Electrical conduit is a tubular system designed to protect and route electrical wiring, typically made from metal or plastic, offering robust mechanical protection and compliance with electrical codes. Electrical duct, on the other hand, is a wider channel primarily used for housing multiple cables, often in telecommunication or data installations, providing organized cable management but less protection against physical damage. Choosing between electrical conduit and electrical duct depends on the specific application requirements, including protection level, cable type, and installation environment.
Table of Comparison
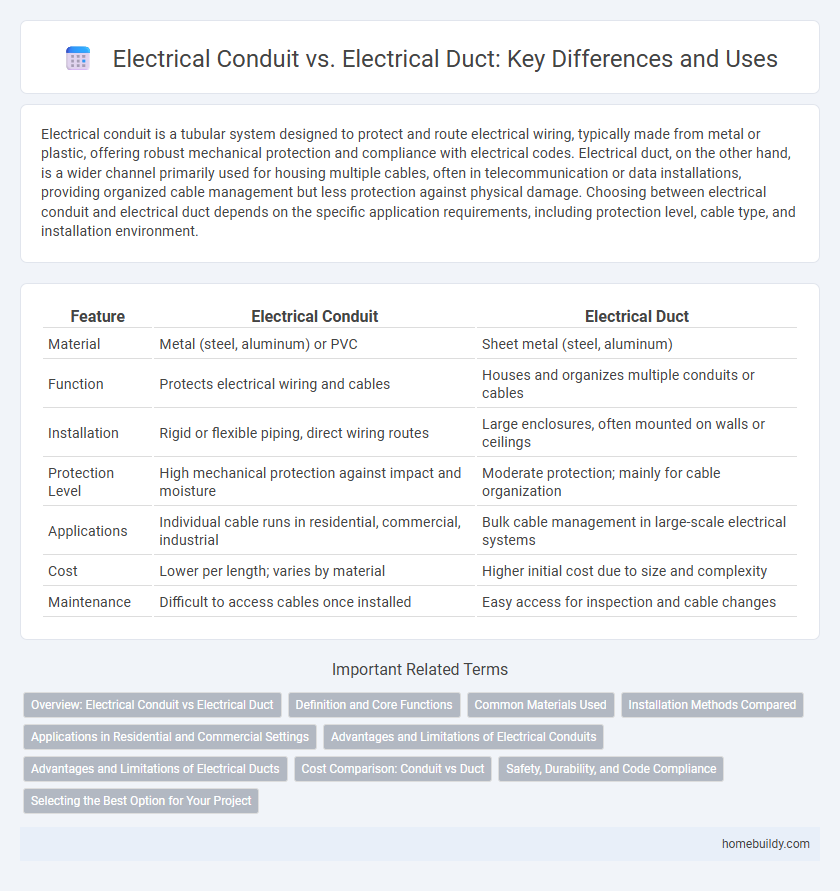
| Feature | Electrical Conduit | Electrical Duct |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Metal (steel, aluminum) or PVC | Sheet metal (steel, aluminum) |
| Function | Protects electrical wiring and cables | Houses and organizes multiple conduits or cables |
| Installation | Rigid or flexible piping, direct wiring routes | Large enclosures, often mounted on walls or ceilings |
| Protection Level | High mechanical protection against impact and moisture | Moderate protection; mainly for cable organization |
| Applications | Individual cable runs in residential, commercial, industrial | Bulk cable management in large-scale electrical systems |
| Cost | Lower per length; varies by material | Higher initial cost due to size and complexity |
| Maintenance | Difficult to access cables once installed | Easy access for inspection and cable changes |
Overview: Electrical Conduit vs Electrical Duct
Electrical conduit is a tubing system designed to protect and route electrical wiring in buildings, typically made from metal or rigid plastic. Electrical ducts are larger channels primarily used for housing bundles of cables and cooling systems, often constructed from sheet metal or fiberglass. Conduits offer greater protection against physical damage and environmental factors, while ducts provide more space for extensive wiring and improve ventilation.
