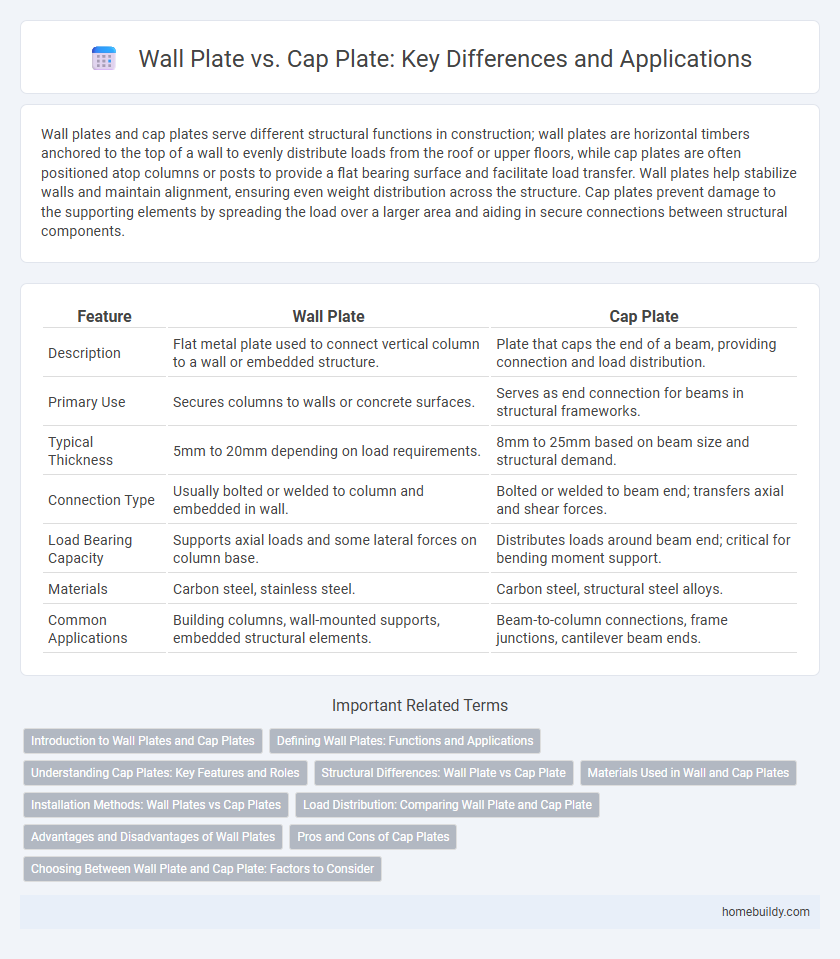
Wall plates and cap plates serve different structural functions in construction; wall plates are horizontal timbers anchored to the top of a wall to evenly distribute loads from the roof or upper floors, while cap plates are often positioned atop columns or posts to provide a flat bearing surface and facilitate load transfer. Wall plates help stabilize walls and maintain alignment, ensuring even weight distribution across the structure. Cap plates prevent damage to the supporting elements by spreading the load over a larger area and aiding in secure connections between structural components.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wall Plate | Cap Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Flat metal plate used to connect vertical column to a wall or embedded structure. | Plate that caps the end of a beam, providing connection and load distribution. |
| Primary Use | Secures columns to walls or concrete surfaces. | Serves as end connection for beams in structural frameworks. |
| Typical Thickness | 5mm to 20mm depending on load requirements. | 8mm to 25mm based on beam size and structural demand. |
| Connection Type | Usually bolted or welded to column and embedded in wall. | Bolted or welded to beam end; transfers axial and shear forces. |
| Load Bearing Capacity | Supports axial loads and some lateral forces on column base. | Distributes loads around beam end; critical for bending moment support. |
| Materials | Carbon steel, stainless steel. | Carbon steel, structural steel alloys. |
| Common Applications | Building columns, wall-mounted supports, embedded structural elements. | Beam-to-column connections, frame junctions, cantilever beam ends. |
Introduction to Wall Plates and Cap Plates
Wall plates serve as the foundational support structures in framing, typically positioned at the top or bottom of walls to bear loads and provide attachment points for studs. Cap plates are specific types of wall plates installed on top of the wall plate system, often used to distribute weight evenly and enhance structural stability. Both wall plates and cap plates are essential components in construction, ensuring the integrity and alignment of wall assemblies.
