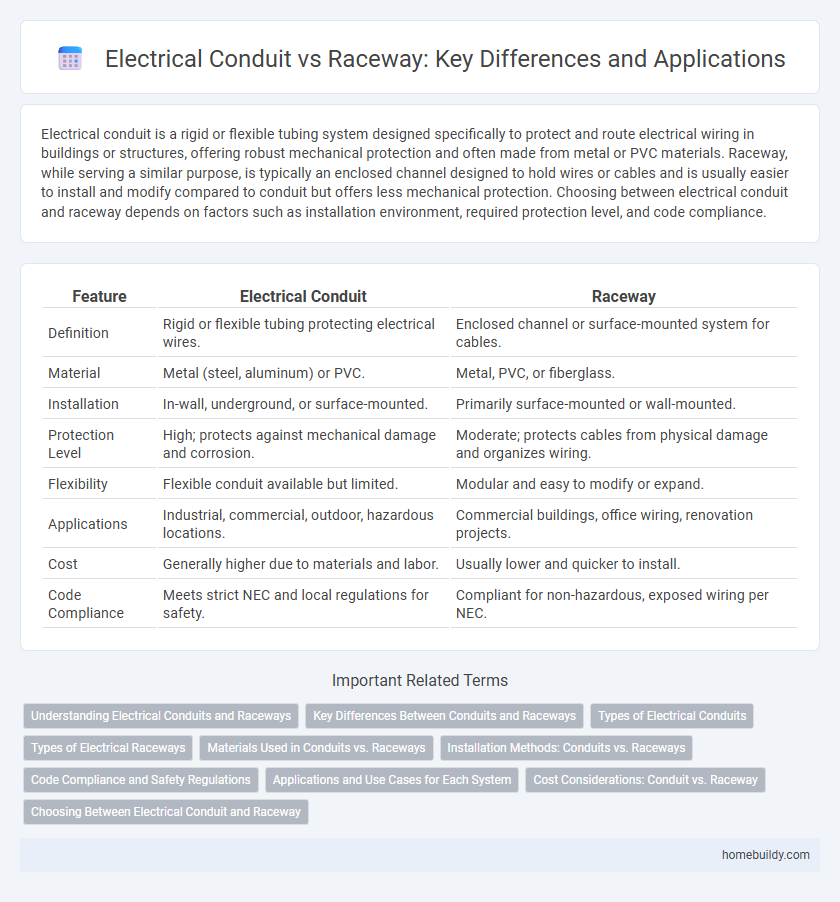
Electrical conduit is a rigid or flexible tubing system designed specifically to protect and route electrical wiring in buildings or structures, offering robust mechanical protection and often made from metal or PVC materials. Raceway, while serving a similar purpose, is typically an enclosed channel designed to hold wires or cables and is usually easier to install and modify compared to conduit but offers less mechanical protection. Choosing between electrical conduit and raceway depends on factors such as installation environment, required protection level, and code compliance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrical Conduit | Raceway |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rigid or flexible tubing protecting electrical wires. | Enclosed channel or surface-mounted system for cables. |
| Material | Metal (steel, aluminum) or PVC. | Metal, PVC, or fiberglass. |
| Installation | In-wall, underground, or surface-mounted. | Primarily surface-mounted or wall-mounted. |
| Protection Level | High; protects against mechanical damage and corrosion. | Moderate; protects cables from physical damage and organizes wiring. |
| Flexibility | Flexible conduit available but limited. | Modular and easy to modify or expand. |
| Applications | Industrial, commercial, outdoor, hazardous locations. | Commercial buildings, office wiring, renovation projects. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to materials and labor. | Usually lower and quicker to install. |
| Code Compliance | Meets strict NEC and local regulations for safety. | Compliant for non-hazardous, exposed wiring per NEC. |
Understanding Electrical Conduits and Raceways
Electrical conduits are rigid or flexible tubes designed to protect and route electrical wiring in buildings, offering superior mechanical protection against physical damage. Raceways, encompassing a broader category including trays, channels, and surface-mounted systems, provide easier access for wiring modifications and generally accommodate larger cable volumes. Understanding the differences between electrical conduits and raceways is essential for selecting appropriate wiring protection solutions based on installation environment, accessibility needs, and code requirements.
