A wall plate, also known as a top plate, is a horizontal structural element placed at the top of a wall framing to support roof loads or the structure above. A sole plate, or bottom plate, is positioned at the base of the wall framing and anchors the wall to the floor or foundation. Both plates are crucial in framing, providing stability and transferring loads between different parts of the building.
Table of Comparison
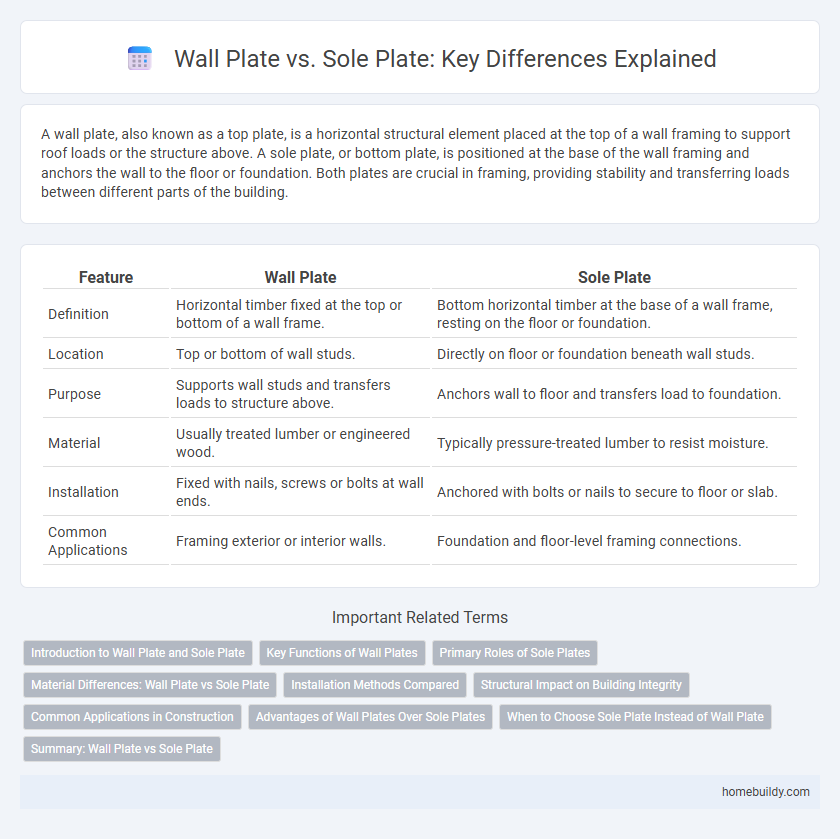
| Feature | Wall Plate | Sole Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Horizontal timber fixed at the top or bottom of a wall frame. | Bottom horizontal timber at the base of a wall frame, resting on the floor or foundation. |
| Location | Top or bottom of wall studs. | Directly on floor or foundation beneath wall studs. |
| Purpose | Supports wall studs and transfers loads to structure above. | Anchors wall to floor and transfers load to foundation. |
| Material | Usually treated lumber or engineered wood. | Typically pressure-treated lumber to resist moisture. |
| Installation | Fixed with nails, screws or bolts at wall ends. | Anchored with bolts or nails to secure to floor or slab. |
| Common Applications | Framing exterior or interior walls. | Foundation and floor-level framing connections. |
Introduction to Wall Plate and Sole Plate
Wall plates and sole plates are essential components in framing construction, providing structural support in walls and floors respectively. A wall plate typically runs horizontally along the top or bottom of a wall, anchoring studs and distributing loads evenly, while a sole plate is positioned at the base to secure the wall to the floor foundation. Understanding the distinct roles of wall plates and sole plates is crucial for ensuring stability and alignment in building frameworks.
Key Functions of Wall Plates
Wall plates serve as structural elements that distribute load from the framing to the wall studs, providing stability and alignment in construction. They also act as a mounting surface for wall coverings and fixtures, enhancing both functionality and finish quality. Unlike sole plates, which rest on the foundation or floor, wall plates are positioned at various heights to support wall segments and openings.
Primary Roles of Sole Plates
Sole plates serve as the foundational horizontal framing members anchored to the floor, providing stability and alignment for wall studs above. Unlike wall plates, which cap the top or bottom of a wall frame, sole plates primarily distribute loads evenly to the subfloor and prevent uplift or shifting. Their crucial role ensures structural integrity and proper load transfer within framed walls.
Material Differences: Wall Plate vs Sole Plate
Wall plates are typically made from treated lumber or metal to resist moisture and provide structural support for vertical framing, while sole plates are usually constructed from untreated wood or pressure-treated lumber to withstand ground contact and prevent rot. The material choice for wall plates emphasizes durability and stability for walls, whereas sole plates prioritize resistance to soil-borne decay and termite damage. Understanding these material distinctions is crucial for ensuring the longevity and integrity of framing components in residential and commercial construction.
Installation Methods Compared
Wall plates are installed vertically on walls to support electrical outlets and switches, typically secured using screws through pre-drilled holes directly into drywall or masonry. Sole plates are positioned horizontally at the base of framed walls, fastened to the foundation using anchor bolts or nails that ensure structural stability. Installation of wall plates focuses on precise alignment for electrical safety, while sole plate installation emphasizes securing the frame to the floor.
Structural Impact on Building Integrity
Wall plates distribute vertical loads from walls to the foundation, ensuring even weight transfer and preventing structural imbalance. Sole plates serve as a base for wall framing and anchor the structure to the floor, providing stability and resistance against lateral forces. The combined function of wall and sole plates is critical for maintaining building integrity by supporting load paths and reducing stress on framing components.
Common Applications in Construction
Wall plates are horizontal framing members that provide a sturdy base for attaching walls and support vertical studs in residential and commercial construction. Sole plates, located at the bottom of a wall frame, anchor the wall to the subfloor and distribute structural loads evenly. Common applications of wall plates include securing roof trusses and ceiling joists, while sole plates are essential for stabilizing wall frames and ensuring proper alignment on foundation slabs.
Advantages of Wall Plates Over Sole Plates
Wall plates provide superior structural support for framing walls by evenly distributing loads along vertical studs, enhancing stability and durability in construction. Their installation facilitates easy attachment of drywall and electrical components, improving workflow efficiency and reducing labor time compared to sole plates. Wall plates also offer better moisture resistance when elevated above floors, minimizing the risk of rot and extending the lifespan of the wall assembly.
When to Choose Sole Plate Instead of Wall Plate
Choose a sole plate instead of a wall plate when framing the bottom support of a wall, as the sole plate anchors the wall structure to the floor or foundation. Sole plates are essential for providing stability and transferring loads directly to the ground surface, especially in wood-frame construction. Wall plates, on the other hand, are typically used at the top of walls to support roof trusses or upper framing elements.
Summary: Wall Plate vs Sole Plate
Wall plates and sole plates are essential components in framing, with wall plates typically installed at the top and sole plates at the bottom of a wall structure. Wall plates provide support for roof loads and help distribute weight evenly, while sole plates anchor the wall to the floor, ensuring stability and alignment. Both plates are critical for structural integrity, but their distinct positions and functions differentiate their roles in construction projects.
Wall plate vs Sole plate Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com