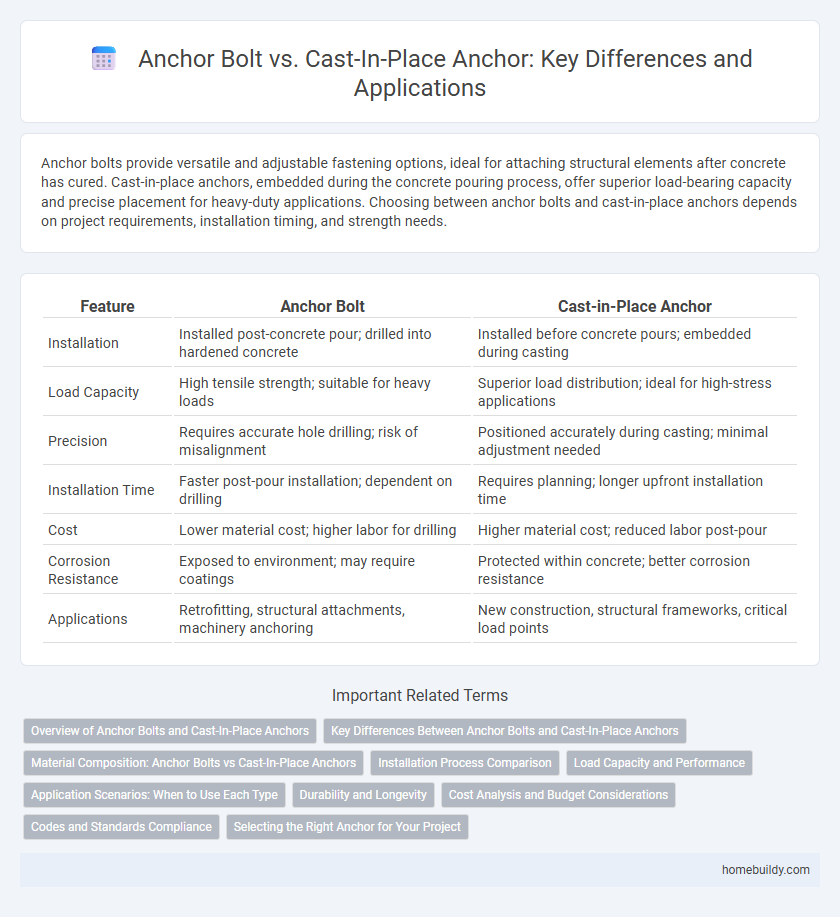
Anchor bolts provide versatile and adjustable fastening options, ideal for attaching structural elements after concrete has cured. Cast-in-place anchors, embedded during the concrete pouring process, offer superior load-bearing capacity and precise placement for heavy-duty applications. Choosing between anchor bolts and cast-in-place anchors depends on project requirements, installation timing, and strength needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anchor Bolt | Cast-in-Place Anchor |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Installed post-concrete pour; drilled into hardened concrete | Installed before concrete pours; embedded during casting |
| Load Capacity | High tensile strength; suitable for heavy loads | Superior load distribution; ideal for high-stress applications |
| Precision | Requires accurate hole drilling; risk of misalignment | Positioned accurately during casting; minimal adjustment needed |
| Installation Time | Faster post-pour installation; dependent on drilling | Requires planning; longer upfront installation time |
| Cost | Lower material cost; higher labor for drilling | Higher material cost; reduced labor post-pour |
| Corrosion Resistance | Exposed to environment; may require coatings | Protected within concrete; better corrosion resistance |
| Applications | Retrofitting, structural attachments, machinery anchoring | New construction, structural frameworks, critical load points |
Overview of Anchor Bolts and Cast-In-Place Anchors
Anchor bolts are mechanical fasteners embedded in concrete during or after curing to secure structural elements, offering flexibility for post-construction adjustments. Cast-in-place anchors are specifically positioned and fixed within the concrete formwork before pouring, providing enhanced load transfer and stability for heavy structural applications. Both types serve critical roles in construction, with anchor bolts favoring adaptability and cast-in-place anchors delivering superior integration and strength.
