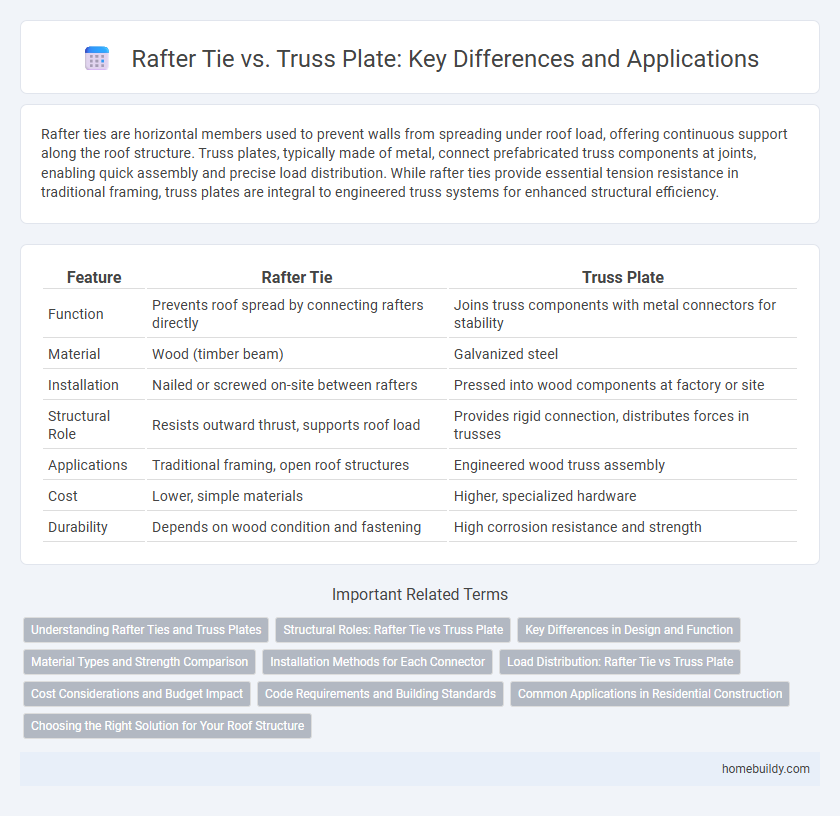
Rafter ties are horizontal members used to prevent walls from spreading under roof load, offering continuous support along the roof structure. Truss plates, typically made of metal, connect prefabricated truss components at joints, enabling quick assembly and precise load distribution. While rafter ties provide essential tension resistance in traditional framing, truss plates are integral to engineered truss systems for enhanced structural efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rafter Tie | Truss Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Prevents roof spread by connecting rafters directly | Joins truss components with metal connectors for stability |
| Material | Wood (timber beam) | Galvanized steel |
| Installation | Nailed or screwed on-site between rafters | Pressed into wood components at factory or site |
| Structural Role | Resists outward thrust, supports roof load | Provides rigid connection, distributes forces in trusses |
| Applications | Traditional framing, open roof structures | Engineered wood truss assembly |
| Cost | Lower, simple materials | Higher, specialized hardware |
| Durability | Depends on wood condition and fastening | High corrosion resistance and strength |
Understanding Rafter Ties and Truss Plates
Rafter ties are horizontal wooden members installed between opposing rafters to prevent roof spreading and maintain structural integrity in traditional framing. Truss plates are metal connectors used in prefabricated trusses to join multiple wood components securely, allowing for complex roof designs and faster construction. Understanding the function of rafter ties versus truss plates highlights their roles in load distribution and roof stability, with rafter ties resisting uplift forces and truss plates providing rigid, engineered connections.
Structural Roles: Rafter Tie vs Truss Plate
Rafter ties function as horizontal tension members that prevent roof rafters from spreading and collapsing, maintaining the integrity of traditional roof framing by resisting outward thrust forces. Truss plates serve as metal connectors that join multiple wooden components in prefabricated trusses, efficiently transferring loads and providing rigid structural stability in complex roof systems. While rafter ties focus on stabilizing pair-wise rafter assemblies, truss plates enable the creation of engineered trusses with optimized load distribution and reduced material use.
