Rigid conduit provides superior protection for electrical wiring due to its sturdy, non-bendable structure, making it ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty applications. Flexible conduit offers greater ease of installation and adaptability in tight or complex spaces, accommodating bends and movements without compromising the wiring inside. Choosing between rigid and flexible conduit depends on the specific requirements of durability, environmental exposure, and installation complexity.
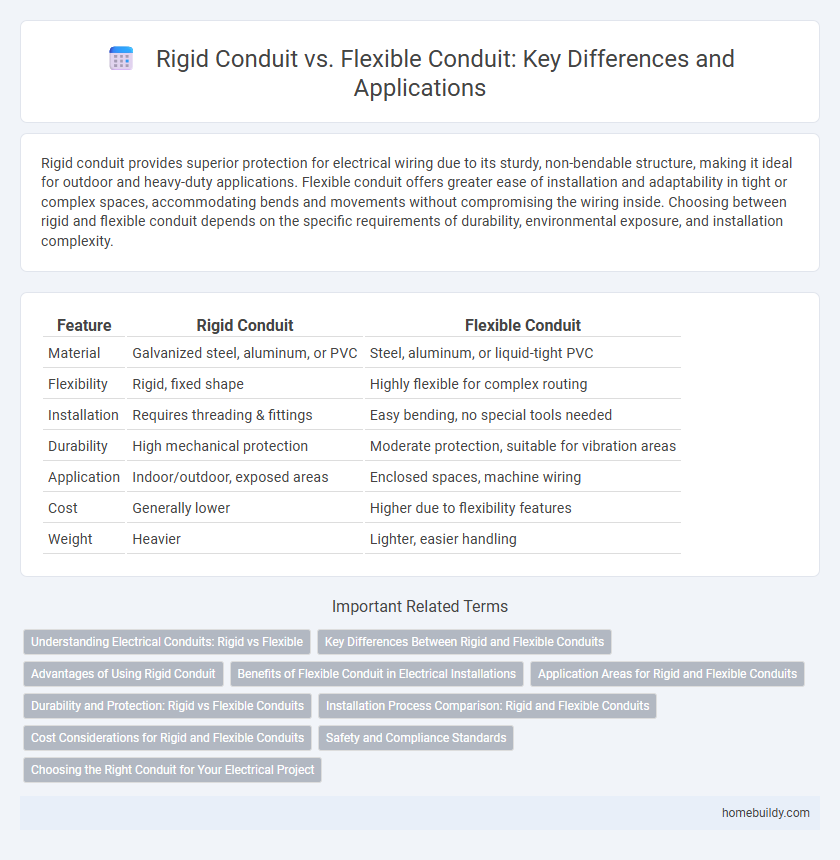
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rigid Conduit | Flexible Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Galvanized steel, aluminum, or PVC | Steel, aluminum, or liquid-tight PVC |
| Flexibility | Rigid, fixed shape | Highly flexible for complex routing |
| Installation | Requires threading & fittings | Easy bending, no special tools needed |
| Durability | High mechanical protection | Moderate protection, suitable for vibration areas |
| Application | Indoor/outdoor, exposed areas | Enclosed spaces, machine wiring |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to flexibility features |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter, easier handling |
Understanding Electrical Conduits: Rigid vs Flexible
Rigid conduits, typically made of steel or PVC, provide robust protection against physical damage and are ideal for outdoor or industrial applications requiring high durability. Flexible conduits, often constructed from metal or plastic, allow easier routing through complex spaces and absorb vibrations, making them suitable for residential or light commercial use. Selecting between rigid and flexible conduits depends on factors like environmental exposure, mechanical protection needs, and installation complexity.
Key Differences Between Rigid and Flexible Conduits
Rigid conduit, typically made from galvanized steel or PVC, offers superior protection against physical damage and environmental hazards for electrical wiring, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Flexible conduit, often constructed from steel or plastic, provides enhanced maneuverability around obstacles and is preferred in tight spaces or where frequent adjustments are necessary. Key differences include rigidity, ease of installation, durability, and cost, with rigid conduits being more robust but less adaptable compared to the lightweight and flexible nature of flexible conduits.
Advantages of Using Rigid Conduit
Rigid conduit offers superior protection against physical damage, making it ideal for environments with high impact risks. Its durability provides enhanced resistance to corrosion and environmental factors, ensuring long-lasting electrical system integrity. The solid structure of rigid conduit also supports easy grounding and bonding, contributing to improved electrical safety.
Benefits of Flexible Conduit in Electrical Installations
Flexible conduit offers superior adaptability for electrical installations, easily navigating around obstacles and accommodating complex wiring layouts. Its enhanced vibration resistance reduces stress on electrical components, increasing system longevity and safety. Installation efficiency improves with flexible conduit as it requires fewer fittings and adjustments compared to rigid conduit systems.
Application Areas for Rigid and Flexible Conduits
Rigid conduits are extensively used in industrial and commercial settings where protection from physical damage is critical, such as factories, warehouses, and outdoor installations. Flexible conduits are preferred in environments requiring bending and vibration resistance, including machinery enclosures, HVAC systems, and tight spaces in residential or commercial buildings. Selecting between rigid and flexible conduits depends on factors like installation complexity, exposure to mechanical stress, and the need for frequent maintenance access.
Durability and Protection: Rigid vs Flexible Conduits
Rigid conduits offer superior durability and protection due to their corrosion-resistant metal or PVC construction, providing robust shielding against physical damage and environmental factors. Flexible conduits, often made from metal or plastic materials, prioritize adaptability and ease of installation but may compromise on impact resistance and long-term durability compared to rigid options. Choosing between rigid and flexible conduits depends on the specific application's needs for mechanical protection and environmental exposure.
Installation Process Comparison: Rigid and Flexible Conduits
Rigid conduit installation requires precise measurements, bending tools, and secure fittings to ensure a straight, consistent pathway for electrical wiring, making it ideal for permanent and exposed applications. Flexible conduit offers easier and faster installation, especially around corners or in confined spaces, due to its flexibility and minimal need for bending tools or connectors. While rigid conduit provides superior protection against physical damage, flexible conduit reduces labor time and adapts well to complex routing needs.
Cost Considerations for Rigid and Flexible Conduits
Rigid conduits generally have a higher initial cost due to their sturdy materials such as galvanized steel or aluminum, but their durability reduces long-term maintenance expenses. Flexible conduits typically cost less upfront and allow easier installation around complex structures, though they may require more frequent replacement in demanding environments. Evaluating project requirements and lifecycle costs is essential to determine the most cost-effective conduit type.
Safety and Compliance Standards
Rigid conduit offers superior protection against physical damage and environmental hazards, making it highly compliant with National Electrical Code (NEC) safety standards for exposed or outdoor wiring applications. Flexible conduit provides enhanced adaptability for complex or vibrating installations but requires careful selection to meet specific NEC grounding and fire resistance requirements. Both conduit types must adhere to local electrical regulations and UL listings to ensure maximum safety and compliance in electrical system design.
Choosing the Right Conduit for Your Electrical Project
Rigid conduit offers superior protection and durability for electrical wiring, making it ideal for outdoor or industrial applications exposed to harsh conditions. Flexible conduit provides ease of installation in tight spaces and complex pathways, suitable for indoor use where bending and maneuverability are essential. Selecting the right conduit depends on factors like environmental exposure, mechanical protection needs, and installation complexity to ensure safety and code compliance.
Rigid conduit vs Flexible conduit Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com