EMT conduit offers a rigid, metallic solution with excellent protection against physical damage and is ideal for indoor wiring in commercial and industrial settings. FMC conduit, also known as flexible metal conduit, provides greater flexibility for wiring in tight or complex spaces, simplifying installation around obstacles. Choosing between EMT and FMC conduit depends on the project's requirements for durability, flexibility, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
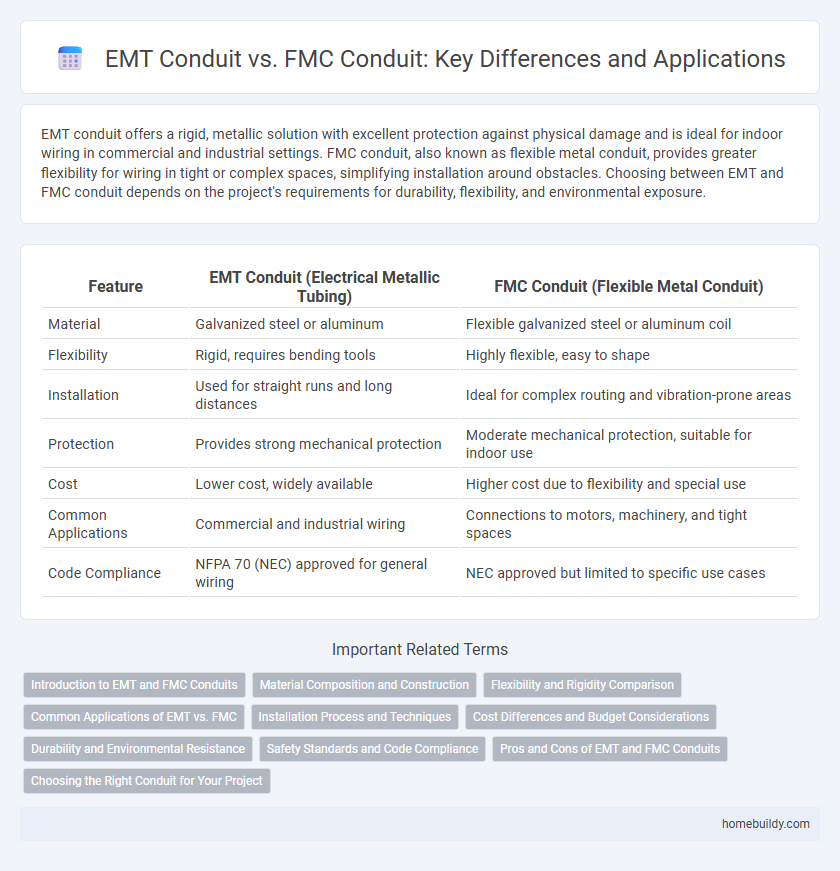
| Feature | EMT Conduit (Electrical Metallic Tubing) | FMC Conduit (Flexible Metal Conduit) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Galvanized steel or aluminum | Flexible galvanized steel or aluminum coil |
| Flexibility | Rigid, requires bending tools | Highly flexible, easy to shape |
| Installation | Used for straight runs and long distances | Ideal for complex routing and vibration-prone areas |
| Protection | Provides strong mechanical protection | Moderate mechanical protection, suitable for indoor use |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to flexibility and special use |
| Common Applications | Commercial and industrial wiring | Connections to motors, machinery, and tight spaces |
| Code Compliance | NFPA 70 (NEC) approved for general wiring | NEC approved but limited to specific use cases |
Introduction to EMT and FMC Conduits
EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) conduit is a lightweight, thin-walled steel tubing commonly used for indoor electrical wiring due to its durability and ease of installation. FMC (Flexible Metal Conduit) consists of a spiral-wound steel core covered with a protective jacket, allowing flexible routing in tight or irregular spaces. EMT is preferred for straight runs and exposed installations, while FMC provides flexibility for dynamic or vibration-prone environments.
