellent, inherently UV resistant |
| Typical Applications | Indoor, commercial, industrial wiring | Outdoor, underground, wet locations |
Introduction to EMT and PVC Conduits
EMT conduit, or Electrical Metallic Tubing, is a lightweight, steel or aluminum tubing commonly used for indoor electrical wiring due to its durability and ease of installation. PVC conduit, made from polyvinyl chloride, provides excellent corrosion resistance and is ideal for outdoor or underground applications where moisture exposure is a concern. Both EMT and PVC conduits serve to protect electrical wiring, but their material composition and environmental suitability differentiate their usage.
Material Composition and Design Differences
EMT conduit is constructed from galvanized steel, offering superior strength, durability, and resistance to physical damage, making it ideal for indoor applications requiring robust protection. PVC conduit, made from rigid polyvinyl chloride, provides excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight handling, and ease of installation, especially in outdoor or underground environments where moisture exposure is a concern. The design of EMT conduit features a thin, hollow metal tube often with a smooth surface for easy wire pulling, whereas PVC conduit typically has a thicker wall and can be UV-resistant or flexible to accommodate various installation needs.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
EMT conduit, made from galvanized steel, offers superior durability and corrosion resistance in indoor and dry environments, typically lasting 40-50 years with proper installation. In contrast, PVC conduit provides excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure, extending its lifespan to over 50 years in outdoor and underground applications. Both materials ensure long-term protection for electrical wiring, with the choice depending on specific environmental conditions.
Installation Process: EMT vs PVC
EMT conduit installation requires precise cutting, bending with specialized tools, and securing with metal connectors, making it ideal for indoor applications where structural rigidity and grounding are essential. PVC conduit offers a simpler installation process involving solvent welding or mechanical fittings, allowing for easier handling, flexibility, and corrosion resistance in outdoor or wet environments. The choice between EMT and PVC conduits depends on project requirements, environmental conditions, and labor skills related to cutting, joining, and securing materials.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
EMT conduit generally offers lower material costs compared to PVC conduit, making it a cost-effective choice for budget-conscious electrical projects. Installation expenses for EMT can be higher due to the need for specialized tools and skilled labor, whereas PVC conduit allows for quicker and simpler installations, reducing labor costs. When planning budgets, consider EMT's durability and electrical conductivity benefits against PVC's corrosion resistance and lower maintenance needs to determine the most economical option over the project's lifespan.
Electrical and Fire Safety Features
EMT conduit provides superior electrical grounding and is made of galvanized steel, enhancing its durability and resistance to physical damage, which contributes significantly to electrical safety. PVC conduit, being non-metallic and non-conductive, prevents electrical shock hazards and offers excellent corrosion resistance but lacks the grounding capabilities of metal conduits. In fire safety, EMT conduit has a higher fire resistance rating due to its metal composition, while PVC conduit can emit toxic fumes when exposed to high heat, requiring careful consideration in fire-prone environments.
Applications and Best Use Cases
EMT conduit is ideal for indoor electrical installations requiring a lightweight, durable, and easily bendable solution, commonly used in commercial buildings and exposed areas where grounding is necessary. PVC conduit excels in underground, wet, or corrosive environments due to its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and rust, making it perfect for residential wiring and outdoor applications. Choosing EMT conduit offers enhanced mechanical protection and grounding capabilities, while PVC conduit provides superior insulation and flexibility in harsh conditions.
Code Compliance and Standards
EMT conduit and PVC conduit must both comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) standards, specifically NEC Article 358 for EMT and Article 352 for PVC. EMT conduit is typically preferred in indoor installations due to its steel construction meeting grounding and mechanical protection requirements outlined in NEC 250. PVC conduit, while compliant in damp or corrosive environments under NEC guidelines, must be properly supported and marked for electrical use to fulfill code mandates.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
EMT conduit, typically made from steel, offers high recyclability and durability, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing long-term environmental footprint. PVC conduit, while lightweight and corrosion-resistant, is derived from non-renewable petrochemicals and poses challenges in recycling, contributing to plastic waste concerns. Choosing EMT conduit supports sustainability goals through metal recycling infrastructure and lower environmental toxicity compared to PVC's chemical additives and production emissions.
Choosing the Right Conduit: EMT or PVC
Choosing the right conduit between EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) and PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) depends on factors such as environmental exposure, mechanical protection, and installation requirements. EMT conduit offers superior durability and is ideal for indoor applications with strict fire safety codes, while PVC conduit excels in corrosion resistance and suitability for underground or wet locations. Considering project-specific needs ensures optimal electrical system protection and compliance with local electrical codes.
EMT conduit vs PVC conduit Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com