A sill plate is the bottom horizontal member of a wall frame that sits directly on the foundation, providing a sturdy base for the wall studs. In contrast, a stud plate refers to the horizontal framing members located at the top and sometimes bottom of a wall section, which connect and support the vertical studs. Understanding the distinction between sill plates and stud plates is essential for proper framing and ensuring structural stability in construction projects.
Table of Comparison
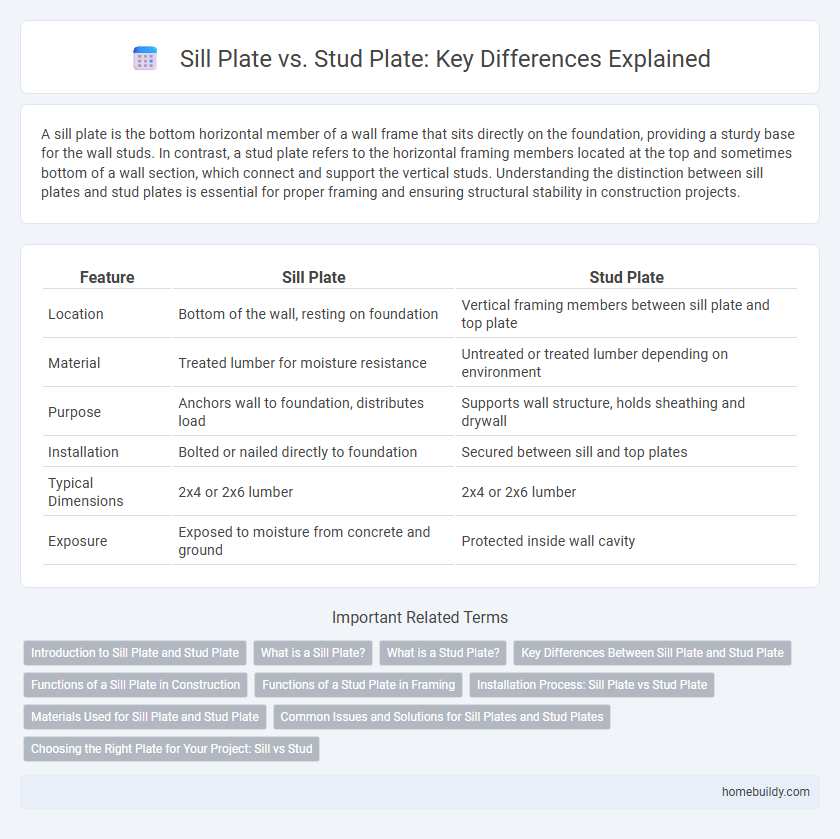
| Feature | Sill Plate | Stud Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Bottom of the wall, resting on foundation | Vertical framing members between sill plate and top plate |
| Material | Treated lumber for moisture resistance | Untreated or treated lumber depending on environment |
| Purpose | Anchors wall to foundation, distributes load | Supports wall structure, holds sheathing and drywall |
| Installation | Bolted or nailed directly to foundation | Secured between sill and top plates |
| Typical Dimensions | 2x4 or 2x6 lumber | 2x4 or 2x6 lumber |
| Exposure | Exposed to moisture from concrete and ground | Protected inside wall cavity |
Introduction to Sill Plate and Stud Plate
Sill plates are horizontal wooden boards anchored to the foundation, serving as the base for wall framing, while stud plates refer to horizontal members at the top or bottom of wall studs that connect vertical framing components. Sill plates are typically treated lumber to resist moisture and decay due to their direct contact with the foundation, whereas stud plates form the structural framework for walls above the sill plate. Understanding the distinct roles of sill plates and stud plates is essential in framing for ensuring structural integrity and moisture protection in building construction.
What is a Sill Plate?
A sill plate is a horizontal wooden board anchored directly to the foundation of a building, serving as the base for the wall framing. Unlike a stud plate, which is positioned vertically or horizontally within the wall to connect studs, the sill plate ensures a stable and level surface for construction while providing moisture and pest resistance through treated lumber. Proper installation of sill plates is crucial for structural integrity and efficient load transfer from the walls to the foundation.
What is a Stud Plate?
A stud plate, also known as a bottom plate or sole plate, is the horizontal timber that lies flat against the foundation and serves as the base for vertical wall studs in framing construction. Unlike the sill plate, which is anchored directly to the foundation to provide a moisture barrier and structural connection, the stud plate simply supports the wall studs and transfers loads to the sill plate. This distinction makes the stud plate crucial for framing stability, aligning wall studs, and distributing structural loads evenly across the foundation.
Key Differences Between Sill Plate and Stud Plate
The sill plate is a horizontal timber anchored to the foundation, providing a base for the wall framing, whereas the stud plate consists of two horizontal members at the top and bottom of wall studs, serving as connectors for vertical studs. Sill plates are typically treated lumber to resist moisture and decay due to direct contact with concrete, while stud plates are usually untreated as they are located within the wall cavity. Key differences include their placement, function in load distribution, and material treatment to accommodate exposure conditions.
Functions of a Sill Plate in Construction
A sill plate serves as the critical interface between the foundation and the framing structure, anchoring the building securely to the concrete or masonry base. It distributes the load from the walls to the foundation while providing a flat, level surface for wall construction. Unlike stud plates, which connect vertical studs within the framing, sill plates ensure overall structural stability and moisture barrier at the building's base.
Functions of a Stud Plate in Framing
A stud plate in framing serves as a horizontal nailing surface that connects and aligns vertical studs, ensuring structural stability and load transfer from walls to the foundation. Unlike sill plates, which anchor the wall frame to the foundation, stud plates maintain the vertical elements' spacing and support wall sheathing installation. By providing rigidity and alignment, stud plates contribute to the overall integrity and durability of the framed structure.
Installation Process: Sill Plate vs Stud Plate
The installation process of a sill plate involves anchoring the wood directly to the foundation using anchor bolts or straps to create a stable base for the wall framing. In contrast, stud plates, also known as top or bottom plates, are installed by nailing or screwing them horizontally to the studs, serving as connectors for vertical framing members during wall assembly. Proper alignment and secure fastening in both sill and stud plate installations are critical to ensuring structural stability and load distribution in building construction.
Materials Used for Sill Plate and Stud Plate
Sill plates are typically constructed from pressure-treated lumber to resist moisture and prevent rot where the wood contacts the concrete foundation, ensuring durability and structural stability. Stud plates, also known as bottom plates, commonly use untreated lumber since they are positioned within the wall framing and are less exposed to environmental factors. The choice of material for sill plates emphasizes moisture resistance, while stud plates prioritize ease of installation and cost-effectiveness in interior framing.
Common Issues and Solutions for Sill Plates and Stud Plates
Sill plates often face issues like moisture damage, wood rot, and improper anchoring, which can be mitigated by using pressure-treated lumber and ensuring a proper moisture barrier installation. Stud plates, also known as top plates or bottom plates, commonly encounter problems such as misalignment and inadequate fastening, solvable by precise measurement and using appropriate fasteners like nails or bolts. Regular inspection and maintenance of both sill and stud plates are crucial to prevent structural weakening and ensure long-term durability.
Choosing the Right Plate for Your Project: Sill vs Stud
Selecting between a sill plate and a stud plate depends on the specific role each plays in framing construction. The sill plate anchors the structure to the foundation, typically made of treated lumber to resist moisture and decay, while the stud plate serves as the horizontal base or top piece where studs are attached, providing vertical support for walls. Understanding the distinct functions and material requirements ensures the right plate enhances stability and longevity in your building project.
Sill plate vs Stud plate Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com