Key Differences in Design and Function
Rafter ties are horizontal beams installed across rafters to prevent outward roof spread, ensuring structural stability in traditional roof framing. Truss plates are metal connectors used in prefabricated wood trusses to join multiple members at joints, allowing for precise load distribution and increased manufacturing efficiency. Unlike rafter ties which provide tensile resistance on-site, truss plates enable complex geometric configurations and rapid assembly in engineered roof systems.
Material Types and Strength Comparison
Rafter ties are typically made from galvanized steel or heavy-duty timber, providing flexibility in residential roofing applications, whereas truss plates are manufactured from zinc-coated galvanized steel designed for high-strength load distribution. The strength of truss plates, reinforced through engineered stamping patterns, surpasses that of standard rafter ties, ensuring superior resistance to tension and shear forces in complex roof assemblies. Material composition directly influences performance, with truss plates optimized for structural integrity in prefabricated trusses and rafter ties offering simpler solutions for basic roof framing reinforcement.
Installation Methods for Each Connector
Rafter ties are installed by nailing or screwing directly into the rafters and ceiling joists to prevent roof spreading, requiring precise alignment and sufficient fastening to ensure structural integrity. Truss plates, on the other hand, are metal connectors pressed into pre-cut wooden members using hydraulic presses or pneumatic tools, providing strong, factory-controlled joints in prefabricated trusses. Installation of rafter ties typically involves manual on-site fastening, whereas truss plates require specialized equipment for secure embedding during truss assembly.
Load Distribution: Rafter Tie vs Truss Plate
Rafter ties primarily function to resist outward thrust and maintain roof stability by connecting opposite rafters, distributing load tension across the span. Truss plates offer enhanced load distribution by fastening multiple wood members together at joints, allowing for greater structural support and load transfer through metal connector plates. Compared to rafter ties, truss plates provide superior load dispersion across complex timber frameworks, improving overall roof strength and durability.
Cost Considerations and Budget Impact
Rafter ties generally offer a more budget-friendly solution compared to truss plates, as they require less specialized hardware and can often be installed using standard carpentry tools. Truss plates, while providing superior structural integrity and faster assembly, tend to increase overall project costs due to their material price and need for precise installation equipment. Evaluating the cost impact of each option involves balancing the immediate expense of rafter ties against the long-term durability benefits and higher upfront investment of truss plate systems.
Code Requirements and Building Standards
Rafter ties must comply with local building codes, which often specify minimum sizes, fastening methods, and placement to prevent roof spreading and structural failure. Truss plates, typically used in prefabricated wood trusses, are engineered connectors that meet ASTM standards for load-bearing capacity and corrosion resistance, ensuring compliance with structural safety requirements. Building standards such as the International Residential Code (IRC) provide clear guidelines on when to use rafter ties versus truss plates, emphasizing correct installation techniques to maintain roof integrity and overall building stability.
Common Applications in Residential Construction
Rafter ties are commonly used in residential construction to prevent roof rafters from spreading and provide lateral stability in traditional stick-framed roofs. Truss plates, made of galvanized steel, are primarily utilized in prefabricated wood trusses for quick assembly and consistent structural performance. While rafter ties are ideal for customizing roof designs on-site, truss plates streamline construction in large-scale housing developments through factory-built components.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Roof Structure
Rafter ties provide essential tension support in traditional roof framing by connecting opposing rafters and preventing outward wall spread. Truss plates, made of galvanized steel, enable efficient prefabricated truss assembly, offering enhanced strength and faster installation for modern roof systems. Selecting the right solution depends on your roof's design requirements, load capacity, and construction timeline, with rafter ties suited for custom builds and truss plates ideal for standardized, high-strength frameworks.
Rafter tie vs Truss plate Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com