Wall plates serve as horizontal timber or metal members that are fixed at the top of a wall to support roof structures or floor joists, distributing loads evenly across the wall. Purlins are horizontal beams running parallel to the ridge of a roof, providing intermediate support to rafters or roof decking and enhancing the overall stability of the roof framework. Both components play crucial roles but differ in placement and structural function within the building envelope.
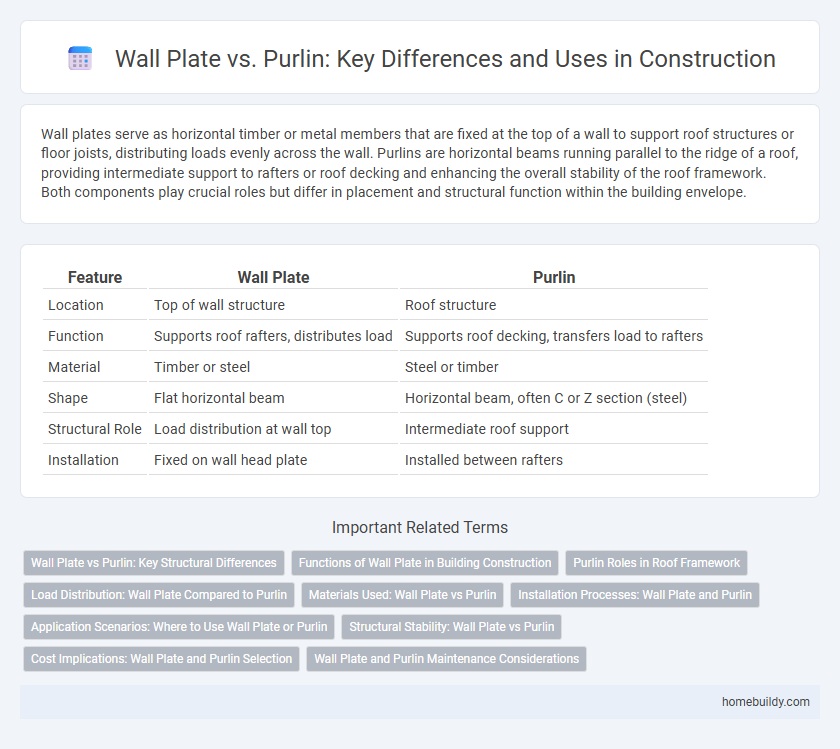
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wall Plate | Purlin |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Top of wall structure | Roof structure |
| Function | Supports roof rafters, distributes load | Supports roof decking, transfers load to rafters |
| Material | Timber or steel | Steel or timber |
| Shape | Flat horizontal beam | Horizontal beam, often C or Z section (steel) |
| Structural Role | Load distribution at wall top | Intermediate roof support |
| Installation | Fixed on wall head plate | Installed between rafters |
Wall Plate vs Purlin: Key Structural Differences
Wall plates distribute roof and floor loads evenly across studs and serve as a critical connection point in timber framing, while purlins provide horizontal support for roof decking or sheeting by spanning between rafters or trusses. Wall plates are typically fixed on top of masonry or wall studs to anchor structural elements, whereas purlins are positioned longitudinally to resist bending and carry roof loads. Understanding the load-bearing role and placement of wall plates versus purlins is essential for ensuring structural stability and proper load transfer in building construction.
Functions of Wall Plate in Building Construction
Wall plates serve as critical structural components that distribute roof and floor loads evenly to the building's framework, ensuring stability and alignment. Unlike purlins, which primarily support roof sheathing and are placed horizontally along the roof, wall plates provide a secure base for vertical wall studs and connect the roof structure to the walls. Their function in building construction includes anchoring the walls to the foundation and preventing lateral movement, which enhances overall building integrity.
Purlin Roles in Roof Framework
Purlins are horizontal structural members in a roof framework that provide crucial support to the roof decking and transfer loads to the primary framing elements such as rafters or trusses. Unlike wall plates, which serve as a base for wall studs and distribute loads from the wall to the foundation, purlins specifically enhance the stability and load-bearing capacity of the roof by preventing sagging and ensuring proper alignment. Purlins play an essential role in maintaining the overall integrity and durability of roof systems, especially in large-span or industrial buildings where roof load distribution is critical.
Load Distribution: Wall Plate Compared to Purlin
Wall plates distribute roof load evenly across supporting walls, providing a stable base for rafters and preventing point loads that could cause structural damage. Purlins primarily support roofing materials and transfer loads to rafters rather than directly to walls, resulting in a more localized load distribution. This difference makes wall plates essential for maintaining overall structural integrity in timber framing.
Materials Used: Wall Plate vs Purlin
Wall plates are typically crafted from strong, durable timber such as treated softwood or hardwood to provide a stable base for wall framing and roof structures. Purlins are often made from timber, steel, or engineered wood products like laminated veneer lumber to support roof decking and distribute loads efficiently. The choice of material for wall plates versus purlins depends on structural requirements, exposure to elements, and load-bearing needs within construction frameworks.
Installation Processes: Wall Plate and Purlin
Wall plates are installed horizontally at the top of a wall to provide a stable base for roof trusses, secured with anchor bolts or nails driven into the top studs for structural integrity. Purlins are placed horizontally across roof rafters or trusses to support roofing materials and are typically fastened using metal brackets, screws, or nails depending on the roof design. The installation of wall plates requires precise alignment with the building's structural frame, while purlin installation demands careful spacing to evenly distribute roof loads.
Application Scenarios: Where to Use Wall Plate or Purlin
Wall plates are primarily used in timber frame construction to distribute loads from roof trusses or rafters to the building's vertical supports, making them ideal for wall tops and structural framing in residential and light commercial buildings. Purlins serve as horizontal beams supporting roof decking or sheathing, commonly applied in metal or steel roof systems, industrial structures, and large-span buildings where enhanced roof stability and load distribution are required. Selecting between wall plates and purlins depends on structural design, load requirements, and material type, with wall plates focusing on load transfer to walls and purlins emphasizing roof support and span management.
Structural Stability: Wall Plate vs Purlin
Wall plates provide crucial horizontal support by distributing roof loads evenly across wall studs, enhancing structural stability and preventing wall deformation. Purlins serve as horizontal beams that support roof rafters, reducing span length and helping to resist lateral forces such as wind and snow loads. Together, wall plates and purlins work synergistically to maintain the overall integrity and durability of the roof structure.
Cost Implications: Wall Plate and Purlin Selection
Wall plates typically incur lower material and labor costs compared to purlins due to their simpler installation and use of readily available timber. Purlins, often made from steel or engineered wood, involve higher upfront expenses but can reduce long-term maintenance and structural reinforcement costs. Selecting between wall plates and purlins requires evaluating budget constraints alongside load-bearing requirements to optimize overall project expenditure.
Wall Plate and Purlin Maintenance Considerations
Wall plate maintenance involves regular inspection for rot, moisture damage, and secure fastening to ensure structural stability in timber framing. Purlin maintenance requires checking for corrosion, especially in metal purlins, and ensuring bolts and welds remain intact to support roof loads effectively. Both components demand preventative upkeep to extend lifespan and prevent costly repairs in building frameworks.
Wall plate vs Purlin Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com