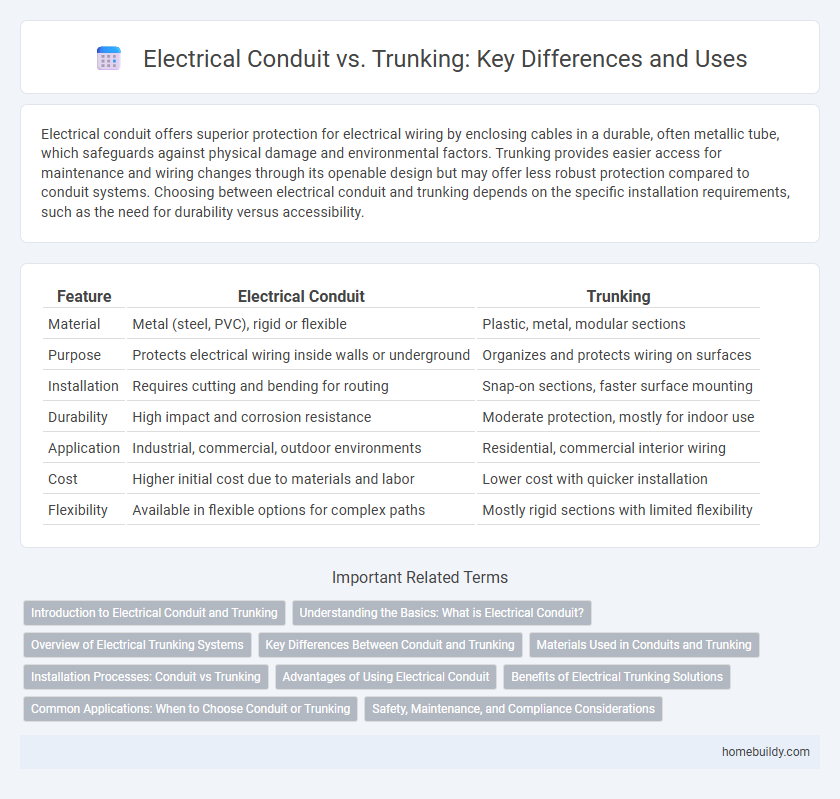
Electrical conduit offers superior protection for electrical wiring by enclosing cables in a durable, often metallic tube, which safeguards against physical damage and environmental factors. Trunking provides easier access for maintenance and wiring changes through its openable design but may offer less robust protection compared to conduit systems. Choosing between electrical conduit and trunking depends on the specific installation requirements, such as the need for durability versus accessibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrical Conduit | Trunking |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Metal (steel, PVC), rigid or flexible | Plastic, metal, modular sections |
| Purpose | Protects electrical wiring inside walls or underground | Organizes and protects wiring on surfaces |
| Installation | Requires cutting and bending for routing | Snap-on sections, faster surface mounting |
| Durability | High impact and corrosion resistance | Moderate protection, mostly for indoor use |
| Application | Industrial, commercial, outdoor environments | Residential, commercial interior wiring |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to materials and labor | Lower cost with quicker installation |
| Flexibility | Available in flexible options for complex paths | Mostly rigid sections with limited flexibility |
Introduction to Electrical Conduit and Trunking
Electrical conduit and trunking are essential components in electrical wiring systems, providing protection and organization for cables. Electrical conduit is a tubular raceway, typically made of metal or plastic, designed to route and shield wiring from physical damage and environmental hazards. Trunking offers a rectangular, openable channel that allows easy access for cable installation and maintenance, making it suitable for organizing multiple cables in commercial and industrial settings.
Understanding the Basics: What is Electrical Conduit?
Electrical conduit is a protective tubing system designed to house and safeguard electrical wiring from physical damage, moisture, and corrosive elements. Unlike trunking, which is open or semi-open and primarily used for surface mounting, electrical conduit provides a fully enclosed pathway that enhances safety and durability in electrical installations. Common materials include PVC, steel, and EMT, chosen based on environmental conditions and regulatory requirements.
Overview of Electrical Trunking Systems
Electrical trunking systems provide a structured pathway for electrical wiring, offering enhanced protection and easier access compared to traditional electrical conduit. Made primarily from steel, aluminum, or PVC, trunking accommodates multiple cables in a single enclosed channel, ensuring organized and efficient cable management. These systems simplify installation and maintenance in commercial and industrial settings by enabling quick modifications and expansions without extensive rewiring.
Key Differences Between Conduit and Trunking
Electrical conduit is a rigid or flexible tubing designed to protect and route electrical wiring, whereas trunking is a rectangular or square enclosure used for surface cable management. Conduit offers superior protection against mechanical damage and environmental factors, making it suitable for outdoor and industrial applications, while trunking provides easier access for wiring changes in commercial and residential settings. The choice between conduit and trunking depends on installation environment, protection needs, and aesthetic preferences.
Materials Used in Conduits and Trunking
Electrical conduits are typically made from rigid materials such as galvanized steel, PVC, or aluminum, providing strong mechanical protection and resistance to corrosion. Trunking, on the other hand, is commonly constructed from sheet metal or PVC, designed to house multiple cables and facilitate easy access for maintenance and modifications. The choice of material in conduits prioritizes durability and environmental resistance, while trunking materials emphasize flexibility and cable management efficiency.
Installation Processes: Conduit vs Trunking
Electrical conduit installation requires threading or bending rigid tubing to protect wiring, with fittings sealed to ensure safety and durability, often demanding specialized tools and skilled labor. Trunking installation involves mounting pre-formed channels or boxes onto surfaces, allowing easier access for wire laying and modifications without extensive tooling. Conduit systems offer superior mechanical protection and compliance with stringent electrical codes, while trunking provides flexibility and quicker installation for surface-mounted wiring.
Advantages of Using Electrical Conduit
Electrical conduit offers superior protection for electrical wiring against physical damage, moisture, and corrosion, ensuring longer durability and safety in various environments. Its rigid structure provides enhanced mechanical strength and easy grounding, which reduces the risk of electrical faults and fire hazards. Conduits also allow for easier future upgrades or replacements of wiring without extensive surface modifications, making them a cost-effective solution in long-term electrical installations.
Benefits of Electrical Trunking Solutions
Electrical trunking solutions offer superior flexibility and easier access for wiring maintenance compared to traditional electrical conduit systems, allowing for quicker modifications and expansions. Their modular design simplifies installation and enhances organization by neatly housing multiple cables within a single pathway, reducing clutter and improving safety. Electrical trunking also provides better aesthetic integration in commercial and residential environments, with customizable covers and finishes that blend seamlessly into interior designs.
Common Applications: When to Choose Conduit or Trunking
Electrical conduit is commonly used in industrial and outdoor settings where robust protection against environmental factors and physical damage is required, making it ideal for wiring in harsh conditions. Trunking suits commercial and residential installations that prioritize easy access for wiring inspection and maintenance, often used in office buildings and homes. Choosing conduit is essential when compliance with stringent safety codes is necessary, while trunking works better for applications demanding flexibility and rapid modification of electrical systems.
Safety, Maintenance, and Compliance Considerations
Electrical conduit offers superior safety by providing robust protection against physical damage and environmental hazards, ensuring electrical wiring remains intact and reducing fire risks. Maintenance is simplified with conduit systems, allowing easier inspection and replacement of cables without disrupting the building structure, unlike trunking which often requires dismantling. Compliance with electrical codes typically favors conduit for critical installations due to its higher durability and secure containment, making it essential for meeting safety standards in commercial and industrial environments.
Electrical conduit vs Trunking Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com