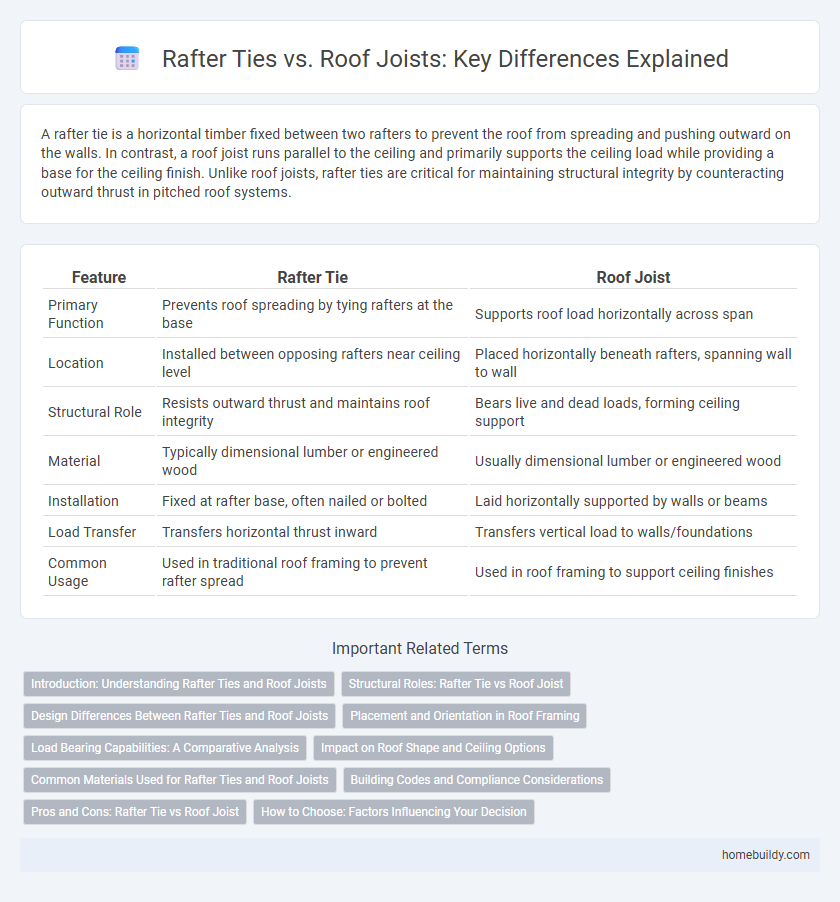
A rafter tie is a horizontal timber fixed between two rafters to prevent the roof from spreading and pushing outward on the walls. In contrast, a roof joist runs parallel to the ceiling and primarily supports the ceiling load while providing a base for the ceiling finish. Unlike roof joists, rafter ties are critical for maintaining structural integrity by counteracting outward thrust in pitched roof systems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rafter Tie | Roof Joist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Prevents roof spreading by tying rafters at the base | Supports roof load horizontally across span |
| Location | Installed between opposing rafters near ceiling level | Placed horizontally beneath rafters, spanning wall to wall |
| Structural Role | Resists outward thrust and maintains roof integrity | Bears live and dead loads, forming ceiling support |
| Material | Typically dimensional lumber or engineered wood | Usually dimensional lumber or engineered wood |
| Installation | Fixed at rafter base, often nailed or bolted | Laid horizontally supported by walls or beams |
| Load Transfer | Transfers horizontal thrust inward | Transfers vertical load to walls/foundations |
| Common Usage | Used in traditional roof framing to prevent rafter spread | Used in roof framing to support ceiling finishes |
Introduction: Understanding Rafter Ties and Roof Joists
Rafter ties are horizontal structural members that connect opposite rafters to prevent the roof from spreading and maintain the integrity of the roof framework. Roof joists, in contrast, are horizontal supports installed beneath the roof sheathing to bear loads and provide a flat surface for the ceiling. Understanding the distinct functions and placements of rafter ties and roof joists is essential for effective roof construction and stability.
