An outlet box is designed to house electrical connections and devices such as switches and receptacles, offering easy access for maintenance and wiring changes. In contrast, a conduit box serves as a junction point for electrical conduits, protecting and organizing wires running through the conduit system. While both are essential for electrical installations, outlet boxes prioritize device mounting, whereas conduit boxes focus on wire protection and routing.
Table of Comparison
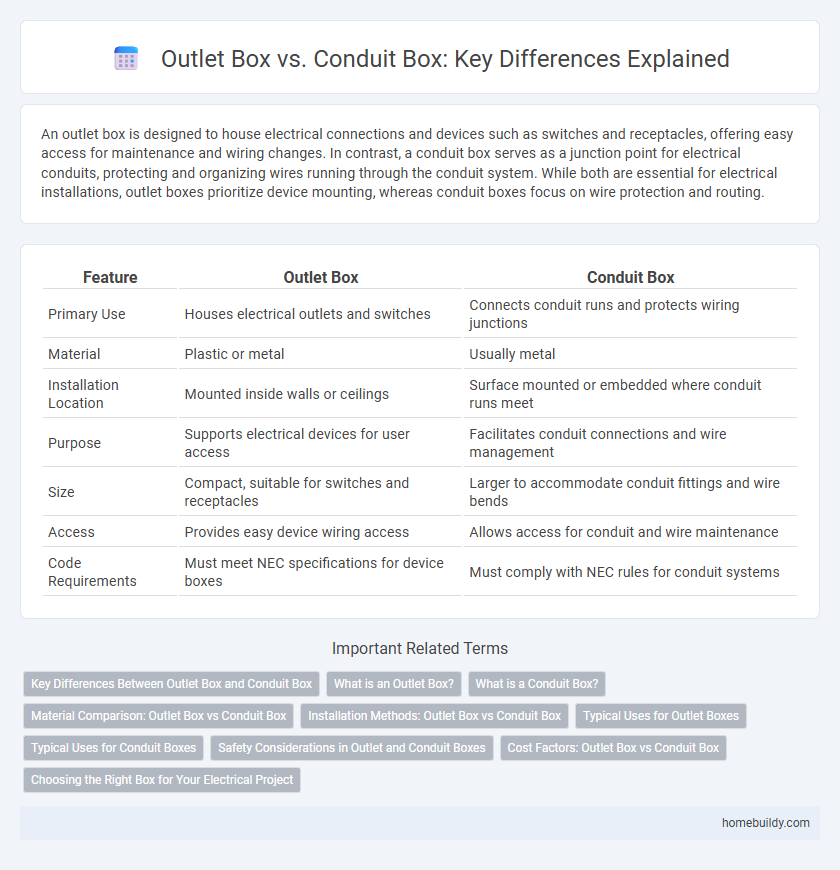
| Feature | Outlet Box | Conduit Box |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Houses electrical outlets and switches | Connects conduit runs and protects wiring junctions |
| Material | Plastic or metal | Usually metal |
| Installation Location | Mounted inside walls or ceilings | Surface mounted or embedded where conduit runs meet |
| Purpose | Supports electrical devices for user access | Facilitates conduit connections and wire management |
| Size | Compact, suitable for switches and receptacles | Larger to accommodate conduit fittings and wire bends |
| Access | Provides easy device wiring access | Allows access for conduit and wire maintenance |
| Code Requirements | Must meet NEC specifications for device boxes | Must comply with NEC rules for conduit systems |
Key Differences Between Outlet Box and Conduit Box
Outlet boxes are designed primarily to house electrical outlets, switches, and receptacles, featuring internal compartments for wiring connections and easy access for maintenance. Conduit boxes serve as junction points for multiple conduit runs, providing a secure enclosure to protect and route electrical wiring paths, often without built-in outlet mounting capabilities. The key difference lies in their function: outlet boxes support device installation and accessibility, whereas conduit boxes focus on cable management and protection within electrical conduit systems.
What is an Outlet Box?
