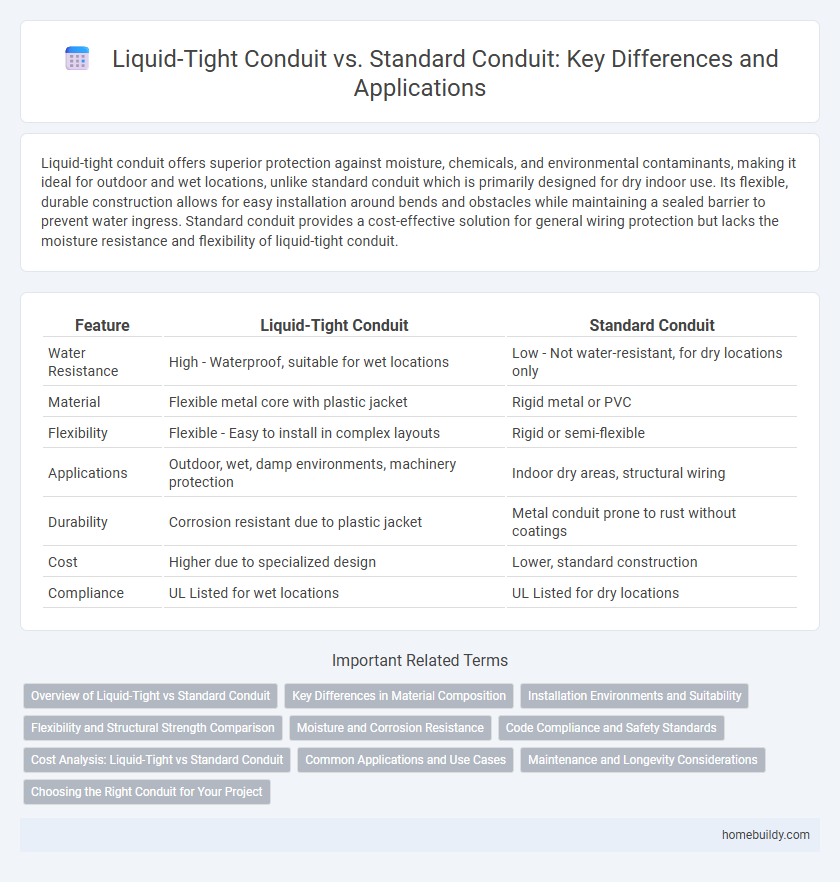
Liquid-tight conduit offers superior protection against moisture, chemicals, and environmental contaminants, making it ideal for outdoor and wet locations, unlike standard conduit which is primarily designed for dry indoor use. Its flexible, durable construction allows for easy installation around bends and obstacles while maintaining a sealed barrier to prevent water ingress. Standard conduit provides a cost-effective solution for general wiring protection but lacks the moisture resistance and flexibility of liquid-tight conduit.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Liquid-Tight Conduit | Standard Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | High - Waterproof, suitable for wet locations | Low - Not water-resistant, for dry locations only |
| Material | Flexible metal core with plastic jacket | Rigid metal or PVC |
| Flexibility | Flexible - Easy to install in complex layouts | Rigid or semi-flexible |
| Applications | Outdoor, wet, damp environments, machinery protection | Indoor dry areas, structural wiring |
| Durability | Corrosion resistant due to plastic jacket | Metal conduit prone to rust without coatings |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized design | Lower, standard construction |
| Compliance | UL Listed for wet locations | UL Listed for dry locations |
Overview of Liquid-Tight vs Standard Conduit
Liquid-tight conduit features a flexible, waterproof PVC jacket that protects electrical wiring in wet or corrosive environments, making it ideal for outdoor or industrial applications. Standard conduit, typically rigid metal or PVC, offers basic protection against physical damage but lacks waterproofing and flexibility. Choosing between liquid-tight and standard conduit depends on environmental exposure, with liquid-tight conduits providing superior moisture resistance and durability.