Defining Wall Plates: Functions and Applications
Wall plates serve as protective coverings for electrical outlets, switches, and wiring, providing safety and an organized appearance while preventing accidental contact with live electrical components. They are essential in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to ensure compliance with electrical codes and enhance aesthetic appeal. Unlike cap plates, which primarily seal unused junctions or boxes, wall plates allow access to wiring components for maintenance and operation.
Understanding Cap Plates: Key Features and Roles
Cap plates serve as protective and structural covers typically placed at the top of wall frames or columns, enhancing stability and preventing moisture or debris intrusion. Unlike wall plates that distribute load across a wall's length, cap plates focus on capping vertical elements, providing a finished surface and reinforcing attachment points for roofing or additional framing. Key features include corrosion resistance, precise fitting, and compatibility with various materials, making cap plates essential in both residential and commercial construction for long-term durability.
Structural Differences: Wall Plate vs Cap Plate
Wall plates are horizontal timber members fixed atop a masonry or concrete wall to evenly distribute roof or floor loads, while cap plates are typically metal or timber components placed on top of columns or posts to provide a bearing surface for beams or trusses. Wall plates extend along the length of the wall, anchoring structural elements and preventing lateral wall movement; cap plates are smaller, localized connectors enhancing load transfer at column-beam junctions. The key structural difference lies in their position and function: wall plates serve as continuous load spreaders along walls, whereas cap plates act as discrete bearing and connection points atop vertical supports.
Materials Used in Wall and Cap Plates
Wall plates are typically constructed from durable materials such as steel, aluminum, or high-strength composite plastics to ensure structural support and long-term stability. Cap plates, often made from similar metals but can include lighter materials like zinc or brass, mainly serve a finishing or protective purpose rather than load-bearing. The choice of materials impacts corrosion resistance, strength, and suitability for different environmental conditions in both wall and cap plates.
Installation Methods: Wall Plates vs Cap Plates
Wall plates are typically installed by securing them directly onto electrical boxes with screws, ensuring a flush and stable fit that conceals wiring and outlets effectively. Cap plates, on the other hand, usually snap onto existing plates or surface-mounted boxes, offering a quick and less invasive installation without the need for additional hardware. Understanding the installation methods helps in selecting the appropriate plate type for specific electrical or decorative applications, optimizing both functionality and aesthetics.
Load Distribution: Comparing Wall Plate and Cap Plate
Wall plates distribute loads evenly across the framing members, providing structural stability by transferring weight directly to studs or joists. Cap plates primarily serve as a protective covering or finishing element, with limited impact on load distribution in structural applications. Understanding the load-bearing capacity differences between wall plates and cap plates is essential for ensuring proper support and preventing structural failures in construction projects.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wall Plates
Wall plates provide a stable and secure covering for electrical outlets and switches, offering easy access for maintenance while protecting wiring from damage. They come in various materials and designs, enhancing aesthetic appeal and durability, but may require precise installation to avoid gaps or misalignment. Unlike cap plates, wall plates offer better functionality for repeated use, though they can be less effective in environments requiring complete sealing from dust or moisture.
Pros and Cons of Cap Plates
Cap plates offer superior protection against environmental elements by covering wall edges completely, reducing moisture infiltration and enhancing durability. However, they can be more expensive and require precise installation compared to wall plates, which are simpler and more cost-effective for basic coverage. The choice between cap plates and wall plates hinges on balancing budget constraints with the need for long-term protection and aesthetic finish.
Choosing Between Wall Plate and Cap Plate: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a wall plate and a cap plate depends on structural requirements and installation context. Wall plates distribute loads evenly across wall surfaces, providing stability for mounted fixtures, while cap plates primarily serve as finishing elements that cover top surfaces or edges. Assess factors such as load capacity, aesthetic preference, and compatibility with existing construction to determine the best option for your project.
Wall plate vs Cap plate Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com