An outlet box is designed to house electrical outlets securely, providing protection and support for wiring and devices. A wall box, while similar, is a broader term that includes boxes used for various electrical fixtures such as switches, outlets, and junction points. Choosing the right box depends on the specific installation requirements, ensuring safety and compliance with electrical codes.
Table of Comparison
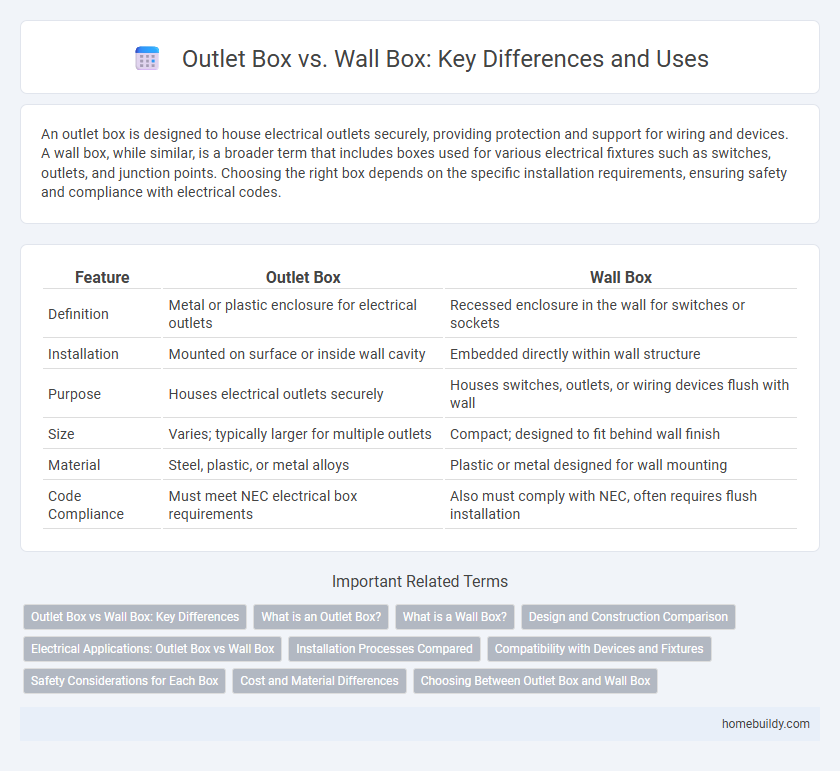
| Feature | Outlet Box | Wall Box |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Metal or plastic enclosure for electrical outlets | Recessed enclosure in the wall for switches or sockets |
| Installation | Mounted on surface or inside wall cavity | Embedded directly within wall structure |
| Purpose | Houses electrical outlets securely | Houses switches, outlets, or wiring devices flush with wall |
| Size | Varies; typically larger for multiple outlets | Compact; designed to fit behind wall finish |
| Material | Steel, plastic, or metal alloys | Plastic or metal designed for wall mounting |
| Code Compliance | Must meet NEC electrical box requirements | Also must comply with NEC, often requires flush installation |
Outlet Box vs Wall Box: Key Differences
Outlet boxes are specifically designed to house electrical outlets and switches, offering secure mounting and protection for wiring connections. Wall boxes, often used interchangeably with outlet boxes, serve a broader purpose by accommodating various devices such as light fixtures, dimmers, and receptacles while fitting flush within wall cavities. The key difference lies in their intended use and size, with outlet boxes tailored for outlet installation and wall boxes providing versatile options for different electrical components.
What is an Outlet Box?
An outlet box is a protective enclosure installed within walls to house electrical connections, switches, or receptacles, ensuring safety and compliance with electrical codes. Unlike a wall box, which primarily refers to recessed boxes used for mounting devices flush with the wall, an outlet box is specifically designed to securely contain power outlets and manage wiring. Materials for outlet boxes include plastic, metal, or cast iron, each providing grounding and fire resistance tailored to different installation requirements.
What is a Wall Box?
A wall box is a recessed electrical enclosure installed within a wall cavity, designed to house wiring devices such as outlets, switches, or junction points. Unlike an outlet box, which may be surface-mounted or designed for specific applications, a wall box provides a flush, secure mounting solution that maintains the integrity of the wall surface. Wall boxes come in various materials like plastic or metal and sizes to accommodate different electrical components and comply with building codes.
Design and Construction Comparison
Outlet boxes often feature a more robust construction with integrated mounting brackets and knockouts designed for electrical conduit connections, whereas wall boxes prioritize a flush design to fit seamlessly within drywall or masonry. Material differences also play a role; outlet boxes typically use metal or durable plastic to handle higher electrical loads, while wall boxes may use lightweight plastic optimized for easier installation and compatibility with wall finishes. The design of outlet boxes emphasizes accessibility and safety for wiring tasks, contrasting with wall boxes that focus on aesthetic integration and space-saving installation.
Electrical Applications: Outlet Box vs Wall Box
Outlet boxes are specifically designed to house electrical outlets, switches, or receptacles, providing secure mounting and protection for wiring connections. Wall boxes serve as a broader category encompassing outlet boxes but also include boxes for light switches, junctions, or other electrical devices, often varying in size and depth to accommodate different applications. Choosing between an outlet box and a wall box depends on the specific electrical installation requirements, such as device type, wiring complexity, and code compliance.
Installation Processes Compared
Outlet boxes typically install by mounting directly onto wall studs or within drywall cavities, providing sturdy support for electrical devices and wiring. Wall boxes, designed for surface or shallow mounting, often attach to the cavity within the wall substrate, requiring precise cutting and securing to ensure stability and code compliance. The installation process for outlet boxes demands careful alignment and secure fastening to accommodate electrical fixtures, whereas wall boxes prioritize adaptability in varied wall thicknesses and materials.
Compatibility with Devices and Fixtures
Outlet boxes are designed to securely house electrical outlets and switches, providing compatibility with a wide range of standard devices and fixtures, including receptacles and light switches. Wall boxes, often recessed into the wall, accommodate various fixtures but may differ in depth and mounting style, affecting device compatibility. Ensuring the correct box type and size is critical for proper installation and safe operation of electrical devices and fixtures.
Safety Considerations for Each Box
Outlet boxes are designed to securely house electrical connections and support outlets, offering robust protection against electrical shocks and fires by containing sparks and heat within a fire-resistant enclosure. Wall boxes, while similar in function, vary in material and installation depth, which can affect grounding effectiveness and overall safety, especially in older or improperly installed setups. Selecting the appropriate box type according to electrical code standards and ensuring proper installation reduces risks of short circuits, improves grounding, and enhances user safety.
Cost and Material Differences
Outlet boxes typically cost less than wall boxes due to their simpler design and use of lightweight plastic or thin metal materials. Wall boxes are often constructed from sturdier metals or heavier gauge steel to support heavier fixtures or embedded installations, increasing their overall cost. Material differences impact durability and installation applications, with outlet boxes favoring affordability and convenience while wall boxes prioritize strength and load-bearing capacity.
Choosing Between Outlet Box and Wall Box
Choosing between an outlet box and a wall box depends on the specific electrical installation requirements and the type of fixture being mounted. Outlet boxes are designed to house electrical outlets and switches, providing a secure enclosure for wiring connections, while wall boxes typically serve as larger enclosures for recessed lighting or merging multiple cables. Selecting the correct box ensures compliance with electrical codes, enhances safety, and supports the durability of the electrical setup.
Outlet box vs Wall box Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com