Anchor bolts provide a secure attachment by being embedded into concrete or masonry, offering superior load-bearing capacity for structural applications. Expansion bolts rely on mechanical expansion within a drilled hole, making them ideal for lighter loads and easy installation in solid materials. Choosing between anchor bolts and expansion bolts depends on the required strength, application type, and the substrate material.
Table of Comparison
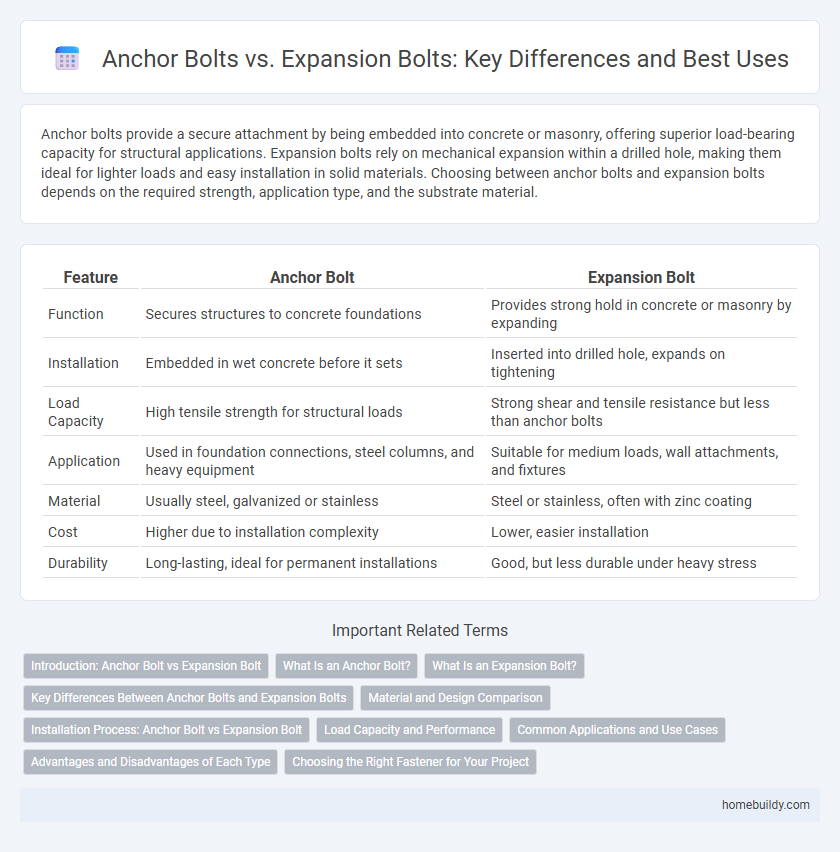
| Feature | Anchor Bolt | Expansion Bolt |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Secures structures to concrete foundations | Provides strong hold in concrete or masonry by expanding |
| Installation | Embedded in wet concrete before it sets | Inserted into drilled hole, expands on tightening |
| Load Capacity | High tensile strength for structural loads | Strong shear and tensile resistance but less than anchor bolts |
| Application | Used in foundation connections, steel columns, and heavy equipment | Suitable for medium loads, wall attachments, and fixtures |
| Material | Usually steel, galvanized or stainless | Steel or stainless, often with zinc coating |
| Cost | Higher due to installation complexity | Lower, easier installation |
| Durability | Long-lasting, ideal for permanent installations | Good, but less durable under heavy stress |
Introduction: Anchor Bolt vs Expansion Bolt
Anchor bolts provide superior load-bearing capacity by embedding directly into concrete or masonry, ensuring strong structural support for heavy-duty applications. Expansion bolts rely on mechanical expansion within pre-drilled holes, offering effective anchoring in solid materials but generally less holding power under dynamic loads. Choosing between anchor bolts and expansion bolts depends on factors like load requirements, base material, and installation environment.
What Is an Anchor Bolt?
