Anchor bolt material directly influences the strength and durability of the bolt, with common options including stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel, each offering different resistance to corrosion and mechanical stress. Anchor bolt finish, such as galvanization, zinc plating, or epoxy coating, enhances surface protection against environmental factors, extending the lifespan of the bolt in various conditions. Choosing the right combination of material and finish ensures optimal performance, especially in demanding construction and industrial applications.
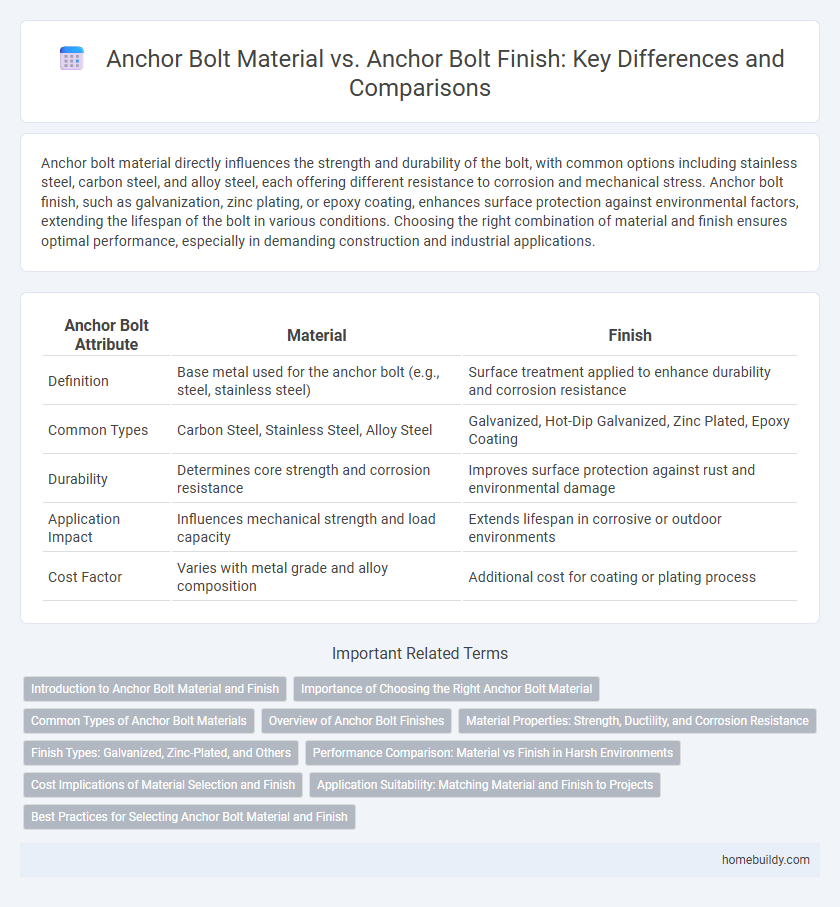
Table of Comparison
| Anchor Bolt Attribute | Material | Finish |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Base metal used for the anchor bolt (e.g., steel, stainless steel) | Surface treatment applied to enhance durability and corrosion resistance |
| Common Types | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel | Galvanized, Hot-Dip Galvanized, Zinc Plated, Epoxy Coating |
| Durability | Determines core strength and corrosion resistance | Improves surface protection against rust and environmental damage |
| Application Impact | Influences mechanical strength and load capacity | Extends lifespan in corrosive or outdoor environments |
| Cost Factor | Varies with metal grade and alloy composition | Additional cost for coating or plating process |
Introduction to Anchor Bolt Material and Finish
Anchor bolt material primarily determines the bolt's strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific environments, with common options including carbon steel, stainless steel, and galvanized steel. Anchor bolt finish enhances durability and corrosion protection, featuring finishes like hot-dip galvanizing, zinc plating, and epoxy coating to extend service life in harsh conditions. Selecting the appropriate material and finish combination is essential for ensuring structural integrity and long-term performance in construction applications.
