A wall plate serves as the horizontal framing member positioned at the top of a wall, providing a stable base for roof trusses or ceiling joists. The bottom plate, also known as the sole plate, is the horizontal timber at the base of a wall, anchoring the wall studs to the floor or foundation. Together, both plates secure the wall structure and ensure even load distribution from top to bottom.
Table of Comparison
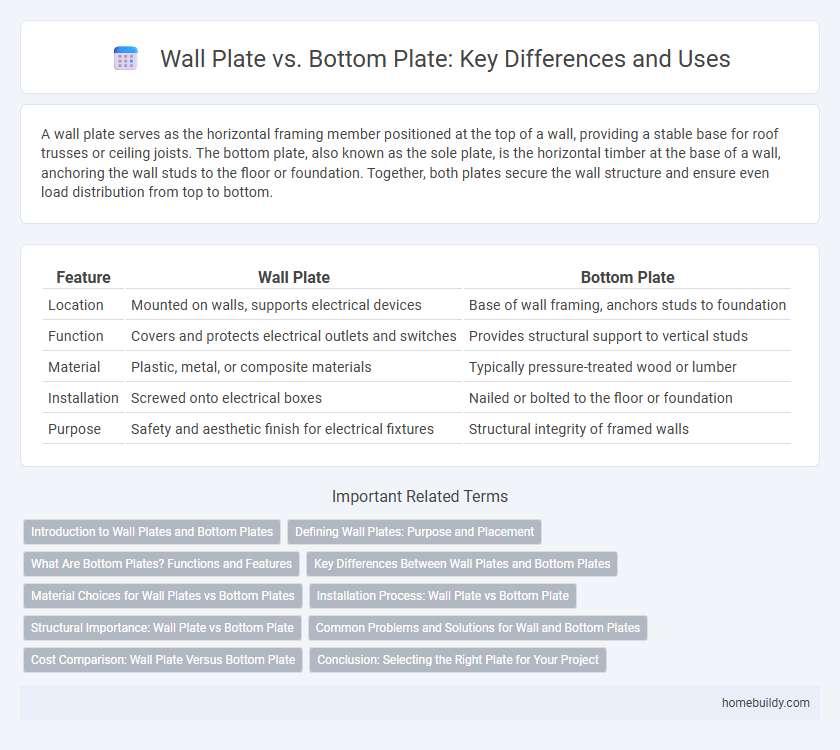
| Feature | Wall Plate | Bottom Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Mounted on walls, supports electrical devices | Base of wall framing, anchors studs to foundation |
| Function | Covers and protects electrical outlets and switches | Provides structural support to vertical studs |
| Material | Plastic, metal, or composite materials | Typically pressure-treated wood or lumber |
| Installation | Screwed onto electrical boxes | Nailed or bolted to the floor or foundation |
| Purpose | Safety and aesthetic finish for electrical fixtures | Structural integrity of framed walls |
Introduction to Wall Plates and Bottom Plates
Wall plates are horizontal framing members installed at the top of walls, serving as the primary support for roof trusses and ceiling joists, providing structural stability. Bottom plates, also known as sole plates, are horizontal members positioned at the base of wall studs, anchoring the wall to the floor or foundation and ensuring alignment. Both plates are essential components in framing, with wall plates distributing roof load while bottom plates secure the wall framework.
Defining Wall Plates: Purpose and Placement
Wall plates serve as critical structural components in framing, providing a horizontal surface where studs are anchored and distributing loads evenly across the framework. Positioned at the top and sometimes the bottom of wall studs, wall plates ensure stability and alignment for vertical framing members. Unlike bottom plates, which rest directly on the floor or foundation, wall plates primarily connect and secure the upper portion of the wall structure.
What Are Bottom Plates? Functions and Features
Bottom plates, also known as sole plates, are horizontal framing members located at the base of a wall, securing the wall studs to the floor or foundation. They provide stability by distributing the load of the wall evenly and anchoring it firmly to the building structure. Unlike wall plates, which are positioned at the top of the wall, bottom plates play a crucial role in preventing moisture infiltration and ensuring structural integrity.
Key Differences Between Wall Plates and Bottom Plates
Wall plates are horizontal framing members attached to wall studs, providing support for drywall and serving as a base for electrical outlets and switches. Bottom plates, also known as sole plates, are the horizontal members that anchor the wall to the floor, distributing weight evenly across the foundation or subfloor. The primary difference lies in their placement and function: wall plates reinforce the wall structure horizontally at various heights, while bottom plates secure and stabilize the wall at its base.
Material Choices for Wall Plates vs Bottom Plates
Wall plates are commonly made from durable materials such as stainless steel, brass, or plastic composites designed to provide aesthetic appeal and resist corrosion in interior and exterior settings. Bottom plates, often referred to as sole plates, are typically constructed from pressure-treated wood or galvanized steel to withstand ground moisture and structural loads in framing applications. Choosing the right material for wall plates versus bottom plates depends on exposure conditions, structural requirements, and longevity needs in construction projects.
Installation Process: Wall Plate vs Bottom Plate
The installation process of a wall plate involves securing it to the wall surface, often using screws to align with existing electrical boxes for outlets or switches. In contrast, a bottom plate, typically part of the framing in construction, requires anchoring to the floor or foundation, ensuring structural stability by connecting studs vertically. Precise measurement and level alignment are crucial in both installations to guarantee safety and functionality.
Structural Importance: Wall Plate vs Bottom Plate
The wall plate serves as a critical horizontal timber or metal beam that supports the load of the roof and upper floors, transferring weight evenly to the studs below. The bottom plate, positioned at the base of the wall frame, anchors the structure to the foundation and provides stability against lateral forces. Together, the wall plate and bottom plate form essential components in distributing structural loads and maintaining the integrity of framed walls.
Common Problems and Solutions for Wall and Bottom Plates
Common problems with wall plates include improper alignment, damaged or loose mounting screws, and outdated or incompatible electrical configurations, which can cause electrical shorts or inefficient device operation. Bottom plates often face issues such as moisture damage, warping, and inadequate sealing, leading to structural instability or pest intrusion. Solutions involve using level tools for precise installation, replacing worn parts with compatible components, applying waterproof sealants, and regularly inspecting plates for signs of wear or damage.
Cost Comparison: Wall Plate Versus Bottom Plate
Wall plates generally incur higher costs compared to bottom plates due to their placement on visible wall surfaces, requiring superior materials and finishes for aesthetic appeal. Bottom plates, positioned at the base of walls, often use more economical materials as they remain largely concealed, reducing overall expense. Choosing between wall plate and bottom plate costs depends on project budget constraints and the desired finish quality.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Plate for Your Project
Choosing the right plate for your project depends on the specific application: wall plates are designed to cover electrical outlets and switches, providing safety and aesthetic appeal, while bottom plates, also known as sill plates, serve as the foundational wood framing at the base of walls, supporting the entire structure. For finishing and protection of electrical components, wall plates are essential, whereas bottom plates are critical for structural integrity and load distribution in framing. Understanding these functional differences ensures optimal material selection and project success.
Wall plate vs Bottom plate Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com