Metal conduit offers superior durability, grounding capabilities, and resistance to physical damage compared to plastic conduit, making it ideal for industrial and outdoor applications. Plastic conduit, typically PVC, provides excellent corrosion resistance, flexibility, and ease of installation, which is beneficial for residential and underground wiring. Choosing between metal and plastic conduit depends on environmental conditions, budget constraints, and specific electrical code requirements.
Table of Comparison
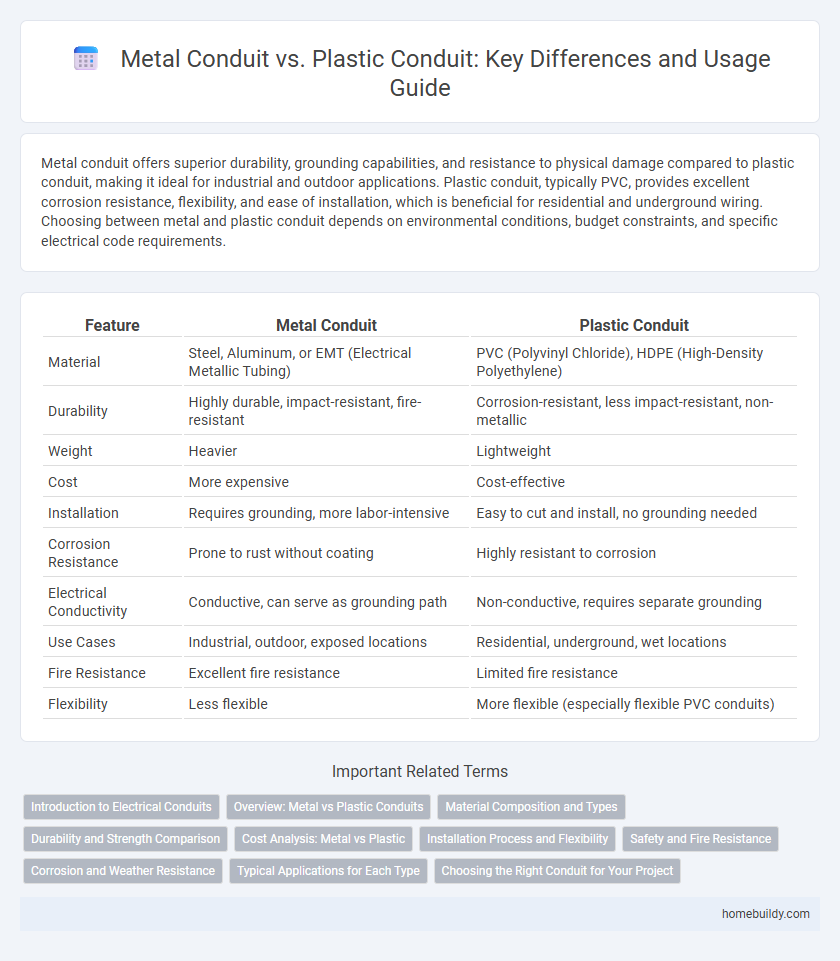
| Feature | Metal Conduit | Plastic Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel, Aluminum, or EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) | PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) |
| Durability | Highly durable, impact-resistant, fire-resistant | Corrosion-resistant, less impact-resistant, non-metallic |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Cost | More expensive | Cost-effective |
| Installation | Requires grounding, more labor-intensive | Easy to cut and install, no grounding needed |
| Corrosion Resistance | Prone to rust without coating | Highly resistant to corrosion |
| Electrical Conductivity | Conductive, can serve as grounding path | Non-conductive, requires separate grounding |
| Use Cases | Industrial, outdoor, exposed locations | Residential, underground, wet locations |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent fire resistance | Limited fire resistance |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible (especially flexible PVC conduits) |
Introduction to Electrical Conduits
Metal conduits offer superior durability, excellent protection against physical damage, and enhanced grounding capabilities, making them ideal for industrial and commercial electrical installations. Plastic conduits, typically PVC, provide lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective solutions favored in residential and underground applications. Both conduit types ensure organized wiring and protection but differ significantly in mechanical strength, installation flexibility, and environmental suitability.
