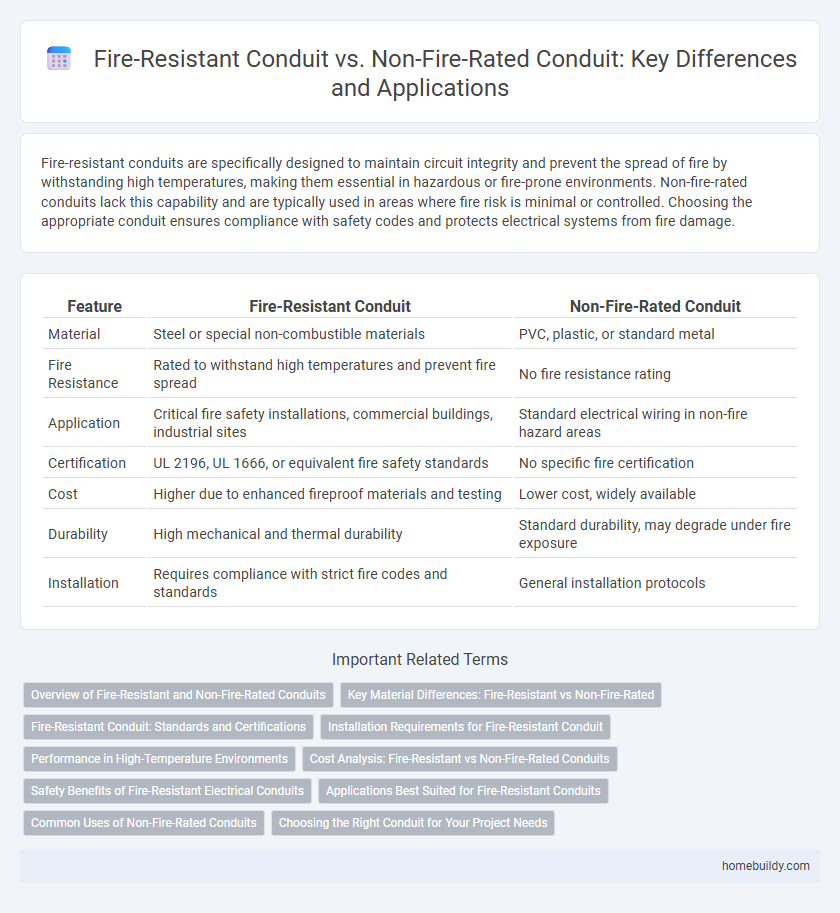
Fire-resistant conduits are specifically designed to maintain circuit integrity and prevent the spread of fire by withstanding high temperatures, making them essential in hazardous or fire-prone environments. Non-fire-rated conduits lack this capability and are typically used in areas where fire risk is minimal or controlled. Choosing the appropriate conduit ensures compliance with safety codes and protects electrical systems from fire damage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Resistant Conduit | Non-Fire-Rated Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel or special non-combustible materials | PVC, plastic, or standard metal |
| Fire Resistance | Rated to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread | No fire resistance rating |
| Application | Critical fire safety installations, commercial buildings, industrial sites | Standard electrical wiring in non-fire hazard areas |
| Certification | UL 2196, UL 1666, or equivalent fire safety standards | No specific fire certification |
| Cost | Higher due to enhanced fireproof materials and testing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Durability | High mechanical and thermal durability | Standard durability, may degrade under fire exposure |
| Installation | Requires compliance with strict fire codes and standards | General installation protocols |
Overview of Fire-Resistant and Non-Fire-Rated Conduits
Fire-resistant conduits are designed to maintain circuit integrity and prevent the spread of fire by withstanding high temperatures, making them ideal for critical safety applications in commercial and industrial settings. Non-fire-rated conduits, typically made from materials like PVC or EMT, offer standard protection against physical damage but do not provide enhanced fire resistance or containment. Choosing between fire-resistant and non-fire-rated conduits depends on building codes, fire safety requirements, and the specific environment where electrical wiring is installed.
