Truss plates offer a lightweight, cost-effective solution specifically designed for connecting wooden truss members, providing strong, reliable joints through their serrated teeth that embed into the wood. Steel plate connectors, while stronger and more durable, are typically heavier and used for applications requiring higher load capacities or metal framing connections. Choosing between truss plates and steel plate connectors depends on factors such as material compatibility, load requirements, and construction design preferences.
Table of Comparison
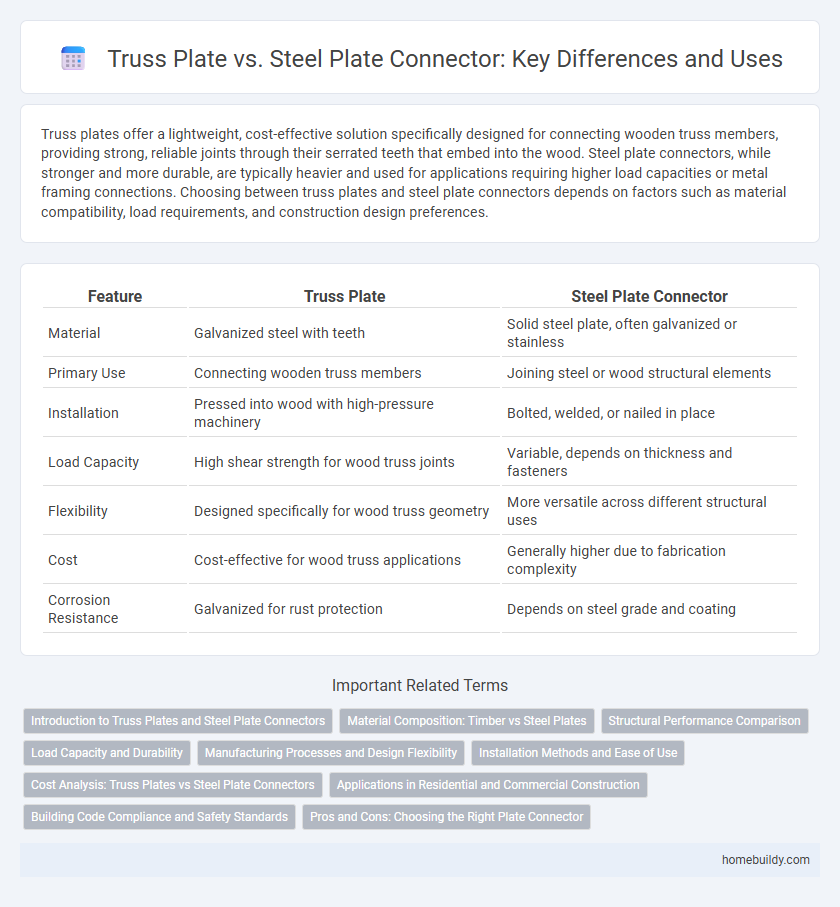
| Feature | Truss Plate | Steel Plate Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Galvanized steel with teeth | Solid steel plate, often galvanized or stainless |
| Primary Use | Connecting wooden truss members | Joining steel or wood structural elements |
| Installation | Pressed into wood with high-pressure machinery | Bolted, welded, or nailed in place |
| Load Capacity | High shear strength for wood truss joints | Variable, depends on thickness and fasteners |
| Flexibility | Designed specifically for wood truss geometry | More versatile across different structural uses |
| Cost | Cost-effective for wood truss applications | Generally higher due to fabrication complexity |
| Corrosion Resistance | Galvanized for rust protection | Depends on steel grade and coating |
Introduction to Truss Plates and Steel Plate Connectors
Truss plates are thin, galvanized steel components with multiple teeth designed to be pressed into timber joints, ensuring high load transfer and structural integrity. Steel plate connectors, typically thicker and heavier, serve as robust fastening elements for joining structural members but may require bolts or welds for installation. Understanding the material properties and application methods distinguishes truss plates as efficient, economical solutions for prefabricated trusses versus the more versatile but labor-intensive steel plate connectors used in heavy-duty construction.
