Steel conduit offers superior durability and impact resistance, making it ideal for industrial settings and outdoor applications where mechanical protection is crucial. Plastic conduit, such as PVC, provides excellent corrosion resistance and is lightweight, simplifying installation in residential or damp environments. Choosing between steel and plastic conduits depends on factors like environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
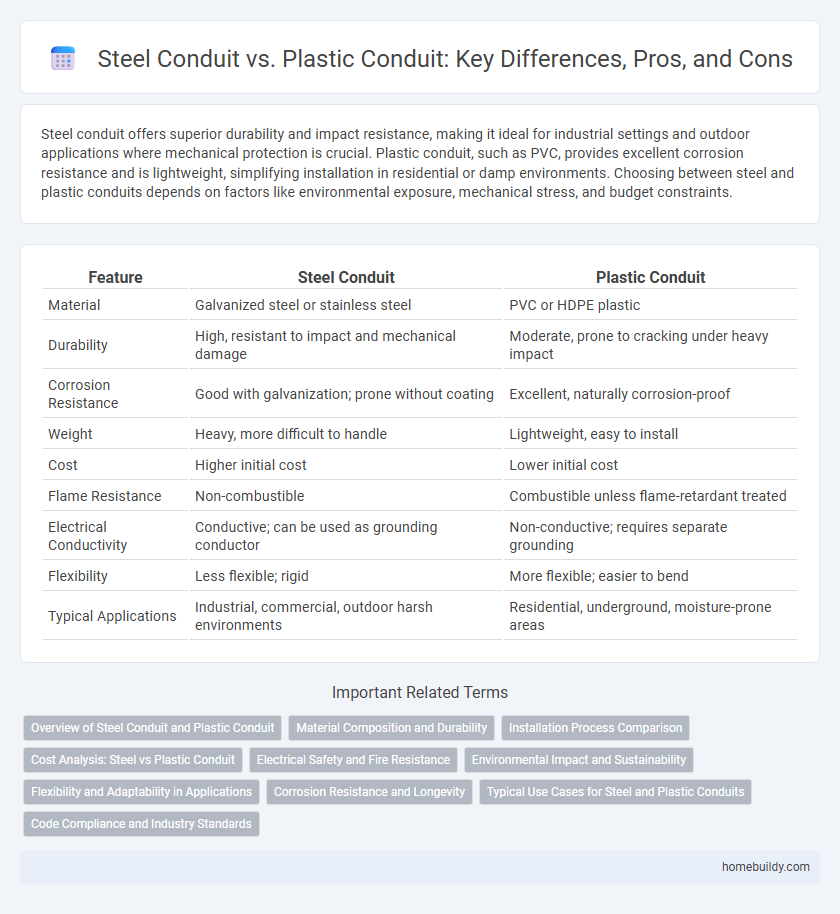
| Feature | Steel Conduit | Plastic Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Galvanized steel or stainless steel | PVC or HDPE plastic |
| Durability | High, resistant to impact and mechanical damage | Moderate, prone to cracking under heavy impact |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good with galvanization; prone without coating | Excellent, naturally corrosion-proof |
| Weight | Heavy, more difficult to handle | Lightweight, easy to install |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Flame Resistance | Non-combustible | Combustible unless flame-retardant treated |
| Electrical Conductivity | Conductive; can be used as grounding conductor | Non-conductive; requires separate grounding |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; rigid | More flexible; easier to bend |
| Typical Applications | Industrial, commercial, outdoor harsh environments | Residential, underground, moisture-prone areas |
Overview of Steel Conduit and Plastic Conduit
Steel conduit provides superior mechanical protection and durability, making it ideal for industrial and outdoor applications where exposure to physical damage or harsh environmental conditions is common. Plastic conduit, typically made from PVC, offers excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight flexibility, and ease of installation, suitable for residential and indoor wiring systems. Both materials comply with National Electrical Code (NEC) standards but differ significantly in cost, strength, and installation requirements.
