A conduit box primarily serves as a protective enclosure for electrical wiring connections within conduits, facilitating organized routing and access for maintenance. In contrast, a junction box is designed specifically to join multiple electrical circuits safely, enabling secure splicing and distribution of power or signals. Both types are essential for electrical system safety and compliance with wiring codes, but their applications and structural features differ based on function.
Table of Comparison
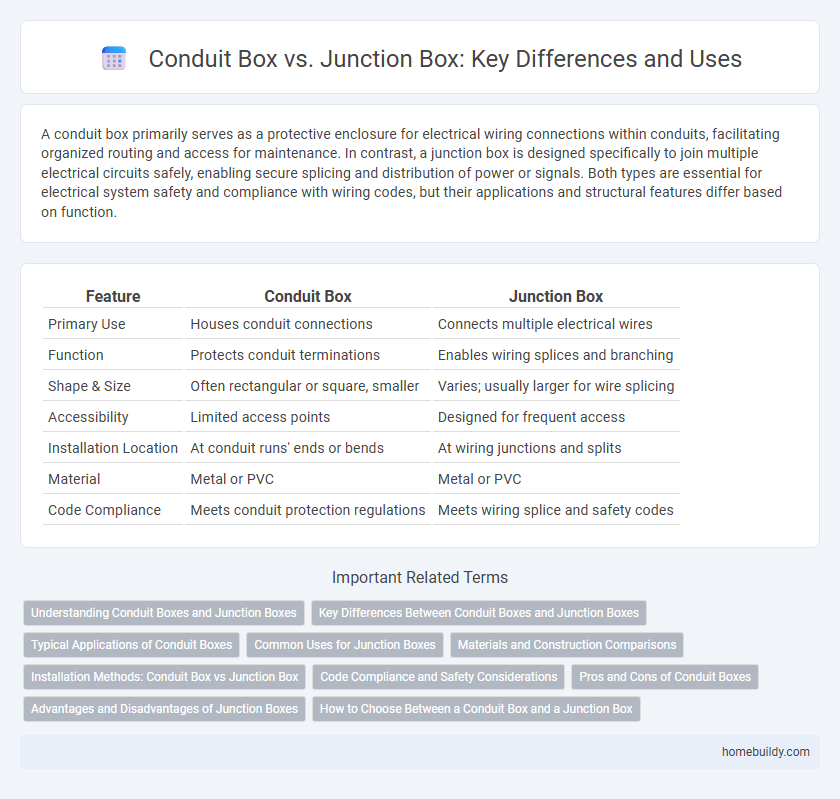
| Feature | Conduit Box | Junction Box |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Houses conduit connections | Connects multiple electrical wires |
| Function | Protects conduit terminations | Enables wiring splices and branching |
| Shape & Size | Often rectangular or square, smaller | Varies; usually larger for wire splicing |
| Accessibility | Limited access points | Designed for frequent access |
| Installation Location | At conduit runs' ends or bends | At wiring junctions and splits |
| Material | Metal or PVC | Metal or PVC |
| Code Compliance | Meets conduit protection regulations | Meets wiring splice and safety codes |
Understanding Conduit Boxes and Junction Boxes
Conduit boxes are metal or plastic enclosures designed to house electrical conduit connections and protect wiring splices, ensuring secure routing of electrical cables. Junction boxes serve as central points where multiple electrical circuits connect, allowing for circuit branching and maintenance access while safeguarding wiring connections. Both types of boxes conform to electrical codes and standards, providing safety, organization, and ease of inspection in electrical systems.
Key Differences Between Conduit Boxes and Junction Boxes
Conduit boxes are specifically designed to house conduit terminations and facilitate connections of electrical conduits, ensuring secure and protected cable routing, whereas junction boxes primarily serve as enclosures for splicing wires and connecting electrical circuits. Conduit boxes are typically sealed to maintain conduit system integrity and prevent moisture ingress, while junction boxes often feature removable covers for easier access during wire splicing and maintenance. The choice between conduit and junction boxes depends on specific installation requirements, such as the need for conduit connection points versus wire splicing capabilities in electrical wiring systems.
Typical Applications of Conduit Boxes
Conduit boxes are typically used to house and protect electrical connections in conduit systems, facilitating the routing of wires in residential, commercial, and industrial installations. They serve as access points for pulling, splicing, and maintaining electrical conductors within conduit runs and are often installed where wires branch off to different circuits. Unlike junction boxes, conduit boxes are specifically designed to accommodate conduit fittings and provide a secure enclosure for terminating conduit ends.
Common Uses for Junction Boxes
Junction boxes are primarily used to protect and organize electrical wire connections in residential, commercial, and industrial wiring systems. They provide a secure enclosure where multiple conduits or cables meet, allowing electricians to splice or branch circuits safely while preventing exposure to moisture and physical damage. Common applications of junction boxes include extending wiring runs, transitioning between different conduit types, and housing electrical splices in accessible locations for maintenance or future expansion.
Materials and Construction Comparisons
Conduit boxes are typically made from rigid metal such as steel or aluminum to provide strong protection for electrical wiring in industrial and outdoor settings, while junction boxes often use plastic or lighter metal materials suitable for residential applications. The construction of conduit boxes features threaded hubs or knockouts designed to connect conduit securely, ensuring a robust, dustproof, and moisture-resistant enclosure. Junction boxes prioritize ease of access and installation with snap-on or screw covers, emphasizing safety and convenience for electrical splicing and connections.
Installation Methods: Conduit Box vs Junction Box
Conduit boxes are installed primarily to protect conduit connections and allow wiring access points, typically mounted flush or surface with conduit runs. Junction boxes serve as enclosure points where multiple electrical wires are joined, often requiring accessible placement for maintenance and wire splicing. Installation of conduit boxes emphasizes securing conduit entry points and maintaining continuity of conduit systems, whereas junction box installation focuses on providing safe, organized wire junctions within accessible reach.
Code Compliance and Safety Considerations
Conduit boxes and junction boxes both serve to protect electrical connections, but conduit boxes are specifically designed to accommodate conduit fittings and must comply with NEC requirements for secure attachment and grounding. Junction boxes focus on housing wire splices and must ensure proper accessibility and protection against electrical hazards, meeting code mandates for volume and fill capacity. Code compliance ensures both types maintain system integrity and prevent potential fire or shock risks in electrical installations.
Pros and Cons of Conduit Boxes
Conduit boxes offer robust mechanical protection for electrical connections, making them ideal for environments with heavy physical stress or exposure to moisture and dust. Their main drawback is their larger size and more complex installation compared to junction boxes, which can increase labor time and cost. Conduit boxes also provide easier accessibility for maintenance and future circuit expansion, enhancing long-term system flexibility.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Junction Boxes
Junction boxes offer significant advantages in electrical conduit systems, providing secure protection for wiring splices and facilitating easier access for maintenance or future upgrades, enhancing overall safety and organization. However, junction boxes can be bulkier and more expensive than conduit boxes, potentially complicating installation in tight spaces. Their exposure to environmental factors also requires proper sealing to prevent moisture ingress and ensure long-term durability.
How to Choose Between a Conduit Box and a Junction Box
Choosing between a conduit box and a junction box depends on the specific electrical application and installation requirements. A conduit box primarily serves as a protective enclosure for conduit connections and wiring terminations, often used in conduit systems where multiple conduits intersect or change direction. A junction box, designed for joining multiple electrical wires or cables, provides easy access for maintenance and troubleshooting, making it ideal for complex wiring splices and connections.
Conduit box vs Junction box Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com