Material Composition: Timber vs Steel Plates
Truss plates are typically made from galvanized steel, designed to provide strong, corrosion-resistant connections in timber frameworks, whereas steel plate connectors are solid steel components used in structural joints for heavy-duty load-bearing applications. The timber in truss plate connections relies on the steel plate's punched or pressed tabs to transfer forces, maximizing the composite strength of wood and steel together. Steel plate connectors, in contrast, are purely metal systems that offer higher tensile and shear strength without relying on timber, making them suitable for applications requiring greater rigidity and durability.
Structural Performance Comparison
Truss plates provide superior load distribution due to their multi-point fastening design, enhancing joint rigidity and reducing localized stress compared to steel plate connectors. Steel plate connectors often rely on fewer fasteners, which can create stress concentrations and potential weak points under dynamic loads. The optimized geometry of truss plates allows for improved structural performance, especially in timber framing applications where weight and flexibility are critical.
Load Capacity and Durability
Truss plates offer superior load capacity due to their multiple embedded teeth that distribute force evenly across timber joints, enhancing structural integrity. Steel plate connectors, while durable and resistant to corrosion, often focus on localized load transfer, which can limit overall load distribution in truss systems. The durability of truss plates is reinforced by galvanized steel construction, providing long-lasting corrosion resistance essential for maintaining joint strength in various environmental conditions.
Manufacturing Processes and Design Flexibility
Truss plates are typically produced using stamping or pressing techniques that allow for high-volume, cost-effective manufacturing with precise hole patterns for fastener integration. Steel plate connectors, often fabricated through cutting, welding, or machining, provide greater design flexibility to accommodate custom shapes and load requirements. The stamping process of truss plates limits intricate designs but ensures uniformity, while steel plate connectors can be tailored for complex structural connections.
Installation Methods and Ease of Use
Truss plates feature a simple installation process involving hammering or pressing the steel plate onto wooden members, requiring minimal specialized tools or skills. Steel plate connectors demand precise welding or bolting, often necessitating skilled labor and additional equipment, which can extend installation time. The ease of use with truss plates supports faster assembly in prefabricated wood trusses compared to the more complex and labor-intensive steel plate connectors.
Cost Analysis: Truss Plates vs Steel Plate Connectors
Truss plates offer a cost-effective solution due to their lower material and manufacturing expenses compared to steel plate connectors, which typically require more complex fabrication and installation processes. The reduced labor costs and faster assembly time associated with truss plates further enhance their economic advantage in large-scale construction projects. However, steel plate connectors provide superior strength and versatility, potentially justifying higher upfront costs in structural applications demanding greater load capacity.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Construction
Truss plates are widely used in residential construction for efficient wood frame connections, offering quick installation and strong load transfer in roof and floor systems. Steel plate connectors, commonly utilized in commercial construction, provide enhanced structural support for heavy-duty applications such as steel framing and large-span beams. Both connectors optimize assembly processes, but truss plates excel in lightweight wood structures while steel plates are preferred for durability in industrial and commercial buildings.
Building Code Compliance and Safety Standards
Truss plates are specifically engineered to meet strict building code compliance and safety standards, ensuring reliable load transfer and structural integrity in wood frame construction. Unlike standard steel plate connectors, truss plates are tested and certified for use in critical joint applications according to ANSI and ASTM regulations. Their corrosion-resistant coatings and precise stamping provide enhanced durability and traceability, crucial for meeting international building regulations and safety certifications.
Pros and Cons: Choosing the Right Plate Connector
Truss plates offer superior load distribution and cost-effectiveness for wood frame connections, making them ideal for lightweight structures requiring quick assembly. Steel plate connectors provide greater strength and durability, suitable for heavy-duty applications and complex joint configurations but often at a higher cost and installation complexity. Selecting the right plate depends on project requirements, balancing factors such as structural demands, budget, and ease of installation.
Truss plate vs Steel plate connector Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com