A register boot is designed specifically for safekeeping and organizing multiple debit or credit cards, often featuring RFID protection to prevent electronic theft. Transition boots are versatile footwear intended to provide comfort and adaptability, suitable for both casual and semi-formal settings, often incorporating materials that balance durability and style. Choosing between the two depends on whether your priority is practical card storage or multifunctional, stylish shoes.
Table of Comparison
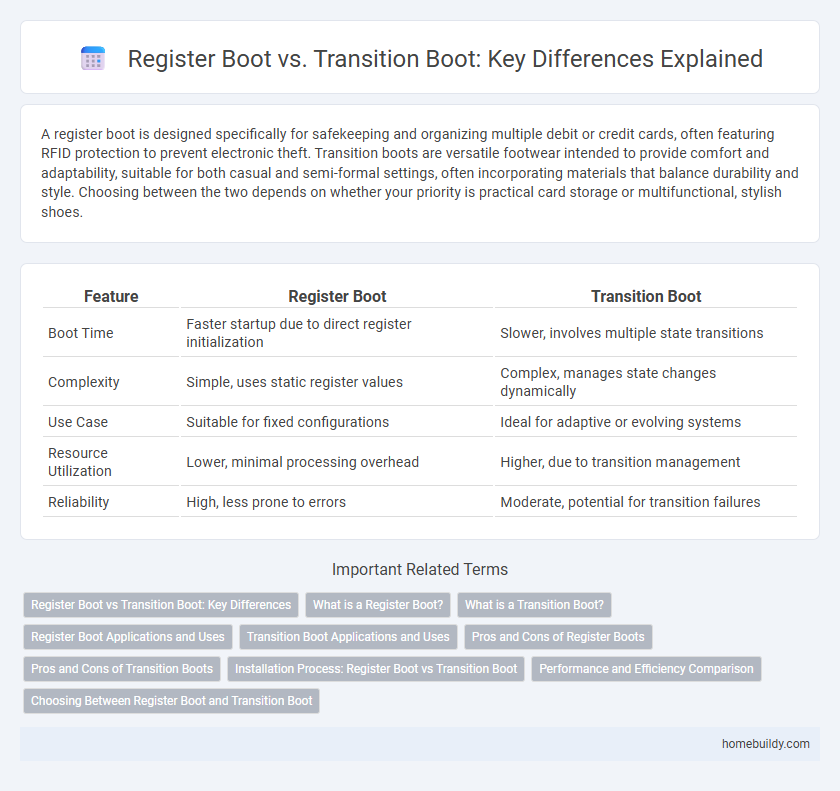
| Feature | Register Boot | Transition Boot |
|---|---|---|
| Boot Time | Faster startup due to direct register initialization | Slower, involves multiple state transitions |
| Complexity | Simple, uses static register values | Complex, manages state changes dynamically |
| Use Case | Suitable for fixed configurations | Ideal for adaptive or evolving systems |
| Resource Utilization | Lower, minimal processing overhead | Higher, due to transition management |
| Reliability | High, less prone to errors | Moderate, potential for transition failures |
Register Boot vs Transition Boot: Key Differences
Register boot focuses on initializing hardware registers to predefined values, ensuring the system's basic configuration is set before the operating system loads. Transition boot involves the process of moving from a minimal initial state to a fully functional operating environment, often involving loading additional firmware or drivers. The key difference lies in register boot handling low-level hardware setup, while transition boot manages system state progression and resource activation.
What is a Register Boot?
A Register Boot is a process where the CPU initializes its register values to predefined states during system startup, ensuring stable and predictable operation. This boot type focuses on setting hardware registers before launching the operating system, contrasting with transition boot, which involves switching from firmware control to OS control. Register Boot optimizes system reliability by preparing the processor's internal state early in the boot sequence.
What is a Transition Boot?
A transition boot is a type of footwear designed to facilitate the change from running shoes to cycling shoes during multisport events like triathlons, enabling quick and efficient transitions. Unlike traditional register boots, transition boots prioritize lightweight materials and quick-release features to improve speed and comfort during the switch between disciplines. Their construction often includes breathable fabrics and adaptable fittings to support rapid movement and minimize downtime.
Register Boot Applications and Uses
Register boot is primarily utilized in embedded systems, where it allows for faster startup by directly loading the operating system kernel into the CPU registers, optimizing system initialization time. Register boot applications are common in microcontrollers and real-time systems that demand minimal latency and reliable performance from power-up. This method contrasts with transition boot, making it ideal for devices requiring quick and deterministic boot processes without intermediate loading stages.
Transition Boot Applications and Uses
Transition boots are designed to provide flexible connections between rotating shafts and stationary components, accommodating misalignment and movement in mechanical systems. They find extensive applications in automotive drive shafts, industrial machinery, and heavy equipment to protect joints from dirt, moisture, and debris, thereby enhancing durability and performance. Unlike register boots, transition boots are preferred in scenarios requiring greater flexibility and protection under dynamic operating conditions.
Pros and Cons of Register Boots
Register boots offer faster access times and more precise control over specific memory locations compared to transition boots, enhancing performance in low-level system initialization. However, their complexity and limited flexibility can lead to increased development time and difficulty in adapting to varied hardware environments. While register boots excel in speed and fine-grained control, they may not provide the broad compatibility and simplicity characteristic of transition boots.
Pros and Cons of Transition Boots
Transition boots provide a smoother shift between gait phases by offering increased flexibility and cushioning, which enhances comfort and reduces joint impact. However, their more complex design can lead to decreased durability and higher maintenance compared to simpler register boots. Athletes and individuals with specific foot issues benefit from transition boots' support, but those requiring long-lasting footwear might prefer register boots for their robustness.
Installation Process: Register Boot vs Transition Boot
Register boot involves initializing hardware registers directly through low-level firmware code during the system startup sequence, ensuring immediate hardware configuration and system readiness. Transition boot, by contrast, begins with a minimal bootloader that hands over control to a more complex software layer responsible for further hardware initialization and system setup. The installation process for register boot requires precise firmware programming and direct hardware access, while transition boot installation focuses on loading and chaining bootloaders to progressively initialize system components.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Register boot offers faster initialization by directly loading essential system registers, reducing startup latency compared to transition boot methods that rely on multiple intermediate states. This streamlined approach minimizes CPU cycles and power consumption, enhancing overall energy efficiency during system startup. Consequently, systems employing register boot demonstrate superior performance metrics and lower resource usage in comparison to those using transition boot processes.
Choosing Between Register Boot and Transition Boot
Choosing between register boot and transition boot depends on system initialization speed and complexity requirements. Register boot offers faster startup by directly loading processor registers, while transition boot provides flexibility through a staged loading process ideal for complex firmware updates. Evaluating the trade-off between rapid initialization and configuration adaptability is essential for optimal boot strategy selection.
Register boot vs transition boot Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com