Key Differences in Material Composition
Liquid-tight conduit features a flexible core made of galvanized steel or aluminum combined with a durable, non-metallic outer jacket that resists moisture, chemicals, and corrosion. Standard conduit, typically composed of rigid galvanized steel or PVC, lacks the protective outer jacket and is less adaptable to wet or dynamic environments. These material composition differences directly impact the suitability of liquid-tight conduit for outdoor or industrial applications where exposure to liquids and mechanical stress is common.
Installation Environments and Suitability
Liquid-tight conduit offers superior protection against moisture, chemicals, and corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor, wet, or industrial environments where exposure to liquids is frequent. Standard conduit, often made from rigid metal or PVC, is suitable for dry, indoor installations with minimal exposure to harsh elements. Choosing between these conduits depends heavily on the environmental conditions and the need for flexibility and moisture resistance during installation.
Flexibility and Structural Strength Comparison
Liquid-tight conduit offers superior flexibility due to its construction with a plastic outer covering and a steel inner coil, allowing it to bend easily around corners without kinking. Standard conduit, typically made of rigid galvanized steel or aluminum, provides greater structural strength and impact resistance but lacks the same degree of flexibility for complex routing. Choosing between liquid-tight and standard conduit depends on balancing the need for mechanical protection versus maneuverability in electrical installations.
Moisture and Corrosion Resistance
Liquid-tight conduit offers superior moisture and corrosion resistance compared to standard conduit, making it ideal for wet or damp environments. Its flexible polymer jacket prevents water ingress and provides a barrier against corrosive elements, extending the conduit's lifespan. Standard conduit, often made of rigid metal, lacks this protective coating and is more susceptible to rust and moisture damage when exposed to harsh conditions.
Code Compliance and Safety Standards
Liquid-tight conduit complies with NEC Article 350, providing superior protection against moisture, corrosion, and environmental hazards, making it essential for wet or damp locations. Standard conduit, typically rigid or EMT, meets code requirements for indoor dry locations but lacks the sealing properties necessary for exposure to liquids. Ensuring compliance with UL Listing and NFPA 70 standards, liquid-tight conduit enhances safety by preventing water ingress and electrical faults in challenging environments.
Cost Analysis: Liquid-Tight vs Standard Conduit
Liquid-tight conduit typically costs 20-40% more than standard conduit due to its flexible design and waterproof properties. While standard conduit provides basic protection at a lower price point, liquid-tight conduit reduces long-term maintenance and damage repair costs in wet or corrosive environments. Evaluating project-specific conditions is essential for deciding between the initial expense of liquid-tight conduit and the durability cost-effectiveness over time.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Liquid-tight conduit is commonly used in outdoor and wet environments where moisture protection is essential, such as in commercial HVAC systems and industrial machinery. Standard conduit is frequently installed in indoor, dry locations like office buildings and residential wiring to protect electrical cables from physical damage. Liquid-tight conduit supports applications requiring flexibility and environmental sealing, whereas standard conduit suits static installations with less exposure to harsh conditions.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Liquid-tight conduit offers superior protection against moisture, chemicals, and corrosion, significantly reducing maintenance requirements in harsh or wet environments compared to standard conduit. Standard conduit, typically made of rigid metal or PVC, may require more frequent inspections and repairs due to increased susceptibility to rust and damage. Choosing liquid-tight conduit extends the lifespan of electrical systems by ensuring a more durable and sealed conduit pathway, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Choosing the Right Conduit for Your Project
Liquid-tight conduit offers superior protection against moisture, chemicals, and corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor or wet environments. Standard conduit is suitable for dry, indoor applications where flexibility and environmental exposure are minimal. Selecting the right conduit depends on the project's specific conditions, including exposure to elements, electrical code requirements, and installation environment.
Liquid-tight conduit vs Standard conduit Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com