Wall plates provide a finished cover for electrical outlets and switches, ensuring safety and a clean appearance. Blocking refers to the installation of supportive wood or metal braces inside walls to secure fixtures like cabinets, handrails, or heavy trim. While wall plates focus on aesthetics and protection, blocking enhances structural stability for mounting purposes.
Table of Comparison
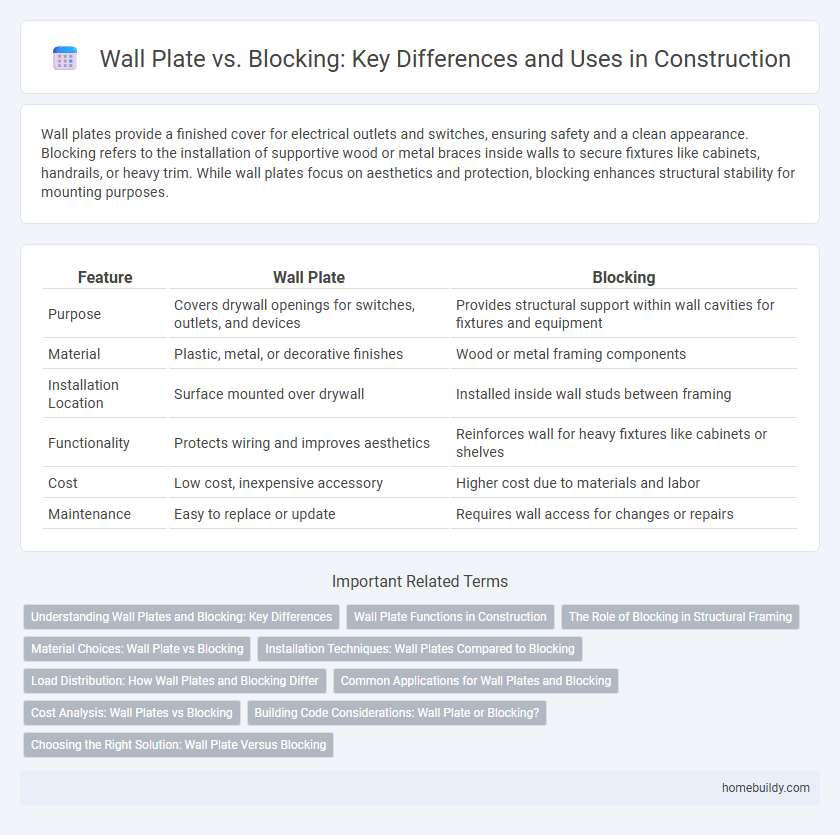
| Feature | Wall Plate | Blocking |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Covers drywall openings for switches, outlets, and devices | Provides structural support within wall cavities for fixtures and equipment |
| Material | Plastic, metal, or decorative finishes | Wood or metal framing components |
| Installation Location | Surface mounted over drywall | Installed inside wall studs between framing |
| Functionality | Protects wiring and improves aesthetics | Reinforces wall for heavy fixtures like cabinets or shelves |
| Cost | Low cost, inexpensive accessory | Higher cost due to materials and labor |
| Maintenance | Easy to replace or update | Requires wall access for changes or repairs |
Understanding Wall Plates and Blocking: Key Differences
Wall plates serve as the visible, finished cover for electrical outlets and switches, ensuring safety and aesthetic appeal, while blocking refers to the structural wood framing within walls that provides secure anchorage for these installations. Understanding the distinct roles highlights that wall plates are functional hardware components, whereas blocking acts as the supportive framework enabling proper installation. Effective wall construction requires precise blocking placement to guarantee that wall plates align correctly and remain stable over time.
Wall Plate Functions in Construction
Wall plates serve as essential structural components in construction, providing a stable base for framing studs and distributing loads evenly across walls. Unlike blocking, which reinforces specific sections between studs for attachment points, wall plates run horizontally at the top and bottom of walls to anchor frames securely to floors and ceilings. These plates also facilitate the alignment and securing of wall assemblies, enhancing overall stability and support for wall finishes and fixtures.
The Role of Blocking in Structural Framing
Blocking provides essential lateral support between studs in structural framing, enhancing wall stability and preventing twisting or warping. Unlike wall plates, which serve as horizontal members at the top and bottom of a wall frame to distribute loads, blocking acts as intermediate bracing to reinforce the studs. Properly installed blocking ensures the integrity of drywall attachment and supports the weight of fixtures or cabinets mounted on the wall.
Material Choices: Wall Plate vs Blocking
Wall plates are typically made from durable plastics or metals like stainless steel, designed for aesthetic finishes and ease of installation around electrical outlets or switches. Blocking, usually constructed from solid wood or metal studs, provides structural reinforcement within walls to support heavy fixtures or cabinetry. The choice between wall plate and blocking materials depends on the functional requirements, with wall plates prioritizing surface protection and appearance, while blocking emphasizes load-bearing capacity and stability.
Installation Techniques: Wall Plates Compared to Blocking
Wall plates streamline installation by providing a clean, standardized mounting surface for electrical devices, improving accessibility and aesthetics compared to traditional blocking methods. Blocking involves installing solid wood supports within wall cavities, requiring precise measurement and cutting, which can extend installation time and complexity. Wall plates reduce the need for structural modifications, offering a faster, more efficient solution for securing outlets and switches.
Load Distribution: How Wall Plates and Blocking Differ
Wall plates and blocking both serve to reinforce structural framing, but they differ significantly in load distribution. Wall plates, typically made from sturdy wood or metal, distribute loads evenly across studs and transfer weight to the foundation, enhancing overall wall stability. Blocking, inserted between studs, primarily prevents lateral movement and buckling but does not provide the same broad load distribution as wall plates.
Common Applications for Wall Plates and Blocking
Wall plates provide a clean and secure finish for electrical outlets, switches, and cable connections, commonly used in residential and commercial settings to protect wiring and enhance aesthetics. Blocking is typically applied during framing to reinforce wall sections, support heavy fixtures like shelving or cabinetry, and ensure stability where wall plates alone cannot provide structural support. Both are essential for different stages of construction: wall plates for electrical and networking interface protection, and blocking for structural reinforcement and fixture mounting.
Cost Analysis: Wall Plates vs Blocking
Wall plates generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to blocking, as they reduce labor time and material expenses during installation. Blocking requires additional framing materials and labor for securing fixtures, which increases overall project costs. Choosing wall plates can streamline the installation process, leading to lower total expenses without compromising structural integrity or functionality.
Building Code Considerations: Wall Plate or Blocking?
Building codes typically require blocking rather than just wall plates for securing heavy fixtures, as blocking provides solid, structural support between studs. Wall plates are often used to protect wiring and plumbing from fasteners but do not meet code requirements for anchoring heavy loads. Compliance with local building codes mandates proper blocking installation to ensure safety and structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Solution: Wall Plate Versus Blocking
Selecting the appropriate installation solution involves understanding the key differences between wall plates and blocking. Wall plates provide a clean, finished look by covering outlet boxes and securing devices, ideal for situations where aesthetics and easy access are priorities. Blocking, on the other hand, offers structural support within the wall, essential for mounting heavy fixtures or when additional reinforcement is required behind drywall.
Wall plate vs Blocking Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com