An anchor bolt is a fastener used to attach structural elements to concrete, providing stability and load transfer in construction projects. Unlike expansion bolts, which rely on mechanical expansion to grip the material, anchor bolts are embedded into the concrete before it sets, ensuring a secure and permanent hold. Common types include J-bolts, L-bolts, and straight anchor bolts, each designed to resist tensile and shear forces in various applications.
What Is an Expansion Bolt?
An expansion bolt is a fastener designed to anchor objects securely into concrete, masonry, or brick surfaces by expanding a sleeve within the drilled hole upon tightening. Unlike anchor bolts, which are typically embedded into concrete before it sets, expansion bolts create a strong grip by exerting outward pressure against the hole walls after installation. This makes expansion bolts ideal for retrofit applications requiring heavy-duty load support without the need for wet concrete embedment.
Key Differences Between Anchor Bolts and Expansion Bolts
Anchor bolts provide a permanent fastening solution by embedding into concrete or masonry, ensuring high load-bearing capacity and structural stability, while expansion bolts rely on mechanical expansion within drilled holes for a secure fit, suitable for medium load applications. Anchor bolts are ideal for heavy-duty constructions needing long-term durability; expansion bolts offer flexibility for adjustable installations and are easier to remove or replace. The choice depends on the required load strength, installation environment, and whether the fastening is temporary or permanent.
Material and Design Comparison
Anchor bolts typically feature high-strength steel with corrosion-resistant coatings such as galvanization or stainless steel, designed for embedding into concrete to provide strong, permanent fixtures. Expansion bolts are usually made from alloy steel or stainless steel with a sleeve that expands upon tightening, suitable for anchoring in hollow or solid materials. Material composition affects durability and resistance to environmental factors, while design differences determine load distribution and application suitability.
Installation Process: Anchor Bolt vs Expansion Bolt
Anchor bolts require pre-drilling a hole before insertion and are often secured with epoxy or grout to enhance load-bearing capacity. Expansion bolts install by drilling a hole, inserting the bolt, and tightening, which causes the sleeve to expand and grip the surrounding material securely. The anchor bolt installation offers more flexibility in positioning, while expansion bolts provide a faster, self-tightening anchoring solution ideal for solid substrates.
Load Capacity and Performance
Anchor bolts offer superior load capacity in structural applications due to their embedded design that distributes stress deeper into concrete, ensuring enhanced stability under dynamic and heavy loads. Expansion bolts provide reliable performance for lighter to medium loads by expanding within drilled holes to grip the substrate, though their load capacity is generally lower compared to anchor bolts. Performance-wise, anchor bolts excel in high-stress environments with better resistance to shear and tension forces, while expansion bolts are preferred for quick installations where extreme load bearing is not critical.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Anchor bolts are primarily used for securing structural elements to concrete foundations in construction, offering high load-bearing capacity and resistance to shear forces, making them ideal for heavy machinery and steel columns. Expansion bolts are commonly applied in lighter-duty tasks such as fastening fixtures, shelves, and handrails to masonry or drywall, where ease of installation and moderate load support are required. The key difference lies in the anchor bolt's permanent embedment in concrete versus the expansion bolt's reliance on mechanical expansion in pre-drilled holes, influencing their suitability based on the substrate and load demands.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Type
Anchor bolts provide superior load-bearing capacity and are ideal for securing heavy structural elements to concrete due to their embedded design, which ensures strong resistance to shear and tension forces. Expansion bolts offer quick installation and versatility for lighter loads and various base materials but may experience reduced holding power in cracked or weak substrates due to their reliance on expansion forces. While anchor bolts excel in durability and long-term stability, expansion bolts are more convenient for temporary or adjustable fixtures, though they introduce a higher risk of loosening under dynamic loads.
Choosing the Right Fastener for Your Project
Anchor bolts provide superior load-bearing strength by anchoring directly into concrete through embedded threads, making them ideal for structural applications requiring high stability. Expansion bolts rely on mechanical expansion within drilled holes, offering ease of installation but less holding power under dynamic loads. Selecting the right fastener depends on factors like load requirements, material compatibility, and environmental conditions to ensure safety and durability.
Anchor bolt vs Expansion bolt Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com