Material Composition and Construction
EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) conduit is predominantly made of galvanized steel or aluminum, offering a rigid, durable structure that provides strong protection for electrical wiring in commercial and industrial settings. FMC (Flexible Metal Conduit) consists of a helically wound, interlocked steel strip with a flexible design, allowing it to bend around obstacles while maintaining flexibility and mechanical protection. The solid construction of EMT ensures robustness and corrosion resistance, whereas FMC's lightweight, bendable build facilitates installations in tight or complex spaces.
Flexibility and Rigidity Comparison
EMT conduit offers high rigidity and durability, making it ideal for permanent electrical installations requiring strong mechanical protection. FMC conduit provides superior flexibility, allowing for easier bending and installation in tight or complex spaces, but offers less physical protection compared to EMT. Choosing between EMT and FMC depends on the balance between the need for structural strength and installation adaptability in electrical conduit systems.
Common Applications of EMT vs. FMC
EMT conduit is commonly used in commercial and residential wiring for exposed and indoor applications due to its rigidity and ease of installation. FMC conduit is preferred for flexible connections to motors, transformers, and areas requiring vibration resistance or movement. EMT suits fixed, straight runs while FMC accommodates tight bends and dynamic environments.
Installation Process and Techniques
EMT conduit installation involves precise cutting, deburring, and bending using specialized tools like conduit benders, ensuring straight runs secured with straps and connectors to junction boxes. FMC conduit installation requires flexible handling to navigate complex spaces, using clamps and couplings to maintain continuous grounding and mechanical protection. Properly tightening fittings and ensuring alignment are critical for both systems to maintain electrical safety and code compliance.
Cost Differences and Budget Considerations
EMT conduit generally offers a lower upfront cost than FMC conduit due to its thinner walls and ease of installation with standard fittings. FMC conduit, being more flexible and durable, tends to have higher material and labor costs, impacting overall project budgets. Budget considerations should weigh EMT's cost efficiency for straight runs against FMC's flexibility benefits in complex wiring layouts.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
EMT conduit, made of galvanized steel, offers superior durability and corrosion resistance suited for indoor and outdoor dry environments, while FMC conduit, consisting of flexible steel, provides moderate protection but is more vulnerable to physical damage and corrosion in harsh conditions. EMT's rigid structure enhances its longevity against mechanical impacts and environmental elements, whereas FMC is preferred for applications requiring flexibility but should be protected from moisture and chemicals. For long-term environmental resistance, EMT conduit is typically the more reliable choice in industrial and commercial electrical installations.
Safety Standards and Code Compliance
EMT conduit meets National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements for indoor wiring due to its rigid construction and corrosion resistance, providing enhanced protection against physical damage. FMC conduit, while flexible and easier to install in tight spaces, complies with NEC only in specific applications where flexibility is necessary and is not suitable for areas exposed to physical impact. Adhering to safety standards, EMT is preferred for environments requiring durability and code compliance to prevent electrical hazards and ensure long-term system integrity.
Pros and Cons of EMT and FMC Conduits
EMT conduit offers superior durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation, making it ideal for exposed and indoor wiring applications due to its rigid steel construction and smooth surface. FMC conduit provides greater flexibility for complex wiring paths and is easier to bend and route in tight spaces, but it has lower mechanical protection and is less suitable for outdoor or heavy-duty environments due to its flexible metal tubing design. Choosing between EMT and FMC conduits depends on the specific requirements for mechanical protection, installation environment, and wiring complexity.
Choosing the Right Conduit for Your Project
Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) conduit offers a rigid, corrosion-resistant solution ideal for indoor installations requiring robust mechanical protection, while Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC) provides superior flexibility for complex routing and vibration-prone environments. Selecting the proper conduit depends on project specifications such as exposure to physical damage, installation complexity, and compliance with electrical codes like NEC Article 358 for EMT and Article 348 for FMC. Prioritize EMT for straight, long runs in controlled environments and FMC for areas necessitating bends, motion accommodation, or retrofit applications.
EMT conduit vs FMC conduit Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com