Structural Roles: Rafter Tie vs Roof Joist
Rafter ties serve as horizontal members connecting opposing rafters to prevent outward wall thrust and maintain roof stability, primarily resisting tension forces. Roof joists, conversely, are horizontal framing components supporting floor loads and distributing weight from the roof or upper floors to the building's walls or beams. Understanding their distinct structural roles is crucial for ensuring proper load transfer and overall building integrity.
Design Differences Between Rafter Ties and Roof Joists
Rafter ties are horizontal members installed between opposing rafters to prevent the roof from spreading and maintain structural integrity by resisting outward thrust. Roof joists, on the other hand, are horizontal structural elements that support ceiling loads and create the floor structure below the attic space. The key design difference lies in their function: rafter ties primarily counteract lateral roof forces, while roof joists provide vertical load support and floor stability.
Placement and Orientation in Roof Framing
Rafter ties are installed horizontally between opposing rafters near the roof's base, preventing outward wall spread by resisting tension forces. Roof joists run horizontally across the building's width, supporting the ceiling and floor loads directly below the rafters. Proper placement and orientation of rafter ties ensure structural stability by counteracting roof thrust, whereas roof joists primarily provide load distribution and ceiling support.
Load Bearing Capabilities: A Comparative Analysis
Rafter ties primarily function to prevent roof rafters from spreading and transferring lateral loads to walls, offering essential structural support in resisting outward thrust. Roof joists, on the other hand, bear vertical loads from the ceiling and upper floors, distributing weight across walls or beams. While rafter ties resist outward forces, roof joists excel in carrying vertical load capacities, making both critical yet distinct elements in load-bearing roof structures.
Impact on Roof Shape and Ceiling Options
A rafter tie directly connects opposing rafters, preventing roof sagging and allowing for open ceiling designs without interior load-bearing walls, preserving attic space. In contrast, roof joists run horizontally beneath rafters, supporting ceiling loads but limiting ceiling height and attic usability due to their placement. Choosing between rafter ties and roof joists influences roof shape stability and determines the potential for vaulted or flat ceiling options.
Common Materials Used for Rafter Ties and Roof Joists
Common materials used for rafter ties and roof joists include dimensional lumber such as pine, fir, and spruce due to their strength and availability. Engineered wood products like laminated veneer lumber (LVL) and glulam beams are increasingly popular for enhanced stability and uniformity in both rafter ties and roof joists. Steel components are sometimes utilized for commercial or heavy-duty roofing applications to provide superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to environmental factors.
Building Codes and Compliance Considerations
Rafter ties are critical structural members required by building codes to prevent roof spreading by connecting opposing rafters, ensuring roof stability and compliance with load requirements. Roof joists, often governed by different sections of building codes, primarily support ceiling loads and may not suffice as a substitute for rafter ties in resisting outward thrust. Proper installation of rafter ties according to International Residential Code (IRC) sections R802.5 and local amendments is essential to meet compliance and maintain structural integrity in roof framing.
Pros and Cons: Rafter Tie vs Roof Joist
Rafter ties provide critical lateral support by connecting opposing rafters, preventing roof sag and maintaining structural integrity, especially in steep-pitched roofs. Roof joists offer robust horizontal support for floor loads and create a flat ceiling plane but do not prevent outward rafter thrust, which can lead to wall spreading without proper bracing. While rafter ties enhance roof stability and reduce the need for bulky beams, roof joists increase usable attic space and load-bearing capacity but require additional measures to counteract rafter dispersion forces.
How to Choose: Factors Influencing Your Decision
When deciding between a rafter tie and a roof joist, consider factors such as structural load requirements, roof pitch, and attic usage to ensure stability and functionality. Rafter ties are essential for preventing outward spread of rafters in steep-pitched roofs without floor support, while roof joists support flat or low-slope roofs and provide floor framing in attic spaces. Evaluating the design load, span length, and intended use of the attic will guide the selection for optimal roof performance and safety.
Rafter tie vs Roof joist Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com