Anchor bolt design emphasizes precise material selection, load capacity, and corrosion resistance to ensure structural integrity and longevity. Anchor bolt installation requires accurate positioning, proper embedment depth, and secure fastening to achieve the design's intended performance. Coordinating both design and installation phases is critical for optimal safety and stability in construction projects.
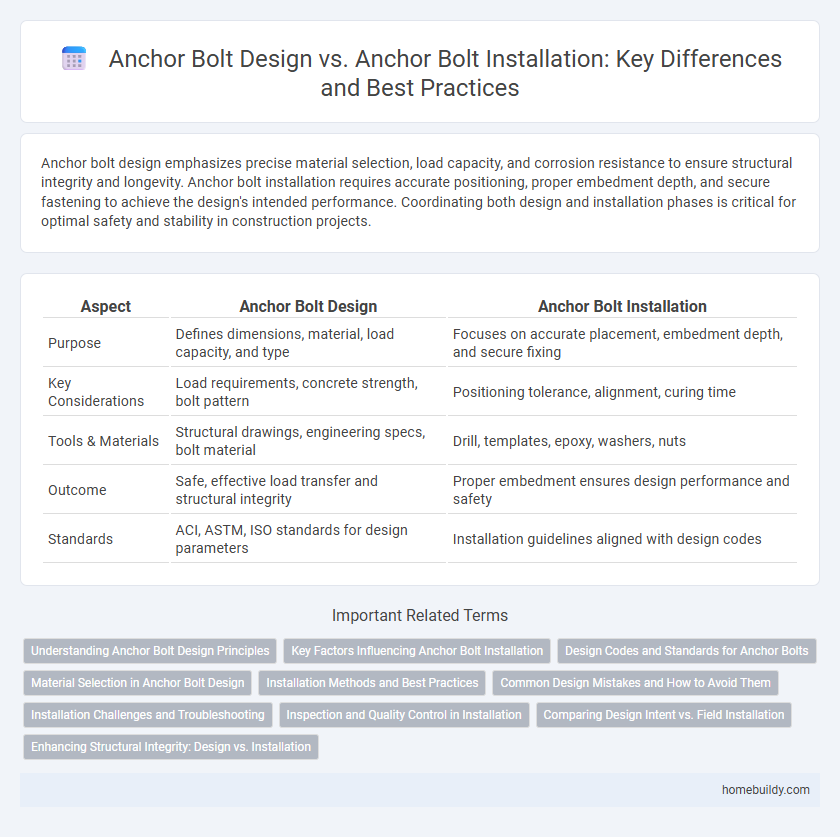
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Anchor Bolt Design | Anchor Bolt Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Defines dimensions, material, load capacity, and type | Focuses on accurate placement, embedment depth, and secure fixing |
| Key Considerations | Load requirements, concrete strength, bolt pattern | Positioning tolerance, alignment, curing time |
| Tools & Materials | Structural drawings, engineering specs, bolt material | Drill, templates, epoxy, washers, nuts |
| Outcome | Safe, effective load transfer and structural integrity | Proper embedment ensures design performance and safety |
| Standards | ACI, ASTM, ISO standards for design parameters | Installation guidelines aligned with design codes |
Understanding Anchor Bolt Design Principles
Anchor bolt design principles focus on ensuring structural integrity by calculating load requirements, embedment depth, and material strength to resist tensile, shear, and bending forces. Proper design considers factors such as concrete strength, bolt diameter, and corrosion protection to optimize anchor bolt performance under various load conditions. Effective design sets the foundation for successful anchor bolt installation, where precise placement and alignment are critical to achieving the intended structural support.
Key Factors Influencing Anchor Bolt Installation
Key factors influencing anchor bolt installation include precise embedment depth, the quality of the base material, and the alignment with structural load requirements. Proper setting ensures optimal load transfer and stability, preventing misalignment that can compromise structural integrity. Temperature, curing time of grout or concrete, and environmental conditions also critically affect installation quality and long-term performance.
Design Codes and Standards for Anchor Bolts
Anchor bolt design adheres to stringent design codes and standards such as ACI 318, ASME B18.2.1, and EN 1992, ensuring structural integrity and load-bearing capacity. Installation standards focus on precise positioning, embedment depth, and alignment according to guidelines like ACI 355.2 and ASTM F1554 to maintain the anchor bolt's performance under applied loads. Compliance with both design and installation codes minimizes failure risks and guarantees safety in construction projects.
Material Selection in Anchor Bolt Design
Material selection in anchor bolt design critically influences durability, load-bearing capacity, and resistance to environmental factors such as corrosion and chemical exposure. High-strength steel alloys and stainless steel variants are commonly chosen for their superior tensile properties and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-term structural integrity. Proper material selection tailored to specific project conditions enhances safety margins and reduces maintenance costs during anchor bolt installation and service life.
Installation Methods and Best Practices
Anchor bolt installation requires precise alignment and embedded depth to ensure structural integrity and load transfer efficiency. Common installation methods include cast-in-place, post-installed using adhesive anchors, and mechanical expansion anchors, each suited for different substrate conditions and load requirements. Best practices emphasize thorough surface preparation, correct torque application, and verification of embedment depth to prevent premature failure and maintain compliance with structural codes.
Common Design Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common anchor bolt design mistakes include incorrect embedment depth, inappropriate bolt diameter, and failure to account for load variations, which compromise structural integrity. Avoid these errors by adhering to engineering standards such as ACI 318 and considering factors like concrete strength, edge distance, and load types during the design phase. Proper coordination between design specifications and installation practices ensures bolts are accurately positioned and fully embedded, preventing costly rework and potential safety hazards.
Installation Challenges and Troubleshooting
Anchor bolt installation challenges often stem from misalignment, incorrect embedment depth, and inadequate grout or concrete curing, which can compromise structural integrity. Troubleshooting these issues requires precise measurement verification, adjustment of bolt positioning before concrete sets, and ensuring proper anchoring materials and techniques are used to achieve desired load capacity. Effective installation demands collaboration between design specifications and on-site adaptability to prevent costly rework and maintain safety standards.
Inspection and Quality Control in Installation
Anchor bolt inspection and quality control during installation rigorously ensure alignment, embedment depth, and torque specifications meet design requirements, preventing structural failures. Detailed verification processes include visual checks, non-destructive testing, and precise measurements against design blueprints to confirm correct placement and material integrity. Effective quality control minimizes deviations and defects, guaranteeing anchor bolts perform their load-bearing function reliably.
Comparing Design Intent vs. Field Installation
Anchor bolt design emphasizes precise specifications for load capacity, embedment depth, and material strength to ensure structural integrity and safety. Field installation often encounters challenges such as positioning errors, inconsistent embedment depths, and deviations from design tolerances due to site conditions and human error. Comparing design intent with actual installation highlights discrepancies that can compromise performance, underscoring the need for stringent quality control measures and real-time adjustments during construction.
Enhancing Structural Integrity: Design vs. Installation
Anchor bolt design directly influences the load-bearing capacity and resistance to shear and tension forces, ensuring optimal structural integrity through precise material selection, length, diameter, and embedment depth. Correct anchor bolt installation guarantees alignment, proper embedment, and secure anchorage, preventing failure modes such as pull-out or concrete cracking under dynamic or static loads. Balancing rigorous design standards with meticulous installation practices maximizes structural safety and longevity in construction projects.
Anchor bolt design vs Anchor bolt installation Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com