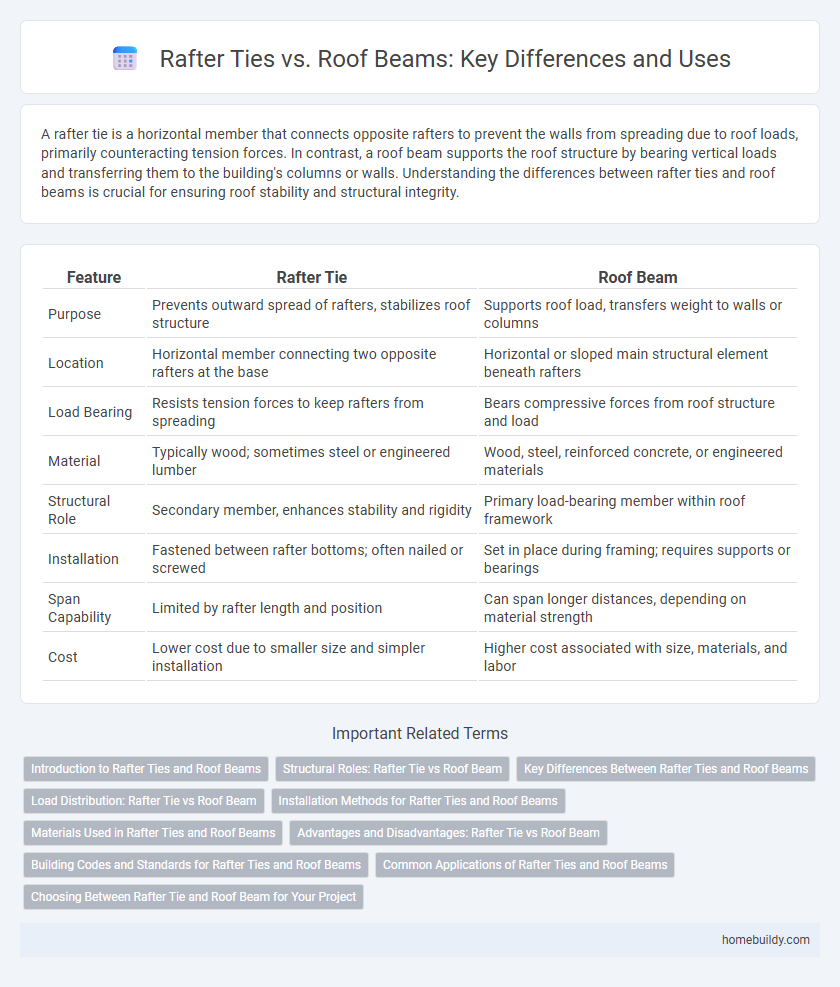
A rafter tie is a horizontal member that connects opposite rafters to prevent the walls from spreading due to roof loads, primarily counteracting tension forces. In contrast, a roof beam supports the roof structure by bearing vertical loads and transferring them to the building's columns or walls. Understanding the differences between rafter ties and roof beams is crucial for ensuring roof stability and structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rafter Tie | Roof Beam |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents outward spread of rafters, stabilizes roof structure | Supports roof load, transfers weight to walls or columns |
| Location | Horizontal member connecting two opposite rafters at the base | Horizontal or sloped main structural element beneath rafters |
| Load Bearing | Resists tension forces to keep rafters from spreading | Bears compressive forces from roof structure and load |
| Material | Typically wood; sometimes steel or engineered lumber | Wood, steel, reinforced concrete, or engineered materials |
| Structural Role | Secondary member, enhances stability and rigidity | Primary load-bearing member within roof framework |
| Installation | Fastened between rafter bottoms; often nailed or screwed | Set in place during framing; requires supports or bearings |
| Span Capability | Limited by rafter length and position | Can span longer distances, depending on material strength |
| Cost | Lower cost due to smaller size and simpler installation | Higher cost associated with size, materials, and labor |
Introduction to Rafter Ties and Roof Beams
Rafter ties are horizontal structural members installed between opposing rafters to prevent the roof from spreading and to maintain structural integrity in pitched roof framing. Roof beams, typically larger and more robust, serve as primary load-bearing elements supporting the roof structure and transferring weight to walls or columns. Understanding the distinct roles of rafter ties and roof beams is essential for effective roof design and ensuring stability under various loads.