Definition and Core Functions
Electrical conduit refers to a tubular system designed to protect and route electrical wiring in a building or structure, typically made from metal or plastic materials. Electrical ducts are larger, often rectangular channels primarily used for housing multiple cables, providing easier access for maintenance and improved organization. The core function of conduits centers on safeguarding individual wires from physical damage and environmental factors, while ducts focus on cable management and airflow within electrical installations.
Common Materials Used
Electrical conduit is commonly made from materials such as galvanized steel, PVC, and aluminum, chosen for their durability and corrosion resistance. Electrical duct often uses sheet metal, including steel or aluminum, offering a flat or rectangular shape for routing multiple cables. While both protect electrical wiring, conduit materials prioritize flexibility and protection against physical damage, whereas duct materials focus on space efficiency and ease of cable management.
Installation Methods Compared
Electrical conduit installation involves threading or pulling wires through rigid or flexible metal or PVC tubes, requiring precise bending and joining techniques to ensure protection and compliance with electrical codes. Electrical ducts, typically larger and used for HVAC or cable management, are installed by assembling prefabricated sections with flanges or welding, often secured with clamps or brackets to support heavier loads. Conduit installation demands careful sealing to prevent moisture ingress, while ducts prioritize airflow efficiency and accessibility for maintenance.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Settings
Electrical conduit offers superior protection for wiring in residential settings, ensuring compliance with building codes and safeguarding against moisture and physical damage. In commercial applications, electrical ducts provide greater flexibility for large-scale installations, accommodating multiple cables and facilitating easier maintenance and future upgrades. Choosing between conduit and duct depends on factors like installation scale, environmental exposure, and specific wiring requirements.
Advantages and Limitations of Electrical Conduits
Electrical conduits provide superior protection for electrical wiring against physical damage, moisture, and chemical exposure, making them ideal for harsh environments and ensuring long-term durability. They offer flexibility in installation, allowing for easy changes or upgrades to wiring systems, but their limited inner space can restrict cable capacity compared to electrical ducts. While conduits are generally cost-effective and provide strong mechanical protection, they may require specialized fittings and tools, increasing installation complexity in large-scale projects.
Advantages and Limitations of Electrical Ducts
Electrical ducts offer superior protection against physical damage and environmental factors compared to electrical conduits, making them ideal for industrial and outdoor installations. Their larger capacity facilitates easier cable management and future upgrades, reducing maintenance time and costs. However, electrical ducts require more installation space and can be more expensive to install initially due to the need for specialized components and tools.
Cost Comparison: Conduit vs Duct
Electrical conduit typically incurs lower initial costs compared to electrical duct due to its simpler installation and reduced material expenses. Electrical ducts, often made from sheet metal or fiberglass, involve higher fabrication and labor costs but provide enhanced capacity and easier cable management for large-scale projects. Cost-efficiency depends on project scale and requirements, with conduits favored for smaller installations and ducts preferred for complex, high-volume wiring systems.
Safety, Durability, and Code Compliance
Electrical conduit offers superior safety by providing robust physical protection for wiring against impact, moisture, and chemical exposure, reducing fire hazards significantly compared to electrical ducts. Durability of conduits is enhanced through materials like rigid metal and PVC, which ensure long-term resistance to corrosion and environmental factors, unlike many duct systems that prioritize airflow over protection. Compliance with electrical codes such as NEC mandates conduit installation in critical areas for grounding and mechanical protection, whereas ducts primarily serve HVAC needs and do not meet stringent electrical safety requirements.
Selecting the Best Option for Your Project
Choosing between electrical conduit and electrical duct depends on factors such as installation environment, flexibility, and cost. Electrical conduit offers superior protection for wiring in harsh or outdoor conditions due to its rigid structure and robust materials like metal or PVC. In contrast, electrical duct provides easier access for maintenance and modifications in indoor settings, making it ideal for large-scale projects with frequent wiring changes.
Electrical conduit vs Electrical duct Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com