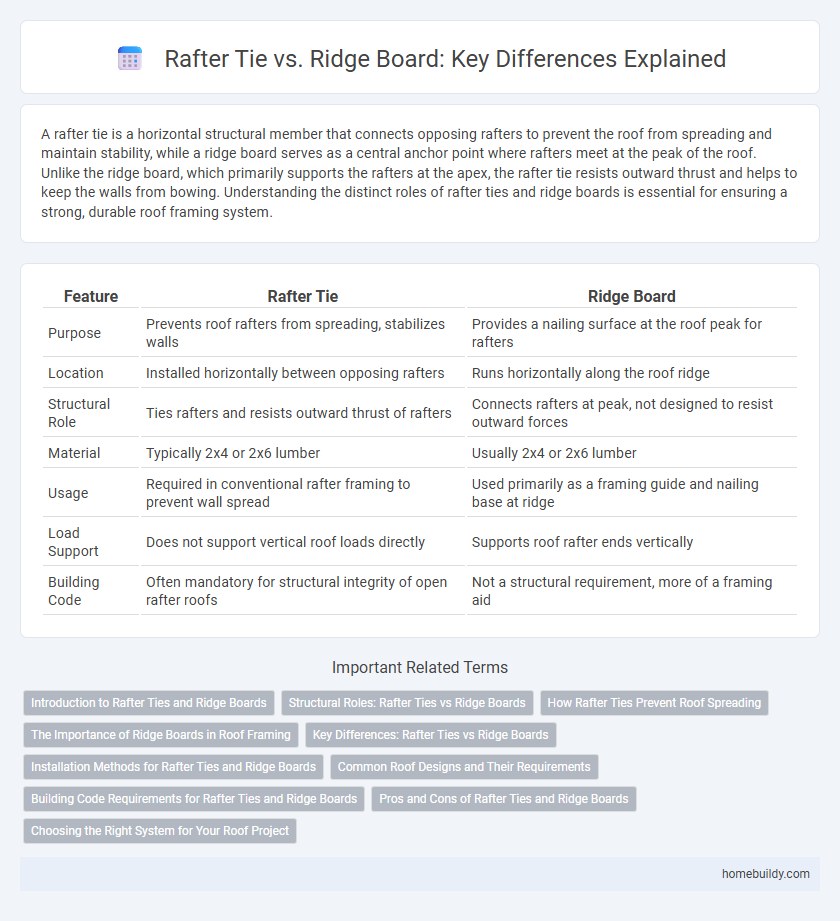
A rafter tie is a horizontal structural member that connects opposing rafters to prevent the roof from spreading and maintain stability, while a ridge board serves as a central anchor point where rafters meet at the peak of the roof. Unlike the ridge board, which primarily supports the rafters at the apex, the rafter tie resists outward thrust and helps to keep the walls from bowing. Understanding the distinct roles of rafter ties and ridge boards is essential for ensuring a strong, durable roof framing system.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rafter Tie | Ridge Board |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents roof rafters from spreading, stabilizes walls | Provides a nailing surface at the roof peak for rafters |
| Location | Installed horizontally between opposing rafters | Runs horizontally along the roof ridge |
| Structural Role | Ties rafters and resists outward thrust of rafters | Connects rafters at peak, not designed to resist outward forces |
| Material | Typically 2x4 or 2x6 lumber | Usually 2x4 or 2x6 lumber |
| Usage | Required in conventional rafter framing to prevent wall spread | Used primarily as a framing guide and nailing base at ridge |
| Load Support | Does not support vertical roof loads directly | Supports roof rafter ends vertically |
| Building Code | Often mandatory for structural integrity of open rafter roofs | Not a structural requirement, more of a framing aid |
Introduction to Rafter Ties and Ridge Boards
Rafter ties are horizontal structural members that connect opposing rafters to prevent the roof from spreading and maintain the integrity of the roof framework. Ridge boards serve as a central horizontal beam at the peak of a roof, providing a nailing surface for the upper ends of rafters but do not bear significant structural loads. Understanding the distinct roles of rafter ties and ridge boards is essential for effective roof framing and load distribution.
