An outlet box is designed for standard wall installations, typically made of plastic or metal, and is ideal for drywall or wood surfaces. Masonry boxes, on the other hand, are constructed to be embedded in concrete, brick, or block walls, featuring a more robust and durable design to withstand the harsher environment. Choosing between an outlet box and a masonry box depends on the wall material and installation requirements to ensure secure and code-compliant electrical connections.
Table of Comparison
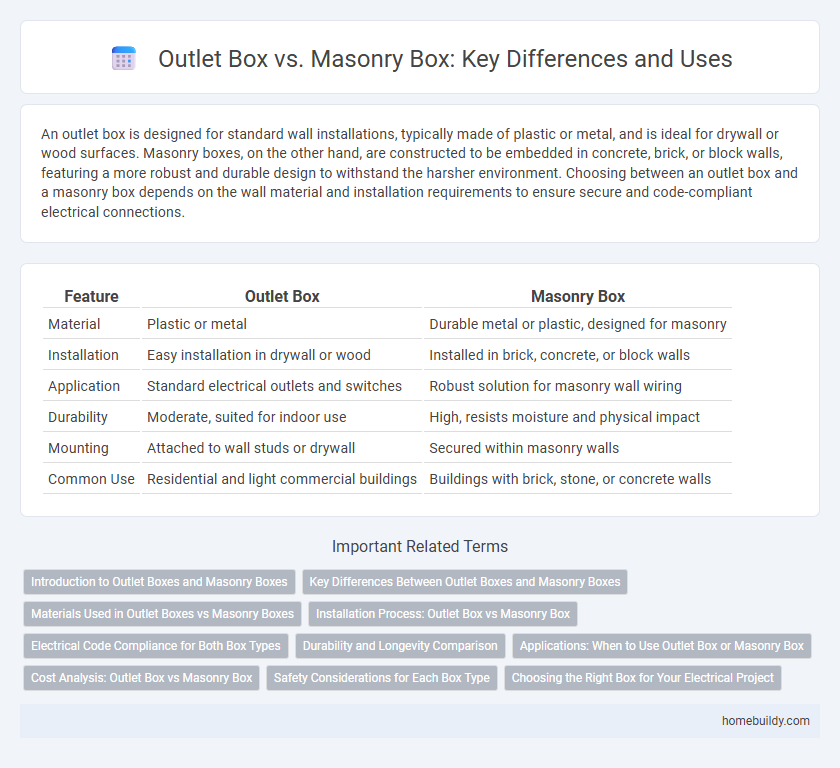
| Feature | Outlet Box | Masonry Box |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Plastic or metal | Durable metal or plastic, designed for masonry |
| Installation | Easy installation in drywall or wood | Installed in brick, concrete, or block walls |
| Application | Standard electrical outlets and switches | Robust solution for masonry wall wiring |
| Durability | Moderate, suited for indoor use | High, resists moisture and physical impact |
| Mounting | Attached to wall studs or drywall | Secured within masonry walls |
| Common Use | Residential and light commercial buildings | Buildings with brick, stone, or concrete walls |
Introduction to Outlet Boxes and Masonry Boxes
Outlet boxes are essential electrical enclosures designed to house wiring connections and devices like switches or outlets, typically made from plastic or metal for installation in walls. Masonry boxes, a specific type of outlet box, are constructed from non-metallic materials such as fiberglass or plastic and are engineered to be installed directly into concrete, brick, or block walls. Understanding the differences in material composition and installation methods is crucial for ensuring safety, durability, and code compliance in electrical projects.
Key Differences Between Outlet Boxes and Masonry Boxes
Outlet boxes, typically made from plastic or metal, are designed for installation in wall studs or drywall, providing secure mounting points for electrical switches and outlets. Masonry boxes, constructed from metal or plastic as well, are specifically engineered for installation within concrete, brick, or block walls, featuring mounting brackets or flanges to anchor firmly in masonry surfaces. The key differences lie in their mounting methods and suitability for various wall types, with outlet boxes suited for wood or drywall and masonry boxes built to withstand the rigors of solid masonry environments.
Materials Used in Outlet Boxes vs Masonry Boxes
Outlet boxes are commonly made from non-metallic materials like PVC or plastic, which provide lightweight, corrosion-resistant options suitable for residential wiring. Masonry boxes, in contrast, are typically composed of metal or fiberglass reinforced plastics designed to withstand harsh conditions and ensure secure mounting within concrete or brick structures. The choice of material directly impacts durability, ease of installation, and compatibility with building codes for electrical safety.
Installation Process: Outlet Box vs Masonry Box
Outlet box installation typically involves securing the box to a stud or framing member using screws or nails, ensuring easy access for wiring and devices in drywall or wood construction. Masonry box installation requires embedding the box into a pre-cut cavity in brick, block, or concrete walls, often using mortar or adhesive to hold it firmly in place, which demands precise alignment and a more labor-intensive process. The choice between outlet box and masonry box installation hinges on the wall material and the need for durability, with masonry boxes providing a robust solution for solid walls.
Electrical Code Compliance for Both Box Types
Outlet boxes and masonry boxes must adhere to the National Electrical Code (NEC) to ensure electrical safety and compliance. Both box types require grounding and support for all connected wiring and devices, with masonry boxes typically installed in concrete or brick surfaces and outlet boxes used in framed walls. Compliance includes correct box sizing for wire fill capacity, secure mounting, and use of appropriate covers, ensuring safe and reliable electrical connections.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Outlet boxes made of metal or high-grade plastic offer superior durability compared to masonry boxes, resisting corrosion, impact, and environmental wear more effectively. Masonry boxes, integrated directly into brick or concrete walls, provide excellent structural support but may degrade faster under moisture exposure and physical stress. For long-term installations, metal outlet boxes maintain integrity and safety over decades, making them a preferred choice in environments requiring maximum longevity.
Applications: When to Use Outlet Box or Masonry Box
Outlet boxes are ideal for drywall or wood framing installations, providing a secure housing for electrical connections in residential or commercial buildings. Masonry boxes are specifically designed for use in concrete, brick, or block walls, ensuring durability and proper fixture mounting in exterior or heavy-duty environments. Choose an outlet box for indoor, framed walls and a masonry box when installing electrical components in solid masonry structures.
Cost Analysis: Outlet Box vs Masonry Box
The cost analysis between outlet boxes and masonry boxes reveals that outlet boxes typically offer a lower upfront expense due to their lighter materials and simpler installation, averaging around $2 to $5 per unit. Masonry boxes, designed for concrete or brick walls, cost more, generally $5 to $10 per unit, reflecting their durable construction and resistance to environmental factors. When factoring in labor, masonry box installation incurs higher costs due to the need for specialized tools and additional mounting time, making outlet boxes more cost-effective for standard drywall applications.
Safety Considerations for Each Box Type
Outlet boxes offer enhanced electrical safety with their insulated, non-conductive materials that reduce the risk of short circuits and electrical fires, making them suitable for drywall installations. Masonry boxes, constructed from metal or durable plastic, provide robust protection against mechanical damage in brick or concrete walls but require proper grounding to prevent electrical hazards. Choosing the correct box type ensures compliance with local electrical codes and optimizes safety by reducing risks associated with improper installation or material incompatibility.
Choosing the Right Box for Your Electrical Project
Choosing the right electrical box depends on the installation environment and surface type. Outlet boxes, typically made of plastic or metal, are suited for drywall or wood installations, providing easy wiring access and mounting options. Masonry boxes are specifically designed for concrete, brick, or block walls, featuring robust construction and anchoring tabs to secure the box firmly in solid surfaces.
Outlet box vs Masonry box Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com