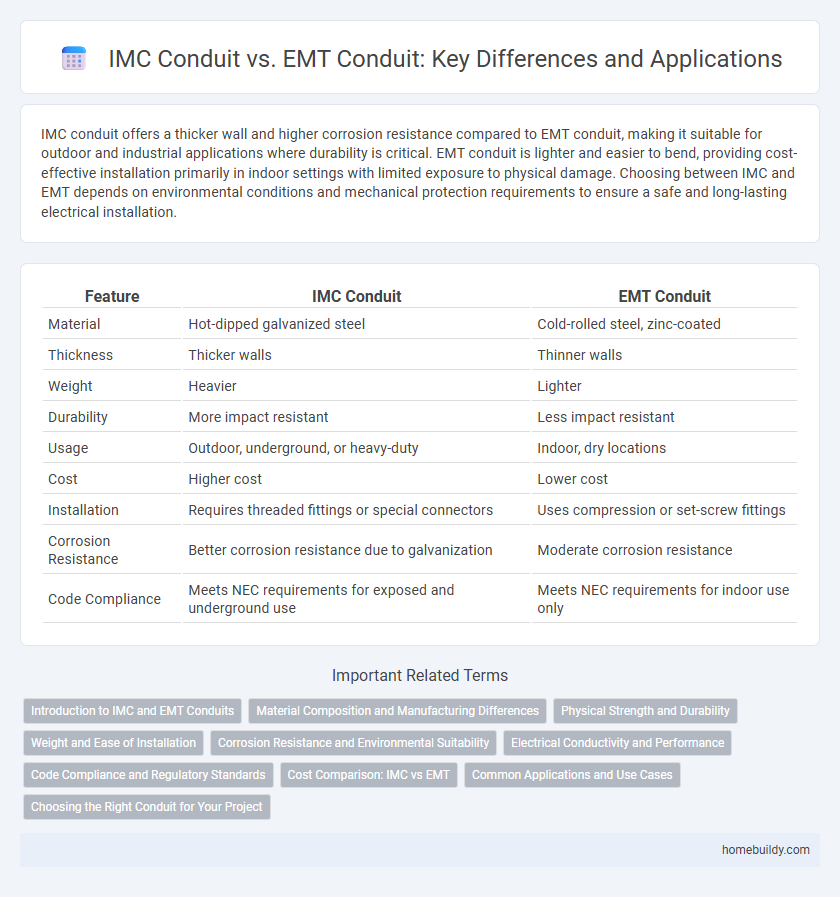
IMC conduit offers a thicker wall and higher corrosion resistance compared to EMT conduit, making it suitable for outdoor and industrial applications where durability is critical. EMT conduit is lighter and easier to bend, providing cost-effective installation primarily in indoor settings with limited exposure to physical damage. Choosing between IMC and EMT depends on environmental conditions and mechanical protection requirements to ensure a safe and long-lasting electrical installation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | IMC Conduit | EMT Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Hot-dipped galvanized steel | Cold-rolled steel, zinc-coated |
| Thickness | Thicker walls | Thinner walls |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Durability | More impact resistant | Less impact resistant |
| Usage | Outdoor, underground, or heavy-duty | Indoor, dry locations |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Installation | Requires threaded fittings or special connectors | Uses compression or set-screw fittings |
| Corrosion Resistance | Better corrosion resistance due to galvanization | Moderate corrosion resistance |
| Code Compliance | Meets NEC requirements for exposed and underground use | Meets NEC requirements for indoor use only |
Introduction to IMC and EMT Conduits
Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC) is a galvanized steel tubing designed to provide superior corrosion resistance and mechanical protection for electrical wiring, commonly used in exposed and outdoor applications. Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) is a thinner, lightweight galvanized steel conduit that is easier to bend and install, often preferred for indoor construction where flexibility and cost efficiency are key. Both IMC and EMT conduits offer reliable electrical grounding and meet National Electrical Code (NEC) standards but differ significantly in strength, weight, and environmental suitability.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Differences
IMC conduit is made from a heavier gauge galvanized steel, providing enhanced corrosion resistance and structural strength compared to the thinner, lighter aluminum or steel used in EMT conduit. IMC undergoes a hot-dip galvanizing process, resulting in a thicker zinc coating that improves durability in harsh environments, while EMT is typically cold-rolled and electro-galvanized with a thinner protective layer. These manufacturing differences make IMC conduit more suitable for outdoor or industrial applications requiring robust mechanical protection and longevity.