An outlet box is a recessed or surface-mounted enclosure designed to house electrical devices like switches, outlets, or receptacles, providing protection and support for wiring connections. Unlike conduit boxes, outlet boxes are specifically intended to hold fixture outlets and facilitate safe electrical connections within residential or commercial buildings. They are typically made from metal or plastic and come in various sizes and configurations to suit different wiring and installation needs.
What is a Conduit Box?
A conduit box is an electrical enclosure designed to protect and house wiring connections within conduit systems, ensuring safe and organized cable routing. Unlike outlet boxes, which primarily serve as mounting points for receptacles and switches, conduit boxes facilitate the junction and distribution of electrical conduits while providing access for maintenance and inspection. Typically made of metal or durable plastic, conduit boxes withstand environmental factors and mechanical impacts, supporting the integrity of electrical installations in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Material Comparison: Outlet Box vs Conduit Box
Outlet boxes are typically made from plastic or metal, offering lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties ideal for residential electrical installations. Conduit boxes, often constructed from galvanized steel or aluminum, provide enhanced durability and protection against mechanical damage in industrial or outdoor environments. The choice between these materials influences the box's suitability for specific applications, environmental exposure, and compliance with electrical codes.
Installation Methods: Outlet Box vs Conduit Box
Outlet boxes are typically installed by securing them directly to wall studs or mounting surfaces, allowing easy access for wiring connections and device mounting. Conduit boxes require attaching conduit pipes that protect and route electrical wiring before connecting to the box, often necessitating additional fittings and supports for proper alignment. Both installation methods follow electrical codes but vary in complexity, with outlet boxes suited for simpler setups and conduit boxes prioritized in industrial or commercial environments for enhanced durability and wiring protection.
Typical Uses for Outlet Boxes
Outlet boxes are primarily used to house electrical outlets, switches, and receptacles in residential and commercial buildings, providing a secure mounting point and protection for wiring connections. They are typically installed in walls, ceilings, or floors to facilitate access to power and control devices in living spaces, offices, and appliances. Unlike conduit boxes, outlet boxes are designed more for consumer-facing fixtures rather than for routing and protecting conduit runs in industrial or high-traffic wiring environments.
Typical Uses for Conduit Boxes
Conduit boxes are commonly used in electrical installations where wiring protection and organization are critical, such as industrial buildings, commercial facilities, and outdoor settings exposed to harsh conditions. Unlike outlet boxes, conduit boxes provide robust housing for conduit connections, enabling secure junctions and easy access for maintenance. They are essential for routing and protecting multiple electrical cables, ensuring compliance with safety standards and durability in complex wiring systems.
Safety Considerations in Outlet and Conduit Boxes
Outlet boxes offer secure housing for electrical connections, minimizing exposure to live wires and reducing the risk of electric shock or fire. Conduit boxes provide enhanced protection by encasing wiring within metallic or non-metallic conduits, preventing physical damage and ensuring compliance with electrical codes in exposed or industrial environments. Selecting between outlet and conduit boxes depends on safety requirements, environmental conditions, and the specific application's need for mechanical protection and moisture resistance.
Cost Factors: Outlet Box vs Conduit Box
Outlet boxes generally cost less than conduit boxes due to simpler design and materials, making them a budget-friendly option for basic electrical installations. Conduit boxes involve higher expenses driven by their robust construction to support conduit connections and increased labor for installation. Cost factors also include the type of material, size, and compliance requirements, with metal conduit boxes typically priced higher than plastic outlet boxes.
Choosing the Right Box for Your Electrical Project
Outlet boxes are designed to house electrical outlets and switches, providing secure mounting and protection for wiring connections. In contrast, conduit boxes serve as junction points for conduit systems, facilitating wire routing and splicing within enclosed conduit pathways. Selecting the right box depends on project requirements: use outlet boxes for device installation in walls or ceilings, while conduit boxes are essential for conduit-supported wiring systems, ensuring compliance with electrical codes and safety standards.
Outlet box vs Conduit box Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com