Structural Roles: Rafter Ties vs Ridge Boards
Rafter ties serve as horizontal supports that prevent roof rafters from spreading outward under load, maintaining the structural integrity of the roof frame. Ridge boards provide a central anchoring point at the peak of the roof, aligning rafters but not bearing significant structural load. While ridge boards offer positioning and stability, rafter ties are critical in resisting outward thrust and ensuring the roof trusses remain securely connected.
How Rafter Ties Prevent Roof Spreading
Rafter ties play a critical role in preventing roof spreading by connecting the opposing rafters at their lower ends, creating tension that resists outward thrust and maintains structural integrity. Unlike ridge boards, which primarily serve as a nailing surface at the roof peak without providing significant structural support, rafter ties counteract the horizontal forces that push walls outward. This tension system effectively stabilizes the roof framework, preventing deformation and maintaining the building's overall load distribution.
The Importance of Ridge Boards in Roof Framing
Ridge boards serve as the central spine in roof framing, providing a stable surface for securing the upper ends of rafters and ensuring proper roof alignment and structural integrity. Unlike rafter ties, which prevent outward wall thrust by connecting opposing rafters at the base, ridge boards maintain the roof's shape and facilitate uniform load distribution along the peak. Proper installation of ridge boards is crucial for preventing roof sagging and enhancing overall durability in residential and commercial buildings.
Key Differences: Rafter Ties vs Ridge Boards
Rafter ties are horizontal structural members installed between opposing rafters to prevent roof spread and maintain the integrity of the building's walls, while ridge boards serve as vertical or horizontal components at the peak of a roof, providing a nailing surface for rafters. Unlike ridge boards, rafter ties carry tensile forces to resist outward wall thrust, enhancing roof stability in timber framing systems. Selecting between rafter ties and ridge boards depends on the roof design, load distribution, and structural requirements, with rafter ties being critical for preventing wall separation in open-ceiling constructions.
Installation Methods for Rafter Ties and Ridge Boards
Installation methods for rafter ties typically involve fastening them horizontally between opposing rafters at the lower third of the roof to prevent outward wall spread, using metal straps, nails, or screws for secure attachment. Ridge board installation requires positioning the board along the roof peak, where rafters are then fastened directly to it with nails or screws, ensuring proper alignment and load distribution. While rafter ties reinforce the roof structure by resisting lateral forces, ridge boards serve as a central anchoring point for rafters but do not carry structural loads on their own.
Common Roof Designs and Their Requirements
Rafter ties are crucial in common roof designs such as gable and hip roofs, preventing outward spread of rafters and maintaining structural integrity by creating a tension member across the base of the rafters. Ridge boards serve primarily as a nailing surface for rafters but do not provide lateral support, making them insufficient alone in roofs without proper rafter ties to handle uplift and spreading forces. Building codes often mandate rafter ties in steep-pitched roofs to ensure stability against wind loads and to meet safety requirements in residential construction.
Building Code Requirements for Rafter Ties and Ridge Boards
Building code requirements for rafter ties mandate their installation to prevent roof spreading and ensure structural stability, typically specified in the International Residential Code (IRC) under section R802.4. Ridge boards serve as a nailing surface for rafters rather than a structural beam, and while codes require ridge boards for alignment, they do not replace the need for rafter ties unless engineered alternatives are used. Proper adherence to these regulations ensures compliance with load distribution standards and prevents roof failure due to outward wall thrust.
Pros and Cons of Rafter Ties and Ridge Boards
Rafter ties effectively prevent outward wall spread by connecting opposite rafters, providing structural stability with minimal material cost and ease of installation; however, they can limit attic space and may require precise placement to avoid interference with roof components. Ridge boards offer a central nailing surface that simplifies rafter alignment and load distribution along the roof peak but can be less effective against wall thrust without supplementary ties and typically involve higher material and installation complexity. Choosing between rafter ties and ridge boards depends on balancing factors such as building design, attic space requirements, and structural load management.
Choosing the Right System for Your Roof Project
Rafter ties prevent roof spread by connecting opposing rafters at their lower ends, providing essential lateral support in traditional roof framing. Ridge boards serve as a central attachment point where rafters meet, offering alignment but not structural tension resistance. Selecting the right system depends on your roof's design load, span, and desired structural integrity; rafter ties are crucial for controlling outward thrust in open truss roofs, while ridge boards are suitable for basic alignment in simpler, lighter roof structures.
Rafter tie vs Ridge board Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com