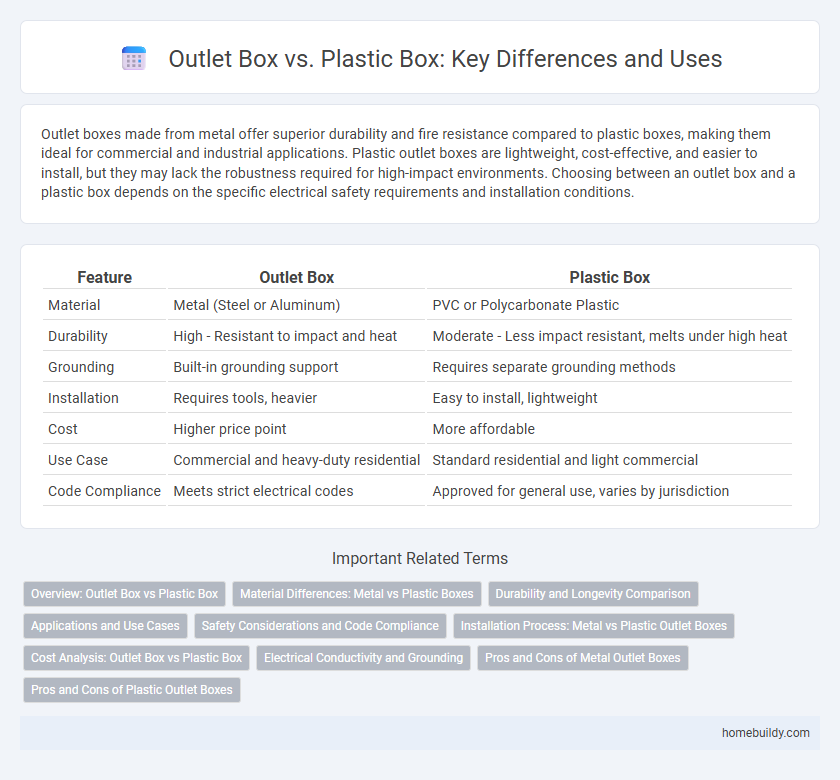
Outlet boxes made from metal offer superior durability and fire resistance compared to plastic boxes, making them ideal for commercial and industrial applications. Plastic outlet boxes are lightweight, cost-effective, and easier to install, but they may lack the robustness required for high-impact environments. Choosing between an outlet box and a plastic box depends on the specific electrical safety requirements and installation conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Outlet Box | Plastic Box |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Metal (Steel or Aluminum) | PVC or Polycarbonate Plastic |
| Durability | High - Resistant to impact and heat | Moderate - Less impact resistant, melts under high heat |
| Grounding | Built-in grounding support | Requires separate grounding methods |
| Installation | Requires tools, heavier | Easy to install, lightweight |
| Cost | Higher price point | More affordable |
| Use Case | Commercial and heavy-duty residential | Standard residential and light commercial |
| Code Compliance | Meets strict electrical codes | Approved for general use, varies by jurisdiction |
Overview: Outlet Box vs Plastic Box
Outlet boxes, typically made of metal, offer superior durability, grounding capabilities, and heat resistance compared to plastic boxes, making them ideal for heavy-duty electrical installations. Plastic boxes are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easier to install, often preferred for residential wiring where cost-efficiency and ease of handling are priorities. Both types comply with electrical codes, but choice depends on specific application requirements such as load type, environmental conditions, and regulatory standards.
Material Differences: Metal vs Plastic Boxes
Metal outlet boxes offer superior durability and grounding capabilities compared to plastic boxes, making them ideal for commercial or industrial applications. Plastic boxes are lightweight, non-conductive, and corrosion-resistant, which suits residential use where electrical grounding is managed differently. The choice between metal and plastic often hinges on safety codes, environmental exposure, and installation requirements.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Outlet boxes made from metal generally offer superior durability and longevity compared to plastic boxes due to their resistance to impact, heat, and wear. Metal outlet boxes are less prone to cracking or deforming under stress, making them ideal for environments that demand robust performance. While plastic boxes are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, they typically have a shorter lifespan and can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light or extreme temperatures.
Applications and Use Cases
Outlet boxes, typically made from metal or durable plastic, are essential for safely housing electrical connections in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Plastic boxes are preferred in environments where corrosion resistance and lightweight installation are critical, such as indoor residential wiring and low-voltage systems, while metal outlet boxes excel in high-demand scenarios requiring greater durability and grounding capabilities, including commercial buildings and industrial settings. Selecting the appropriate outlet box depends on factors like electrical load, environmental conditions, and compliance with local electrical codes.
Safety Considerations and Code Compliance
Outlet boxes made from metal offer superior durability and grounding capabilities compared to plastic boxes, enhancing electrical safety in residential and commercial installations. Plastic boxes must be rated for specific use and meet NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements to ensure proper flame resistance and insulation properties, reducing fire hazards. Compliance with local electrical codes mandates selecting the appropriate box material based on the wiring environment, load capacity, and grounding needs to maintain safety and avoid code violations.
Installation Process: Metal vs Plastic Outlet Boxes
Metal outlet boxes require grounding and more precise alignment during installation to ensure electrical safety, often involving screws to secure devices firmly. Plastic outlet boxes are easier to install, featuring built-in clamps and snap-in mounts that reduce installation time without needing grounding. The choice impacts wiring flexibility, with metal boxes providing superior durability and heat resistance, while plastic boxes offer corrosion resistance and lighter weight.
Cost Analysis: Outlet Box vs Plastic Box
Outlet boxes made from metal typically have a higher upfront cost compared to plastic boxes due to material durability and fire resistance. Plastic boxes offer cost savings in bulk purchases and ease of installation, reducing labor expenses. Long-term expenses may favor metal outlet boxes in commercial or high-usage environments because of their robustness and lower replacement frequency.
Electrical Conductivity and Grounding
Outlet boxes made of metal provide superior electrical conductivity and ensure effective grounding compared to plastic boxes, enhancing safety by preventing electrical faults. Plastic boxes, being non-conductive, require separate grounding methods which can complicate installation and potentially increase the risk of electrical hazards. Metal outlet boxes are preferred in installations where electrical grounding continuity is critical for system protection and compliance with electrical codes.
Pros and Cons of Metal Outlet Boxes
Metal outlet boxes offer superior durability and enhanced grounding capabilities, making them ideal for ensuring electrical safety and compliance with building codes. They resist damage from impacts and heat better than plastic boxes but are heavier and more expensive, which can increase installation time and overall project costs. Metal boxes also conduct electricity, requiring proper grounding to prevent electrical hazards, unlike non-conductive plastic alternatives.
Pros and Cons of Plastic Outlet Boxes
Plastic outlet boxes offer advantages such as affordability, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation, making them suitable for residential electrical wiring. They are lightweight and non-conductive, reducing the risk of electrical shock and simplifying grounding requirements. However, plastic boxes are less durable than metal equivalents, prone to cracking under impact or over-tightening, and may not provide adequate heat dissipation in high-load circuits.
Outlet box vs Plastic box Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com