Structural Roles: Rafter Tie vs Roof Beam
Rafter ties serve as horizontal structural elements that prevent the outward spreading of rafters, ensuring the stability of triangular roof frames by resisting tension forces. Roof beams act as primary vertical supports that carry loads from the roof down to the building's foundation, typically bearing bending forces and compressive stresses. While rafter ties stabilize the roof structure by maintaining the geometry of rafters, roof beams provide essential load-bearing capacity for overall structural integrity.
Key Differences Between Rafter Ties and Roof Beams
Rafter ties serve as horizontal members connecting opposing rafters to prevent outward spreading and maintain roof stability, typically installed in the attic space. Roof beams are larger, load-bearing structural elements that support the weight of the roof and transfer loads to the building's vertical supports, often visible in the building's framework or ceiling. The key differences lie in their function--rafter ties resist lateral thrust to prevent wall spread, while roof beams carry direct vertical loads and provide primary roof support.
Load Distribution: Rafter Tie vs Roof Beam
Rafter ties primarily prevent the outward spread of rafters, transferring horizontal thrust to maintain roof stability, whereas roof beams carry significant vertical loads from the roof structure down to the building's supports. Load distribution in rafter ties is focused on tension forces resisting rafter separation, while roof beams handle both bending moments and shear forces, providing critical structural support. Choosing between a rafter tie and a roof beam depends on the roof design and load requirements, emphasizing tension resistance versus vertical load-bearing capacity.
Installation Methods for Rafter Ties and Roof Beams
Rafter ties are typically installed horizontally between opposing rafters near the ceiling to prevent outward spreading of the roof structure, using nails or screws to secure them to the rafters. Roof beams, often heavier and larger, are installed across or along the length of rafters with additional support such as hangers, brackets, or notching to transfer loads to walls or posts efficiently. Proper installation of rafter ties involves ensuring tight connections to resist lateral forces, while roof beam installation requires precise alignment and reinforced attachments to bear vertical roof loads effectively.
Materials Used in Rafter Ties and Roof Beams
Rafter ties are typically constructed from dimensional lumber such as pine or fir, chosen for their strength and ease of installation in securing opposing rafters to prevent roof sagging. Roof beams often utilize engineered wood products like laminated veneer lumber (LVL) or steel, offering superior load-bearing capacity and spanning capabilities for larger structures. Material selection depends on structural requirements and cost considerations, with rafter ties favoring simpler, cost-effective wood and roof beams employing more robust, engineered materials.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Rafter Tie vs Roof Beam
Rafter ties provide effective resistance against outward thrust in roof structures by connecting opposing rafters, reducing the need for bulky roof beams and saving material costs. Roof beams offer superior load-bearing capacity for larger spans and complex designs but can increase structural weight and require additional support elements. Choosing between rafter ties and roof beams depends on factors like roof span, design complexity, and budget limitations.
Building Codes and Standards for Rafter Ties and Roof Beams
Building codes such as the International Residential Code (IRC) specify rafter ties as critical components to prevent roof spreading by resisting outward thrust from rafters. Roof beams, governed under structural standards like those from the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) or American Concrete Institute (ACI), must meet load-bearing criteria that differ from rafter tie requirements due to their distinct roles in supporting roof loads. Compliance with these codes ensures that rafter ties and roof beams perform their structural functions effectively, maintaining roof stability and safety.
Common Applications of Rafter Ties and Roof Beams
Rafter ties are commonly used in residential roof framing to prevent outward wall spread by connecting opposing rafters, effectively stabilizing the roof structure in standard pitched roofs. Roof beams, on the other hand, are employed in larger or open-span constructions where greater load-bearing capacity is necessary, such as in commercial buildings or roof designs requiring wide, unobstructed interior spaces. Both elements contribute to structural integrity, but rafter ties are preferred for simpler, cost-effective support, while roof beams accommodate more complex architectural demands.
Choosing Between Rafter Tie and Roof Beam for Your Project
Choosing between a rafter tie and a roof beam depends on your project's structural requirements and design preferences. Rafter ties stabilize the roof framework by preventing outward thrust and are ideal for traditional attic spaces with open framing. Roof beams offer greater load-bearing capacity and allow for open, column-free interiors, making them suitable for larger spans or architectural designs emphasizing space and aesthetics.
Rafter tie vs Roof beam Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com