Key Material Differences: Fire-Resistant vs Non-Fire-Rated
Fire-resistant conduits are typically constructed from materials such as steel or specialized composites designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire, while non-fire-rated conduits often use PVC or other plastics that lack thermal resistance. Fire-resistant conduits incorporate insulation layers or intumescent coatings that expand under heat to maintain circuit integrity during a fire event. Non-fire-rated conduits do not provide this protection, making them suitable only for applications where fire resistance is not a critical requirement.
Fire-Resistant Conduit: Standards and Certifications
Fire-resistant conduit must comply with stringent standards such as UL 2196 and NFPA 130, ensuring its ability to maintain circuit integrity under extreme heat conditions. These conduits are often tested for resistance to temperatures exceeding 1000degF, critical for safe electrical performance during fires. Certifications from recognized bodies like Underwriters Laboratories (UL) guarantee that fire-resistant conduit meets rigorous fire safety requirements for use in commercial and industrial buildings.
Installation Requirements for Fire-Resistant Conduit
Fire-resistant conduit installation requires strict adherence to National Electrical Code (NEC) standards, including the use of firestop systems to maintain the conduit's fire-resistance rating at wall or floor penetrations. Proper sealing around the conduit ensures the containment of flames and smoke, preventing the spread of fire through electrical pathways. Installers must select approved materials and follow manufacturer guidelines to achieve certified fire ratings, enhancing building safety and compliance.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Fire-resistant conduit maintains structural integrity and electrical insulation under temperatures exceeding 500degF, preventing system failures during fires. Non-fire-rated conduit often deforms or loses insulation properties at elevated temperatures, compromising safety and functionality. Selecting fire-resistant conduit enhances compliance with building codes and ensures long-term durability in high-temperature environments.
Cost Analysis: Fire-Resistant vs Non-Fire-Rated Conduits
Fire-resistant conduits typically incur higher upfront costs compared to non-fire-rated conduits due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread. Non-fire-rated conduits offer a more economical solution for projects with standard fire safety requirements, resulting in reduced material and installation expenses. Long-term savings may be realized with fire-resistant conduits in applications requiring strict fire codes, given their enhanced durability and potential to minimize fire damage and insurance premiums.
Safety Benefits of Fire-Resistant Electrical Conduits
Fire-resistant electrical conduits provide enhanced protection by preventing the spread of flames and smoke during electrical fires, thereby safeguarding wiring integrity and reducing fire hazards. These conduits are specifically designed to withstand high temperatures, ensuring circuit continuity and minimizing electrical failures in critical systems. Compared to non-fire-rated conduits, fire-resistant conduits contribute significantly to building safety codes compliance and occupant protection in emergency scenarios.
Applications Best Suited for Fire-Resistant Conduits
Fire-resistant conduits are best suited for applications requiring enhanced safety measures, such as emergency systems, hospitals, and high-rise buildings, where maintaining circuit integrity during a fire is critical. These conduits help protect electrical wiring from heat and flames, ensuring continuous operation of life safety and communication systems. Non-fire-rated conduits, while sufficient for general wiring needs, lack the protective features necessary for fire-critical environments.
Common Uses of Non-Fire-Rated Conduits
Non-fire-rated conduits are commonly used in residential and commercial buildings where fire resistance is not a critical requirement, such as in dry, non-hazardous indoor environments. These conduits provide protection for electrical wiring against physical damage and moisture but do not offer fire containment or prevent the spread of flames. Typical applications include wiring in office spaces, retail stores, and general-purpose circuits where fire-rated protection is unnecessary.
Choosing the Right Conduit for Your Project Needs
Fire-resistant conduit is designed to maintain circuit integrity and protect wiring in high-temperature environments, making it essential for projects requiring compliance with strict fire safety codes. Non-fire-rated conduit offers cost-effective protection for general electrical installations where fire resistance is not a critical factor. Selecting the appropriate conduit depends on the building's fire safety requirements, environmental conditions, and the specific application to ensure both safety and regulatory compliance.
Fire-resistant conduit vs Non-fire-rated conduit Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com