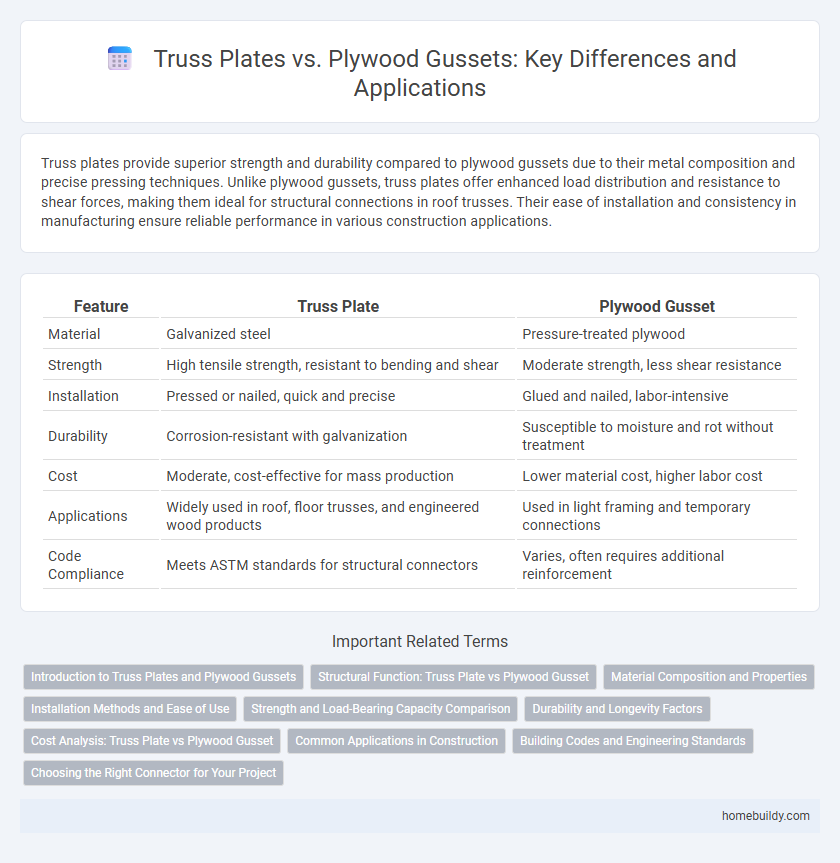
Truss plates provide superior strength and durability compared to plywood gussets due to their metal composition and precise pressing techniques. Unlike plywood gussets, truss plates offer enhanced load distribution and resistance to shear forces, making them ideal for structural connections in roof trusses. Their ease of installation and consistency in manufacturing ensure reliable performance in various construction applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Truss Plate | Plywood Gusset |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Galvanized steel | Pressure-treated plywood |
| Strength | High tensile strength, resistant to bending and shear | Moderate strength, less shear resistance |
| Installation | Pressed or nailed, quick and precise | Glued and nailed, labor-intensive |
| Durability | Corrosion-resistant with galvanization | Susceptible to moisture and rot without treatment |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective for mass production | Lower material cost, higher labor cost |
| Applications | Widely used in roof, floor trusses, and engineered wood products | Used in light framing and temporary connections |
| Code Compliance | Meets ASTM standards for structural connectors | Varies, often requires additional reinforcement |
Introduction to Truss Plates and Plywood Gussets
Truss plates are metal connectors used to join wood members in structural frameworks, offering high strength and consistency through stamped steel designs with teeth for secure fastening. Plywood gussets, made from layered wood sheets, provide a traditional alternative by reinforcing joints through glued or nailed connections, often preferred for cost efficiency and ease of customization. Both components play critical roles in ensuring structural integrity, with truss plates excelling in load distribution and plywood gussets favored for adaptability in various construction contexts.
Structural Function: Truss Plate vs Plywood Gusset
Truss plates provide superior structural integrity by offering high-strength, metal connectivity that evenly distributes load across timber joints, ensuring minimal deformation and enhanced durability. Plywood gussets, while easier to fabricate, rely on adhesive strength and fasteners, which may weaken under sustained loads or moisture exposure, reducing overall load-bearing capacity. The metal composition of truss plates makes them ideal for critical load transfer in engineered wood trusses, whereas plywood gussets serve better in non-critical or temporary structures.
Material Composition and Properties
Truss plates are typically made from galvanized steel, providing high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and rigid connections crucial for structural stability. Plywood gussets consist of engineered wood layers bonded with adhesives, offering flexibility, lightweight properties, and ease of customization but lower shear strength compared to steel plates. The choice between truss plates and plywood gussets depends on load requirements, environmental conditions, and the need for durability versus adaptability in construction applications.
Installation Methods and Ease of Use
Truss plates offer quick installation through simple nailing or pressing onto timber joints, streamlining the assembly process on-site. Plywood gussets require precise cutting, fitting, and fastening with nails or screws, increasing labor time and skill requirements. The pre-engineered design of truss plates enhances ease of use, reducing construction errors compared to the more customizable but complex plywood gussets.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity Comparison
Truss plates offer superior strength and load-bearing capacity compared to plywood gussets due to their steel composition and precise manufacturing standards. They provide consistent performance under high stress and resist deformation, ensuring long-term durability in structural applications. Plywood gussets, while easier to fabricate, generally exhibit lower tensile strength and are more susceptible to moisture-related degradation, impacting their load-bearing reliability.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Truss plates offer superior durability compared to plywood gussets due to their corrosion-resistant galvanized steel composition, which withstands environmental stressors and maintains structural integrity over decades. Unlike plywood, which can degrade from moisture exposure, swelling, and fungal attacks, truss plates provide consistent performance in both indoor and outdoor applications. The longevity of truss plates is further enhanced by their rigid metal teeth, ensuring secure fastenings that resist loosening and wear over time.
Cost Analysis: Truss Plate vs Plywood Gusset
Truss plates generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to plywood gussets due to lower material and labor expenses in mass production settings. Plywood gussets require additional cutting, fitting, and fastening time, increasing overall installation costs. When evaluating long-term durability and maintenance, truss plates may also reduce expenses by providing greater structural integrity with less risk of damage.
Common Applications in Construction
Truss plates are commonly used in prefabricated wood truss systems to provide strong, reliable metal connections that enhance load distribution and structural integrity. Plywood gussets are often applied in custom or onsite wood framing for their ease of cutting and fastening in irregular or smaller-scale joints. Both materials are essential in construction, with truss plates favored for high-volume, industrial production and plywood gussets preferred for flexible, field-adjusted applications.
Building Codes and Engineering Standards
Truss plates, typically made of galvanized steel, comply with building codes such as the International Building Code (IBC) and standards like ANSI/TPI 1, ensuring engineered precision and structural reliability in roof and floor truss connections. Plywood gussets, while sometimes used in light framing, often lack specific prescriptive guidelines under major building codes and may require engineer approval to meet strength and durability requirements. Compliance with ASTM D5456 for plywood gussets and relevant industry standards is critical but generally less standardized compared to the widely accepted metal truss plate systems in structural engineering.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your Project
Truss plates, made from galvanized steel, offer superior strength and corrosion resistance compared to plywood gussets, making them ideal for high-load applications and long-term structural integrity. Plywood gussets, while cost-effective and easier to work with on-site, may compromise durability and require additional sealing against moisture. Selecting the right connector depends on project requirements including load capacity, environmental exposure, and installation speed, with truss plates preferred for demanding designs and plywood gussets suitable for less intensive uses.
Truss plate vs Plywood gusset Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com