Material Composition and Durability
Steel conduit, composed primarily of galvanized or stainless steel, offers superior durability and resistance to impact, corrosion, and high temperatures, making it ideal for industrial and outdoor applications. Plastic conduit, often made from PVC or polyethylene, provides excellent corrosion resistance and flexibility but lacks the mechanical strength of steel, limiting its use in high-impact environments. The choice between steel and plastic conduit depends on specific environmental factors and the need for mechanical protection versus chemical resistance.
Installation Process Comparison
Steel conduit installation requires specialized tools such as conduit benders and threading machines, making the process more labor-intensive and time-consuming compared to plastic conduit. Plastic conduit, commonly made from PVC, is lightweight and easily cut with standard saws, allowing for quicker assembly and flexibility in tight or complex spaces. The anchoring and joining of steel conduits often involve rigid fittings and grounding considerations, whereas plastic conduits use solvent-weld or mechanical couplings that streamline the installation.
Cost Analysis: Steel vs Plastic Conduit
Steel conduit typically incurs higher initial costs due to material and installation expenses, making it more suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring durability and protection. Plastic conduit offers a lower upfront investment with easier installation and corrosion resistance, reducing maintenance costs over time. Considering long-term expenses, plastic conduit often provides better cost efficiency in environments lacking extreme mechanical stress or high temperatures.
Electrical Safety and Fire Resistance
Steel conduit offers superior electrical safety due to its robust metal construction, providing excellent grounding and protection against physical damage, reducing the risk of electrical shocks and short circuits. Its high fire resistance ensures the conduit can withstand extreme heat and prevent fire spread, making it ideal for commercial and industrial applications where fire safety codes are stringent. Plastic conduit, while corrosion-resistant and lightweight, lacks the inherent fire resistance and grounding capabilities of steel, making it less suitable for high-risk environments requiring rigorous electrical safety and fire containment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Steel conduit offers superior durability and recyclability, making it a more sustainable choice with a lower environmental impact over its lifecycle compared to plastic conduit. Plastic conduit, typically made from PVC, poses challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and potential release of harmful chemicals during production and disposal. Choosing steel conduit supports environmental sustainability by reducing landfill waste and promoting material reuse.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Applications
Steel conduit offers superior durability and is ideal for environments requiring strong protection against physical damage, but its rigidity limits flexibility and adaptability in complex installations. Plastic conduit, such as PVC or flexible plastic types, provides excellent flexibility, allowing easier navigation around corners and obstacles, making it highly adaptable for residential and light commercial applications. Choosing between steel and plastic conduit depends on balancing the need for structural strength with the requirement for flexible routing in specific electrical projects.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Steel conduit offers high mechanical strength but is prone to corrosion over time, especially in moist or acidic environments, which can reduce its longevity without protective coatings. Plastic conduit, such as PVC or HDPE, provides superior corrosion resistance since it does not rust or degrade in wet conditions, leading to a longer lifespan in corrosive settings. Choosing plastic conduit ensures durability and reduced maintenance in environments where exposure to moisture and chemicals is a significant concern.
Typical Use Cases for Steel and Plastic Conduits
Steel conduits are typically used in industrial environments requiring high durability and resistance to mechanical damage, such as factories, warehouses, and outdoor installations exposed to harsh weather conditions. Plastic conduits, including PVC and HDPE, are favored for residential and commercial applications due to their corrosion resistance, lightweight nature, and ease of installation in underground or dry indoor settings. In wet or corrosive environments, plastic conduits offer superior longevity, while steel conduits provide better grounding and protection in heavy-duty electrical systems.
Code Compliance and Industry Standards
Steel conduit meets stringent NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements for grounding and physical protection, making it ideal for commercial and industrial installations. Plastic conduit, such as PVC, complies with UL (Underwriters Laboratories) standards and is widely accepted in residential and outdoor applications due to its corrosion resistance. Both materials must adhere to applicable local codes and ANSI (American National Standards Institute) regulations to ensure safety and durability in specific environments.
Steel conduit vs Plastic conduit Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com