Key Differences Between Anchor Bolts and Cast-In-Place Anchors
Anchor bolts are typically pre-installed into concrete foundations and provide a reliable mechanical connection for structural elements, while cast-in-place anchors are embedded directly during the concrete pour, ensuring precise alignment and strong load transfer. Anchor bolts allow for some adjustability during installation, whereas cast-in-place anchors require exact positioning beforehand, limiting field modifications. Both systems offer robust anchorage, but cast-in-place anchors often result in higher installation accuracy and structural integrity due to their integration within the concrete matrix.
Material Composition: Anchor Bolts vs Cast-In-Place Anchors
Anchor bolts are typically made from high-strength steel, often carbon or alloy steel, designed for superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance. Cast-in-place anchors are embedded directly into concrete during pouring and frequently utilize similar steel compositions but may also incorporate stainless steel or epoxy coatings for enhanced durability. Material selection influences load capacity and longevity, with cast-in-place anchors benefiting from integrated concrete bonding while anchor bolts require precise installation and anchoring hardware.
Installation Process Comparison
Anchor bolts offer a simpler installation process as they are pre-fabricated and typically drilled or embedded into hardened concrete after curing, allowing for precise placement and adjustments. Cast-in-place anchors require positioning and securing during the concrete pour, which demands careful coordination and limits flexibility for post-installation modifications. The choice between these methods impacts labor time, accuracy, and project scheduling.
Load Capacity and Performance
Anchor bolts typically offer higher load capacity due to their embedded length and material strength, making them suitable for heavy structural loads. Cast-in-place anchors provide superior performance in terms of alignment accuracy and integration with concrete, preventing slip under dynamic loads. Both anchor types excel in different conditions, with cast-in-place anchors favoring early load application and anchor bolts excelling in retrofit applications.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Each Type
Anchor bolts are ideal for applications requiring precise positioning and high load capacity in pre-fabricated structures, offering strong tensile and shear resistance. Cast-in-place anchors suit concrete foundations and heavy equipment installations where embedding during concrete curing ensures optimal bonding and stability. Use anchor bolts for retrofit and customizable setups, while cast-in-place anchors excel in new construction projects demanding integrated anchoring solutions.
Durability and Longevity
Anchor bolts offer superior durability compared to cast-in-place anchors due to their corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or galvanized coatings, which extend their service life in harsh environments. Unlike cast-in-place anchors that are embedded during concrete pouring and can suffer from concrete shrinkage or cracking, anchor bolts installed post-pour provide better adjustability and maintain structural integrity over time. High-performance anchor bolts ensure long-term stability in construction applications where resistance to environmental stress and mechanical wear is critical.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Anchor bolts generally incur lower upfront installation costs than cast-in-place anchors due to simplified post-pour embedding processes and reduced labor intensity. Cast-in-place anchors, while often more expensive initially because of custom forming and alignment requirements during concrete placement, provide enhanced structural integration that can minimize long-term maintenance expenses. Budget considerations must weigh immediate expenditures against potential lifecycle costs, factoring project scale, design complexity, and installation timeline.
Codes and Standards Compliance
Anchor bolts and cast-in-place anchors must adhere to strict codes and standards such as ACI 318 and ASTM F1554 to ensure structural integrity and safety. Anchor bolts are typically pre-fabricated and installed before concrete pouring, requiring precise placement according to design specifications outlined in these standards. Cast-in-place anchors, integrated during concrete casting, must meet the same code requirements for load capacity and corrosion resistance, ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
Selecting the Right Anchor for Your Project
Selecting the right anchor bolt depends on structural requirements, load capacity, and installation conditions. Anchor bolts offer precise positioning flexibility and are ideal for retrofit applications, while cast-in-place anchors provide superior integration and strength for new concrete pours. Evaluating project specifics such as load type, environmental exposure, and installation timeline ensures optimal anchor performance and durability.
Anchor bolt vs Cast-in-place anchor Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com