Register boots are duct components that connect the main duct system to the floor, wall, or ceiling registers, directing airflow efficiently into the room. Dampers are adjustable devices installed within ducts or at the register opening to control and regulate the volume of air flowing through the HVAC system. Proper use of register boots and dampers helps optimize air distribution, improve energy efficiency, and maintain balanced heating and cooling throughout a space.
Table of Comparison
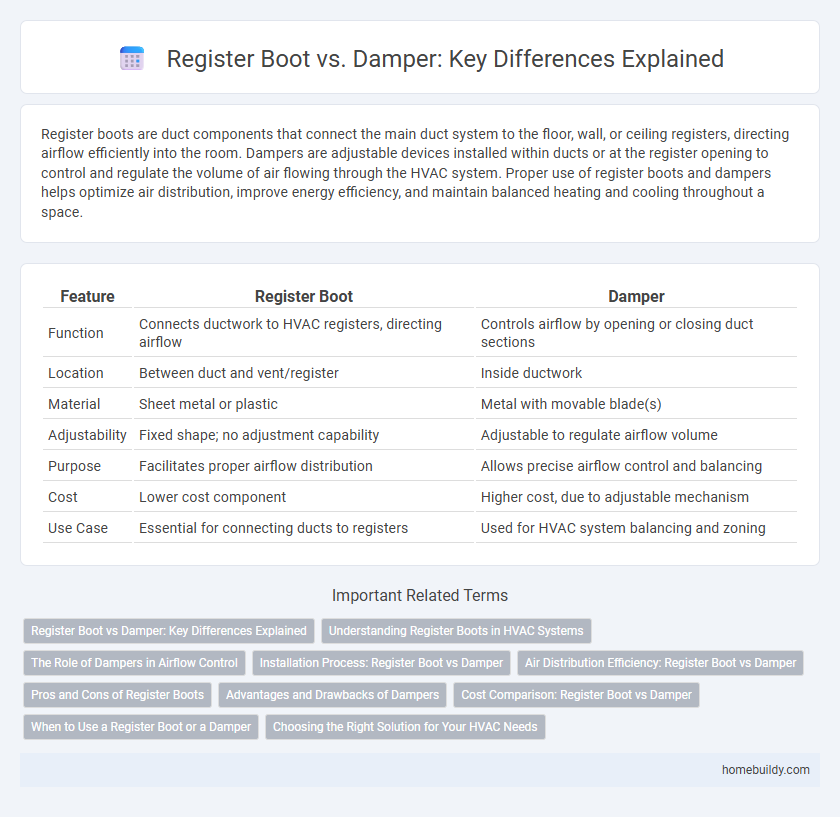
| Feature | Register Boot | Damper |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Connects ductwork to HVAC registers, directing airflow | Controls airflow by opening or closing duct sections |
| Location | Between duct and vent/register | Inside ductwork |
| Material | Sheet metal or plastic | Metal with movable blade(s) |
| Adjustability | Fixed shape; no adjustment capability | Adjustable to regulate airflow volume |
| Purpose | Facilitates proper airflow distribution | Allows precise airflow control and balancing |
| Cost | Lower cost component | Higher cost, due to adjustable mechanism |
| Use Case | Essential for connecting ducts to registers | Used for HVAC system balancing and zoning |
Register Boot vs Damper: Key Differences Explained
Register boots and dampers serve distinct functions in HVAC systems; register boots primarily act as the duct outlet connecting to the floor, wall, or ceiling registers, ensuring efficient airflow distribution. Dampers regulate airflow within the ductwork by opening, closing, or partially obstructing air passages to balance HVAC performance and control temperature. Understanding the structural role of register boots versus the adjustable airflow control provided by dampers is crucial for optimal system efficiency and indoor comfort.
Understanding Register Boots in HVAC Systems
Register boots in HVAC systems serve as the critical connection between the ductwork and the supply registers, ensuring efficient airflow distribution within a building. Unlike dampers, which regulate and control airflow, register boots primarily facilitate the smooth transition of conditioned air from the ducts to individual rooms. Proper installation and sizing of register boots minimize air leakage and pressure loss, improving overall system performance and energy efficiency.
The Role of Dampers in Airflow Control
Dampers play a crucial role in airflow control by regulating the volume of air passing through HVAC ducts, enabling precise adjustment and balancing of air distribution. Unlike registers that primarily direct airflow into rooms, dampers are installed within ductwork and can either restrict or permit airflow to maintain desired pressure levels and improve system efficiency. Effective damper use reduces energy consumption and enhances indoor air quality by preventing airflow imbalances and minimizing drafts.
Installation Process: Register Boot vs Damper
The installation process of a register boot involves securing the boot to the ductwork and attaching the register grille, ensuring a tight fit for efficient airflow distribution. In contrast, installing a damper requires integrating the damper mechanism within the duct to control airflow, often necessitating precise alignment for optimal functionality. Register boots typically simplify installation by serving as direct connectors, while dampers demand careful adjustment to regulate ventilation effectively.
Air Distribution Efficiency: Register Boot vs Damper
Register boots enhance air distribution efficiency by creating a smooth transition from ductwork to the supply register, minimizing airflow resistance and turbulence. Dampers control airflow volume but can introduce pressure drops that reduce overall efficiency if not properly adjusted. Optimizing air distribution involves selecting a register boot design with low resistance and incorporating precision dampers to balance airflow effectively throughout the HVAC system.
Pros and Cons of Register Boots
Register boots offer superior airflow control and improved ventilation efficiency compared to dampers, enabling precise room temperature regulation and reduced energy consumption. They are easier to install and maintain due to their simple design but may have limited adjustability for airflow compared to the more versatile damper systems. However, register boots can create noise issues if not properly sized or installed, potentially affecting comfort levels in the space.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Dampers
Dampers provide precise airflow control and help maintain system balance in HVAC systems, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort. However, dampers can introduce pressure drops and require regular maintenance to prevent operational issues like sticking or noise. Compared to register boots, dampers offer more adjustability but may increase initial costs and complexity in duct design.
Cost Comparison: Register Boot vs Damper
Register boots typically cost less than dampers due to simpler design and fewer moving parts, making them a budget-friendly option for HVAC systems. Dampers involve more complex mechanisms that enable airflow control, leading to higher manufacturing and installation expenses. Choosing between register boots and dampers involves balancing initial costs against the need for precise airflow regulation and energy efficiency.
When to Use a Register Boot or a Damper
Choose a register boot when you need to connect the HVAC ductwork to a floor, wall, or ceiling vent, facilitating smooth air distribution within a room. Opt for a damper when precise airflow control is required inside the duct system, allowing you to regulate or shut off air to specific areas for better zoning and energy efficiency. Register boots support airflow delivery, while dampers focus on adjusting or restricting airflow.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your HVAC Needs
Register boots provide direct airflow control by connecting ductwork to registers, offering efficient air delivery in HVAC systems. Dampers regulate airflow within ducts to balance pressure and optimize system performance. Selecting between register boots and dampers depends on your HVAC design goals, space constraints, and airflow control requirements, ensuring optimal comfort and energy efficiency.
Register boot vs damper Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com