Physical Strength and Durability
IMC conduit offers superior physical strength and durability compared to EMT conduit, featuring a thicker wall and higher resistance to impact and corrosion. IMC's galvanized steel construction makes it suitable for outdoor and industrial environments where mechanical protection is critical. EMT conduit, while lighter and easier to handle, provides less protection and is better suited for indoor applications with minimal exposure to harsh conditions.
Weight and Ease of Installation
IMC conduit weighs approximately 30% less than RMC while being heavier than EMT, offering a balance between durability and manageability. EMT conduit is notably lighter and easier to cut and bend, making it ideal for quick installations in non-corrosive environments. The lightweight nature and simpler handling of EMT reduce labor time, whereas IMC provides enhanced strength with moderate ease of installation.
Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Suitability
IMC (Intermediate Metal Conduit) offers superior corrosion resistance compared to EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing), making it ideal for outdoor and industrial environments exposed to moisture and harsh chemicals. EMT is typically used indoors or in dry locations where corrosion risk is minimal, providing a lightweight and cost-effective solution. The galvanized steel coating on IMC enhances its durability, whereas EMT relies on its thinner, less robust construction, limiting its environmental suitability.
Electrical Conductivity and Performance
IMC (Intermediate Metal Conduit) offers superior electrical conductivity and enhanced mechanical protection compared to EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing), making it ideal for environments requiring robust performance. EMT conduit provides adequate conductivity for most residential and commercial applications but lacks the thicker walls of IMC, which improves grounding and reduces electrical resistance. Choosing IMC ensures better long-term durability and performance in demanding electrical installations where conductivity and physical protection are critical.
Code Compliance and Regulatory Standards
IMC conduit meets stricter UL and ASTM standards, often required by the National Electrical Code (NEC) for outdoor or exposed installations due to its thicker walls and corrosion resistance. EMT conduit, compliant with NEC for indoor use, offers a lighter, more cost-effective solution but lacks the same level of mechanical protection and weather resistance as IMC. Regulatory standards mandate choosing IMC in environments requiring enhanced durability and protection, ensuring code compliance for safety and longevity.
Cost Comparison: IMC vs EMT
IMC conduit generally costs more per foot than EMT conduit due to its thicker walls and increased durability, which enhances its suitability for outdoor and exposed applications. EMT conduit is a more affordable option for indoor projects, offering cost-effectiveness while maintaining adequate protection for electrical wiring. When budgeting electrical installations, the choice between IMC and EMT conduit depends on balancing initial material costs with long-term durability and environmental exposure.
Common Applications and Use Cases
IMC conduit is commonly used in outdoor and industrial environments due to its thicker walls and superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty protection of electrical wiring in harsh conditions. EMT conduit, known for its lightweight and ease of installation, is frequently applied in indoor commercial and residential projects where moderate mechanical protection is sufficient. Both conduit types comply with National Electrical Code standards but are selected based on environmental exposure and mechanical stress requirements.
Choosing the Right Conduit for Your Project
IMC conduit offers superior corrosion resistance and thicker walls, making it ideal for outdoor or industrial environments requiring enhanced durability. EMT conduit is lighter and easier to install, providing cost-effectiveness and flexibility for indoor applications with less exposure to harsh conditions. Selecting between IMC and EMT depends on project requirements for strength, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
IMC conduit vs EMT conduit Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com