A wall plate is a horizontal, structural timber element positioned at the top of a wall to evenly distribute loads from the roof or upper floors and provide a secure base for rafters or joists. Rafters are sloping beams forming the framework of a roof, supporting the roof covering and transferring loads to the wall plates. Understanding the difference ensures correct load transfer and structural stability in building construction.
Table of Comparison
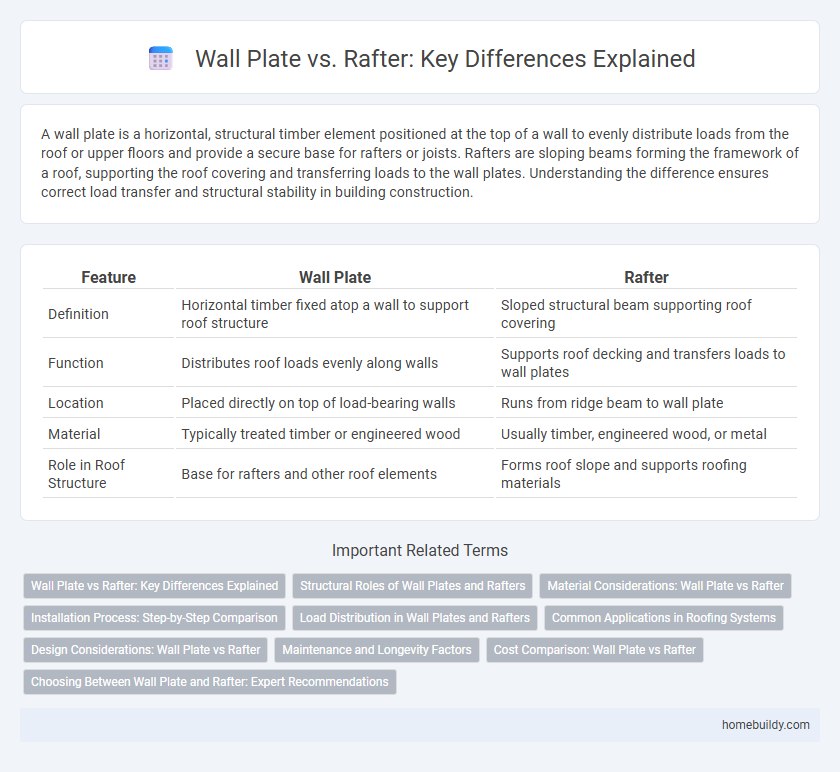
| Feature | Wall Plate | Rafter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Horizontal timber fixed atop a wall to support roof structure | Sloped structural beam supporting roof covering |
| Function | Distributes roof loads evenly along walls | Supports roof decking and transfers loads to wall plates |
| Location | Placed directly on top of load-bearing walls | Runs from ridge beam to wall plate |
| Material | Typically treated timber or engineered wood | Usually timber, engineered wood, or metal |
| Role in Roof Structure | Base for rafters and other roof elements | Forms roof slope and supports roofing materials |
Wall Plate vs Rafter: Key Differences Explained
Wall plates serve as horizontal structural members that distribute loads from the roof or upper floors to the vertical studs, while rafters are sloped beams that support the roof deck and transfer roof loads to the wall plates. Wall plates typically run along the top of a wall and are crucial for anchoring studs and other framing components, whereas rafters form the main skeleton of a pitched roof, shaping its slope and providing direct support for roofing materials. Understanding the distinction between wall plates and rafters is essential for framing stability and proper load transfer in building construction.
Structural Roles of Wall Plates and Rafters
Wall plates serve as the horizontal structural element at the top or bottom of a wall, distributing loads from the roof or floor above evenly across the wall studs. Rafters function as the sloped beams that support the roof deck and transfer the weight of the roof covering down to the wall plates. The interaction between wall plates and rafters is crucial for maintaining overall stability, ensuring load transfer from the roof structure to the walls and foundation.
Material Considerations: Wall Plate vs Rafter
Wall plates are typically made from treated softwood or engineered lumber to resist moisture and provide a stable base for wall framing, while rafters often use stronger, more rigid materials like dimensional lumber or laminated veneer lumber to support roof loads. The choice of material for wall plates prioritizes durability and ease of attachment to foundations, contrasting with rafters that require materials with high structural strength and stiffness to resist bending and shear forces. Understanding these material distinctions ensures proper load distribution and long-term structural integrity in framing systems.
Installation Process: Step-by-Step Comparison
Installing a wall plate involves accurately positioning and securing it on the foundation or sill using anchor bolts and level checks to ensure stability. In contrast, rafter installation requires precise measurement and cutting of timber, followed by nailing or fastening the rafters to the wall plates at specific angles to create roof framing. Both processes demand careful alignment, but wall plate installation emphasizes a solid base connection while rafter installation focuses on structural roof support.
Load Distribution in Wall Plates and Rafters
Wall plates evenly distribute vertical loads from the structure above to the studs below, ensuring stability and preventing localized stress concentrations. Rafters transfer roof loads diagonally to wall plates, which then channel the forces vertically down to the foundation. Proper alignment and secure fastening between rafters and wall plates are essential for effective load transfer and overall structural integrity.
Common Applications in Roofing Systems
Wall plates provide a stable base for attaching rafters in roofing systems, ensuring proper load transfer from the roof to the building framework. Rafters are sloped structural members that support the roof deck and transfer loads to the wall plates, which distribute the weight evenly to the vertical studs. Common applications include residential roof framing where wall plates anchor rafters securely, enhancing structural integrity and resistance to wind and snow loads.
Design Considerations: Wall Plate vs Rafter
When comparing wall plates and rafters in structural design, wall plates serve as the horizontal base that evenly distributes load from the walls to the foundation, while rafters are inclined beams supporting roof loads. Design considerations prioritize load transfer efficiency, with wall plates designed to resist compression and rafter design focusing on bending and shear stress due to roof slope and snow loads. Proper sizing and material selection for both components ensure structural integrity and compliance with building codes in residential and commercial construction.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Wall plates, typically made from treated timber or steel, require regular inspection for moisture damage and termite infestation to ensure structural integrity. Rafters, exposed to roof conditions, demand diligent maintenance such as checking for cracks, rot, or warping to prolong their lifespan. Proper ventilation and timely repairs significantly enhance the durability of both components, preventing costly structural failures.
Cost Comparison: Wall Plate vs Rafter
Wall plates generally cost less than rafters due to simpler materials and installation processes, with prices typically ranging from $2 to $5 per linear foot compared to rafters that can cost $8 to $15 per linear foot. Labor expenses for wall plate installation are lower since wall plates require minimal cutting and fastening, while rafters involve precise cutting angles and structural engineering. Overall, choosing wall plates can reduce both material and labor costs, making them a budget-friendly option for framing in residential construction projects.
Choosing Between Wall Plate and Rafter: Expert Recommendations
When deciding between a wall plate and a rafter, experts emphasize the importance of structural support and load distribution in building construction. Wall plates serve as a crucial horizontal base for securing studs and distributing weight evenly along the foundation, while rafters are angled beams designed to support roof loads and transfer them to the walls. Choosing the appropriate component depends on the specific architectural design and load requirements, ensuring stability and longevity of the structure.
Wall plate vs Rafter Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com