Outlet boxes are designed specifically to house electrical outlets and provide secure mounting for receptacles, while switch boxes are intended to accommodate light switches or other control devices. The key difference lies in size and wiring requirements, as outlet boxes often have different depth and space specifications to support multiple outlets or surge protectors. Both types ensure safe electrical connections and comply with building codes, but choosing the correct box depends on the device it will contain.
Table of Comparison
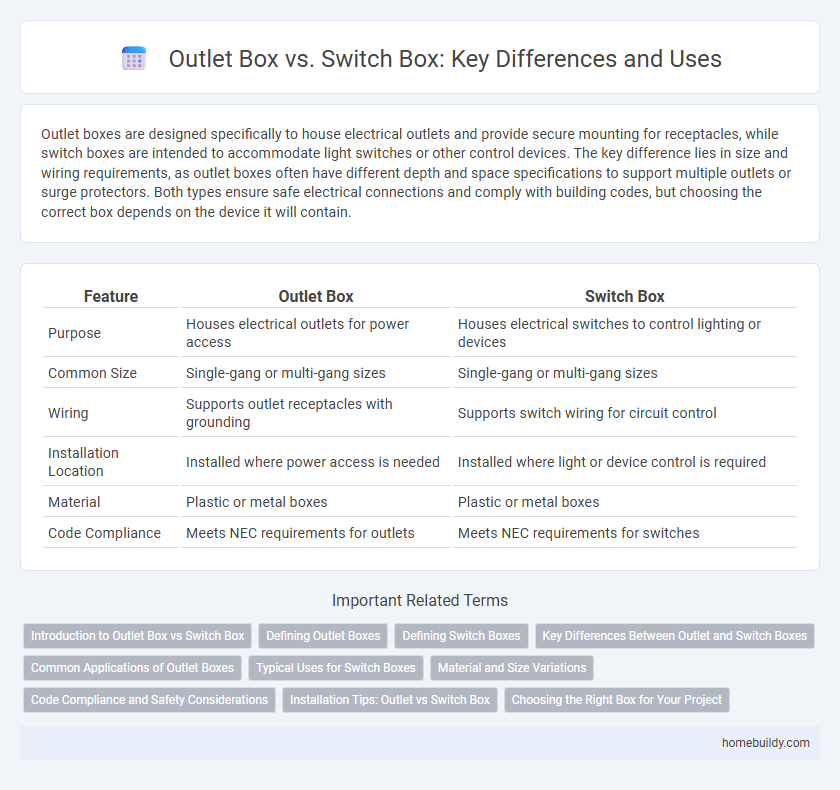
| Feature | Outlet Box | Switch Box |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Houses electrical outlets for power access | Houses electrical switches to control lighting or devices |
| Common Size | Single-gang or multi-gang sizes | Single-gang or multi-gang sizes |
| Wiring | Supports outlet receptacles with grounding | Supports switch wiring for circuit control |
| Installation Location | Installed where power access is needed | Installed where light or device control is required |
| Material | Plastic or metal boxes | Plastic or metal boxes |
| Code Compliance | Meets NEC requirements for outlets | Meets NEC requirements for switches |
Introduction to Outlet Box vs Switch Box
An outlet box is designed to house electrical outlets securely, providing protection and support for wiring connections. In contrast, a switch box is specifically intended to accommodate light switches and control mechanisms within a wall. Both types of boxes are essential components in electrical installations, ensuring safety and code compliance while organizing electrical devices effectively.
Defining Outlet Boxes
Outlet boxes are specifically designed to house electrical outlets, providing secure mounting points and protection for wiring connections. Unlike switch boxes, which accommodate light switches and often have different internal configurations, outlet boxes must support the weight and usage demands of receptacles. Proper selection of the outlet box ensures compliance with electrical codes and enhances safety by preventing electrical hazards.
Defining Switch Boxes
Switch boxes are electrical enclosures designed specifically to house switches and their wiring, providing protection and organization for switch connections. Unlike outlet boxes that accommodate receptacles for power access, switch boxes are tailored to support single-pole, three-way, or dimmer switches commonly used for lighting control. These boxes come in various sizes and materials, ensuring compliance with electrical codes while facilitating safe installation and maintenance of switch circuits.
Key Differences Between Outlet and Switch Boxes
Outlet boxes are designed primarily to house electrical receptacles, enabling the connection of devices to the power supply, while switch boxes are built to accommodate light switches used for controlling lighting circuits. Outlet boxes typically feature a standard depth and size to fit duplex or GFCI receptacles, whereas switch boxes may vary in size to support single or multiple toggle switches and rocker switches. The key differences lie in their wiring configurations, functional purposes, and physical dimensions tailored to the electrical components they contain.
Common Applications of Outlet Boxes
Outlet boxes are primarily used to house electrical outlets, ensuring safe and secure connections for powering devices in residential and commercial buildings. They accommodate various outlet types, such as duplex receptacles, GFCI outlets, and USB outlets, making them essential for general power distribution in kitchens, living rooms, and offices. Unlike switch boxes, outlet boxes support continuous power flow rather than control functions, making them ideal for locations requiring easy access to electricity.
Typical Uses for Switch Boxes
Switch boxes are primarily used to house electrical switches that control lighting or appliances within residential and commercial buildings. They are designed to accommodate toggle or rocker switches and often allow for multiple switches to be installed in a single box for controlling various circuits. Unlike outlet boxes, switch boxes must provide sufficient space to manage wiring connections safely and comply with electrical codes specific to switch installations.
Material and Size Variations
Outlet boxes commonly use non-metallic materials such as PVC or plastic, while switch boxes are often made from metal or heavy-duty plastic to better support switch toggles. The size of outlet boxes typically varies to accommodate multiple receptacles or outlets, generally being deeper and larger than switch boxes that only house single or dual switches. Material choices and dimensional differences directly influence installation requirements and electrical safety standards for both box types.
Code Compliance and Safety Considerations
Outlet boxes and switch boxes differ primarily in their intended electrical uses, with outlet boxes designed to house receptacles and switch boxes intended for light switches, both requiring strict adherence to NEC (National Electrical Code) standards for proper installation and grounding. Compliance mandates that outlet boxes must provide adequate volume to accommodate wiring and devices without overcrowding, ensuring safe heat dissipation and reducing fire hazards. Safety considerations emphasize secure mounting, proper box fill capacity, and the use of UL-listed components, which are critical in preventing electrical shorts and ensuring long-term operational reliability.
Installation Tips: Outlet vs Switch Box
Outlet boxes require precise alignment with wall outlets to ensure secure electrical connections and faceplate fitting, whereas switch boxes must accommodate toggle or rocker switches with appropriate mounting brackets. Proper depth measurement is crucial for both, avoiding damage to wiring or difficulty in mounting devices. Use metal or plastic boxes compatible with local electrical codes and confirm grounding requirements during installation to maintain safety standards.
Choosing the Right Box for Your Project
Outlet boxes are designed to house receptacles for electrical plugs, while switch boxes accommodate light or appliance switches, with each type tailored to specific wiring needs and device sizes. Choosing the right box depends on the device type, volume requirements, and installation location, ensuring safety and compliance with electrical codes. Proper selection enhances durability and ease of future maintenance in residential or commercial electrical projects.
Outlet box vs Switch box Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com