Overview: Metal vs Plastic Conduits
Metal conduits, such as EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) and rigid steel, offer superior durability, electrical grounding, and resistance to physical damage, making them ideal for industrial and outdoor applications. Plastic conduits like PVC and ENT provide corrosion resistance, lightweight installation, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in residential and underground electrical wiring. Selecting between metal and plastic conduit depends on factors including environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and budget constraints.
Material Composition and Types
Metal conduits, typically made from galvanized steel, aluminum, or stainless steel, offer superior mechanical strength and electromagnetic interference shielding compared to plastic conduits. Plastic conduits, including PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and HDPE (high-density polyethylene), provide corrosion resistance, lightweight handling, and flexibility for non-metallic applications. Each material type addresses specific installation requirements, with metal conduits preferred in industrial environments and plastic conduits favored in residential or underground settings.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Metal conduit, typically made from galvanized steel or aluminum, offers superior durability and strength compared to plastic conduit, making it highly resistant to physical damage, impact, and harsh environmental conditions. Plastic conduit, often fabricated from PVC or HDPE, provides corrosion resistance and flexibility but tends to be less robust, with lower impact resistance and susceptibility to cracking under extreme stress or temperature fluctuations. Choosing metal conduit enhances structural protection for electrical wiring in industrial or outdoor applications where mechanical wear and intense conditions are prevalent.
Cost Analysis: Metal vs Plastic
Metal conduit generally incurs higher upfront costs due to material price and labor-intensive installation, while plastic conduit offers a more budget-friendly alternative with lower material expenses and easier handling. Long-term cost considerations favor metal conduit in environments requiring durability and corrosion resistance, reducing maintenance and replacement needs. Plastic conduit serves as a cost-effective solution for non-corrosive, indoor applications with less stringent mechanical protection requirements.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Metal conduit offers robust durability and provides superior protection for electrical wiring, but its installation process is labor-intensive due to the need for precise cutting and threading. Plastic conduit, such as PVC, is lightweight and easier to install, allowing for quicker assembly with solvent cement or push-fit connectors, enhancing project efficiency. The flexibility of plastic conduits enables easier routing around obstacles, whereas metal conduits require bending tools and careful handling to achieve similar flexibility.
Safety and Fire Resistance
Metal conduit offers superior fire resistance due to its non-combustible properties, effectively preventing the spread of flames and protecting electrical wiring from heat damage. Plastic conduit, typically made from PVC or HDPE, is more susceptible to melting and releasing toxic fumes during a fire, posing higher safety risks. Choosing metal conduit enhances overall electrical safety by providing robust physical protection and minimizing fire hazards in residential and commercial installations.
Corrosion and Weather Resistance
Metal conduits, such as galvanized steel and aluminum, offer strong protection against physical damage but require proper coatings to prevent corrosion, especially in moist or outdoor environments. Plastic conduits like PVC and HDPE are inherently resistant to corrosion and chemicals, making them ideal for wet or corrosive conditions and harsh weather exposure. While metal conduits provide superior mechanical strength, plastic conduits excel in long-term weather resistance and non-conductivity, reducing maintenance costs in corrosive settings.
Typical Applications for Each Type
Metal conduit is commonly used in commercial and industrial settings where durability and electromagnetic interference protection are essential, such as in factories, warehouses, and outdoor installations. Plastic conduit, like PVC, is preferred for residential wiring, underground installations, and areas with high moisture due to its corrosion resistance and ease of installation. Each conduit type is selected based on environmental exposure, mechanical protection needs, and local electrical codes.
Choosing the Right Conduit for Your Project
Metal conduit offers superior durability, excellent resistance to physical damage, and electromagnetic interference shielding, making it ideal for industrial and commercial applications requiring robust protection. Plastic conduit, such as PVC or HDPE, provides corrosion resistance, lightweight installation, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for residential or underground projects with less mechanical stress. Selecting the right conduit depends on environmental factors, budget constraints, and specific electrical code requirements for the project location.
Metal conduit vs Plastic conduit Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com