Importance of Choosing the Right Anchor Bolt Material
Selecting the appropriate anchor bolt material ensures superior strength, corrosion resistance, and durability essential for structural integrity in construction projects. High-quality materials like stainless steel or galvanized steel provide enhanced performance compared to standard carbon steel, particularly in harsh environments. Proper material choice minimizes maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of the anchor bolt, preventing costly failures and safety risks.
Common Types of Anchor Bolt Materials
Anchor bolt materials commonly include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, each offering distinct strength and corrosion resistance properties ideal for various construction environments. Carbon steel anchor bolts, often galvanized or zinc-plated for rust protection, are widely used in general applications due to their affordability and mechanical strength. Stainless steel anchor bolts provide superior corrosion resistance in harsh or marine conditions, while alloy steel variants deliver enhanced mechanical properties for heavy-duty structural applications.
Overview of Anchor Bolt Finishes
Anchor bolt finishes play a crucial role in enhancing corrosion resistance and durability, often surpassing the impact of the base material alone. Common finishes include galvanized coatings, zinc plating, and epoxy coatings, each offering specific protection levels tailored to environmental conditions. Selecting the appropriate finish ensures optimal performance and longevity of anchor bolts in construction applications.
Material Properties: Strength, Ductility, and Corrosion Resistance
Anchor bolt material significantly influences strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance, with common options including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, each offering distinct mechanical properties tailored to structural demands. Carbon steel provides high tensile strength but lower corrosion resistance, often necessitating protective finishes such as galvanization or epoxy coating to enhance durability in harsh environments. Stainless steel anchor bolts exhibit superior corrosion resistance and adequate ductility, making them ideal for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals, while alloy steel combines enhanced strength with moderate corrosion resistance, suitable for heavy-load conditions.
Finish Types: Galvanized, Zinc-Plated, and Others
Anchor bolt finish types significantly influence corrosion resistance and durability, with galvanized finishes offering a thick zinc coating that protects against harsh environmental conditions, making them ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Zinc-plated finishes provide a thinner, decorative layer of zinc that enhances corrosion protection for indoor or less demanding environments while maintaining a cost-effective solution. Other finishes include hot-dipped galvanizing, providing enhanced durability, and specialty coatings like epoxy or stainless steel finishes, which are chosen based on specific structural and environmental requirements.
Performance Comparison: Material vs Finish in Harsh Environments
Anchor bolt materials like stainless steel and carbon steel significantly influence corrosion resistance and mechanical strength in harsh environments, outperforming the protective benefits of finishes such as galvanization or epoxy coatings alone. While finishes provide a surface barrier against moisture and chemicals, underlying material properties determine long-term durability and structural integrity under extreme conditions. Selecting high-grade materials tailored for specific exposure scenarios ensures superior performance and reduces maintenance costs compared to relying solely on protective finishes.
Cost Implications of Material Selection and Finish
Anchor bolt material selection, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel, significantly impacts overall project costs due to differing raw material expenses and mechanical properties. Choosing a finish--galvanized, epoxy-coated, or plain--affects corrosion resistance and long-term maintenance costs, with galvanized finishes often providing a cost-effective balance between durability and price. Evaluating the cost implications of both material and finish is essential for optimizing anchor bolt performance without exceeding budget constraints.
Application Suitability: Matching Material and Finish to Projects
Anchor bolt material selection, such as stainless steel or carbon steel, directly impacts corrosion resistance and strength, crucial for structural integrity in diverse environments. The finish, including hot-dip galvanizing or zinc plating, enhances durability by protecting against rust and weathering, ensuring long-term performance. Matching material and finish to specific project requirements optimizes anchor bolts for applications in construction, marine, or industrial settings, aligning with safety standards and environmental conditions.
Best Practices for Selecting Anchor Bolt Material and Finish
Selecting the optimal anchor bolt material involves prioritizing high-strength steel or stainless steel for superior corrosion resistance and load-bearing capacity. Anchor bolt finishes, such as hot-dip galvanizing or epoxy coating, provide critical protection against environmental deterioration and extend service life. Best practices dictate matching the material grade with an appropriate finish aligned to specific project conditions like exposure to moisture, chemicals, or extreme weather for maximum durability and safety.
Anchor bolt material vs Anchor bolt finish Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com