An outlet box is a specific type of electrical box designed to house electrical outlets, switches, or receptacles, ensuring secure and safe connections. Electrical boxes serve a broader purpose, accommodating various wiring devices, including outlets, switches, junction points, and lighting fixtures. Choosing the correct box type is essential for compliance with electrical codes and safety standards in residential or commercial installations.
Table of Comparison
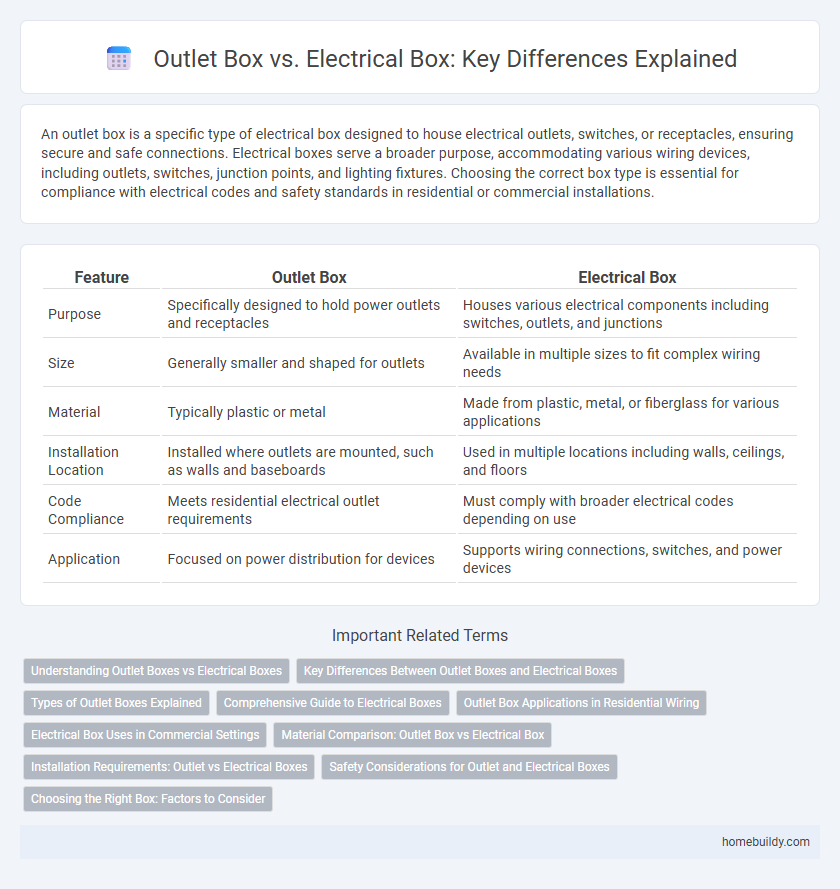
| Feature | Outlet Box | Electrical Box |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Specifically designed to hold power outlets and receptacles | Houses various electrical components including switches, outlets, and junctions |
| Size | Generally smaller and shaped for outlets | Available in multiple sizes to fit complex wiring needs |
| Material | Typically plastic or metal | Made from plastic, metal, or fiberglass for various applications |
| Installation Location | Installed where outlets are mounted, such as walls and baseboards | Used in multiple locations including walls, ceilings, and floors |
| Code Compliance | Meets residential electrical outlet requirements | Must comply with broader electrical codes depending on use |
| Application | Focused on power distribution for devices | Supports wiring connections, switches, and power devices |
Understanding Outlet Boxes vs Electrical Boxes
Outlet boxes and electrical boxes are essential components in electrical wiring systems, but outlet boxes specifically house receptacles and switches, while electrical boxes serve broader purposes including junction points and fixture mounts. Outlet boxes are designed with openings to securely mount outlets and provide easy access for device installation and maintenance. Understanding the distinction ensures proper selection for safety, code compliance, and functionality in residential and commercial electrical installations.