Key Differences Between Conduits and Raceways
Electrical conduits are rigid or flexible tubes designed to protect and route electrical wiring, typically made from metal or plastic, offering high durability and resistance to environmental factors. Raceways, on the other hand, are surface-mounted channels that can house multiple cables and provide easier access for maintenance and future wiring changes. Key differences include the installation method, with conduits often requiring embedded or concealed placement, whereas raceways are more accessible, and the capacity, as raceways can accommodate a larger volume of cables compared to conduits.
Types of Electrical Conduits
Electrical conduit types include rigid metal conduit (RMC), intermediate metal conduit (IMC), electrical metallic tubing (EMT), and non-metallic conduit like PVC and flexible conduit; each serves specific protection and installation needs. RMC offers the highest durability for industrial and outdoor applications, while EMT is lightweight and easier to install for indoor wiring. PVC conduit provides corrosion resistance and electrical insulation in damp or underground environments, making it a versatile raceway alternative.
Types of Electrical Raceways
Electrical raceways include various types such as electrical conduits, cable trays, surface raceways, and wireways, each designed to protect and route electrical wiring. Electrical conduits, typically made of metal or PVC, provide a fully enclosed pathway, while cable trays offer open support systems ideal for large cable volumes. Surface raceways allow for easy installation on existing walls and ceilings, emphasizing accessibility and flexibility in electrical wiring management.
Materials Used in Conduits vs. Raceways
Electrical conduits are primarily constructed from rigid materials such as steel, aluminum, or PVC, providing superior protection against physical damage and corrosion. Raceways, on the other hand, offer a broader range of materials including metal, plastic, and fiber-reinforced composites, allowing for increased flexibility and easier installation in complex wiring systems. The choice of materials in conduits versus raceways directly impacts durability, environmental resistance, and suitability for specific electrical applications.
Installation Methods: Conduits vs. Raceways
Electrical conduit installation involves threading or pulling wires through rigid or flexible metal or plastic tubes, requiring precise bending and secure fittings to ensure protection and grounding. Raceway systems, often surface-mounted, offer easier access for wire pulling and modifications due to their snap-on covers and modular design, simplifying maintenance and future expansions. While conduit demands more labor-intensive preparation and tools, raceways provide faster installation times, especially in retrofit applications or commercial settings where accessibility is critical.
Code Compliance and Safety Regulations
Electrical conduit and raceway systems both comply with National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements, but conduits offer enhanced protection against physical damage and environmental hazards, making them preferable in harsh or hazardous locations. Raceways, while easier to install and modify, must still meet specific NEC guidelines for grounding, support, and fill capacity to ensure safety and code compliance. Prioritizing conduit use in areas subject to moisture, corrosive chemicals, or mechanical impact maximizes adherence to OSHA safety regulations and reduces the risk of electrical faults or fire hazards.
Applications and Use Cases for Each System
Electrical conduit provides a robust and secure pathway for protecting electrical wiring in environments requiring high durability, such as commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and outdoor installations exposed to harsh conditions. Raceway systems offer flexible and easily modifiable solutions ideal for office spaces, data centers, and residential projects where frequent access for wiring changes or additions is necessary. Choosing between conduit and raceway depends on factors like mechanical protection needs, installation complexity, and future maintenance requirements.
Cost Considerations: Conduit vs. Raceway
Electrical conduit generally offers a lower initial cost compared to raceway systems due to its simpler materials and installation processes. Raceway installations involve higher expenses attributed to customizable configurations and enhanced protection for sensitive wiring, justifying the increased project budget. For projects prioritizing budget efficiency, conduit proves more cost-effective, while raceways deliver added value in specialized or high-demand environments.
Choosing Between Electrical Conduit and Raceway
Selecting between electrical conduit and raceway depends on factors such as installation environment, protection requirements, and flexibility needs. Electrical conduit offers superior durability and corrosion resistance, ideal for outdoor or hazardous locations, while raceway provides easier access for wiring changes and is suitable for indoor commercial or industrial settings. Cost-effectiveness and compliance with electrical codes also influence the decision-making process in electrical system design.
Electrical conduit vs Raceway Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com