Key Differences Between Outlet Boxes and Electrical Boxes
Outlet boxes and electrical boxes both house electrical connections, but outlet boxes specifically accommodate receptacles or switches, while electrical boxes serve broader purposes including junctions and splices. Outlet boxes are typically designed with specific mounting brackets to secure outlets, whereas electrical boxes vary in shape and size to fit different installation needs like ceiling fixtures or wiring junctions. Materials differ as well; outlet boxes are often plastic or metal with openings for outlet plugs, whereas electrical boxes may have additional knockouts to facilitate wire entry and exit in multiple directions.
Types of Outlet Boxes Explained
Outlet boxes come in various types including plastic, metal, and weatherproof models, each designed for specific electrical installation needs. Plastic outlet boxes are lightweight and non-conductive, ideal for indoor residential wiring, while metal boxes offer enhanced durability and grounding capabilities suitable for commercial applications. Weatherproof outlet boxes provide protection against moisture and environmental elements, making them essential for outdoor electrical outlets.
Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Boxes
An outlet box is a specific type of electrical box designed to house electrical outlets, switches, or receptacles, ensuring safe and secure connections within residential or commercial wiring systems. Electrical boxes encompass a broader range of enclosures, including junction boxes, switch boxes, and outlet boxes, each serving distinct purposes in electrical installations. Understanding the differences and applications of outlet boxes versus other electrical boxes is essential for compliant and efficient electrical setups according to NEC (National Electrical Code) standards.
Outlet Box Applications in Residential Wiring
Outlet boxes are specifically designed to house electrical outlets safely within residential wiring systems, providing secure mounting points and protection for connections. They differ from general electrical boxes by being optimized for receptacle installations, ensuring compliance with electrical codes and facilitating easier access for device replacement or upgrades. Common applications include supporting wall-mounted power outlets, enabling proper wire management, and minimizing electrical hazards in home environments.
Electrical Box Uses in Commercial Settings
Electrical boxes in commercial settings are essential for housing wiring connections, securing outlets, switches, and fixtures while ensuring compliance with electrical codes. Designed to accommodate higher voltages and more complex wiring systems, commercial electrical boxes provide enhanced durability and fire resistance compared to typical residential outlet boxes. These boxes support efficient electrical distribution, protect against electrical hazards, and facilitate maintenance in large-scale commercial installations.
Material Comparison: Outlet Box vs Electrical Box
Outlet boxes are typically made from plastic or metal, offering lightweight or durable options depending on installation needs, while electrical boxes encompass a wider range of materials including steel, aluminum, and non-metallic compounds tailored for specific electrical systems. Plastic outlet boxes provide corrosion resistance and ease of installation, whereas metal electrical boxes ensure enhanced grounding and durability for high-demand circuits. Choosing between outlet box and electrical box materials depends on environmental factors, load requirements, and safety standards in residential or commercial wiring projects.
Installation Requirements: Outlet vs Electrical Boxes
Outlet boxes and electrical boxes differ primarily in their installation requirements, with outlet boxes specifically designed to house receptacles and switches, requiring secure mounting to a wall stud or ceiling joist for stability. Electrical boxes encompass a broader range of applications, including junctions and splices, and must comply with electrical codes ensuring proper grounding, wire capacity, and fire resistance. Correct installation of outlet and electrical boxes guarantees safe, code-compliant electrical connections, minimizing risks of electrical hazards and ensuring device functionality.
Safety Considerations for Outlet and Electrical Boxes
Outlet boxes and electrical boxes must comply with strict safety regulations to prevent fire hazards and electrical shocks. Proper grounding, secure mounting, and the use of boxes rated for specific environments are critical to ensure safe installation and operation. Choosing the correct type and size of box reduces the risk of overheating and accidental contact with live wires.
Choosing the Right Box: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right box between an outlet box and an electrical box depends on specific installation needs, such as the type of device, electrical wiring requirements, and building codes. Outlet boxes are designed primarily for receptacles and switches, offering features like device mounting and faceplate compatibility, whereas electrical boxes serve broader purposes including housing splices and junctions. Key factors include box size, material (plastic or metal), device compatibility, and compliance with NEC (National Electrical Code) standards to ensure safety and functionality.
Outlet box vs Electrical box Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com