A rafter tie is a horizontal timber connecting opposite rafters to prevent roof spread, offering strong structural stability by resisting outward thrust. A rafter bracket, however, is a metal support fixed at the joint between a rafter and a wall or beam, providing localized reinforcement but less overall tension resistance compared to a tie. Choosing between a rafter tie and a rafter bracket depends on the specific load requirements and framing design of the roof structure.
Table of Comparison
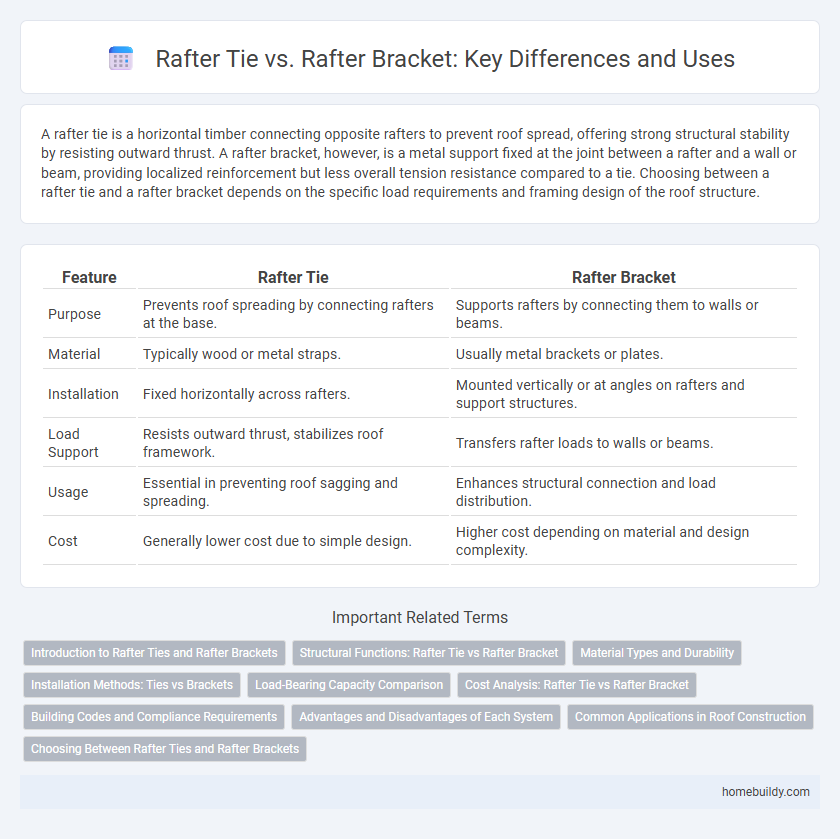
| Feature | Rafter Tie | Rafter Bracket |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents roof spreading by connecting rafters at the base. | Supports rafters by connecting them to walls or beams. |
| Material | Typically wood or metal straps. | Usually metal brackets or plates. |
| Installation | Fixed horizontally across rafters. | Mounted vertically or at angles on rafters and support structures. |
| Load Support | Resists outward thrust, stabilizes roof framework. | Transfers rafter loads to walls or beams. |
| Usage | Essential in preventing roof sagging and spreading. | Enhances structural connection and load distribution. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to simple design. | Higher cost depending on material and design complexity. |
Introduction to Rafter Ties and Rafter Brackets
Rafter ties are horizontal beams that connect opposing rafters to prevent roof spread, providing structural stability in traditional timber framing. Rafter brackets, on the other hand, are metal connectors designed to secure rafters to wall plates or beams, offering enhanced load transfer and ease of installation. Both elements contribute to roof integrity, but rafter ties primarily counteract lateral forces, while rafter brackets focus on fastening and support.
Structural Functions: Rafter Tie vs Rafter Bracket
Rafter ties resist outward thrust forces by connecting opposite rafters, preventing roof spread and ensuring overall structural stability. Rafter brackets provide localized support at the joint between rafters and the wall plate, enhancing load transfer and reducing joint movement. Together, these components play complementary roles in maintaining roof integrity under various loads.
Material Types and Durability
Rafter ties are commonly made from galvanized steel or heavy-duty timber, providing essential tensile strength to resist roof spread and offer long-lasting durability in various environmental conditions. Rafter brackets, often constructed from stainless steel or powder-coated metal, deliver robust support with enhanced corrosion resistance but may require precise installation to maintain structural integrity. Material choice significantly influences durability, with galvanized steel rafter ties excelling in rust prevention for outdoor exposure, while stainless steel brackets offer superior longevity in high-moisture environments.
Installation Methods: Ties vs Brackets
Rafter ties are installed by nailing across opposing rafters near the base, creating a tension connection that prevents outward wall spread and enhances roof stability. Rafter brackets, typically metal, attach via screws or bolts at rafter joints, offering rigid support and load transfer between rafters and wall plates. While ties rely on tensile strength through direct nailing, brackets provide a compressive and shear load path, influencing choice based on structural requirements and ease of installation.
Load-Bearing Capacity Comparison
Rafter ties primarily function to prevent the outward spread of rafters by resisting lateral forces, offering moderate load-bearing capacity in roof framing. In contrast, rafter brackets provide a more robust connection point, distributing loads more effectively across structural members and enhancing overall stability. The load-bearing capacity of rafter brackets typically surpasses that of rafter ties, making them preferable for heavy roof loads or where additional structural support is required.
Cost Analysis: Rafter Tie vs Rafter Bracket
Rafter ties generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to rafter brackets due to lower material and installation expenses. Rafter brackets, while providing increased structural support and ease of installation, typically incur higher upfront costs, including specialized hardware and labor. When balancing budget constraints with long-term durability, rafter ties often present a more economical option for residential roof framing.
Building Codes and Compliance Requirements
Rafter ties are critical in meeting building codes by preventing outward wall thrust and ensuring structural stability in roof framing, often specified in residential construction regulations such as the International Residential Code (IRC). Rafter brackets provide localized support at the rafter-to-wall connection but may not fully address the tension forces that rafter ties counteract, making them insufficient alone for code compliance in many jurisdictions. Building inspectors typically require rafter ties or approved equivalents that satisfy specific load and span criteria outlined in structural standards to pass compliance inspections.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each System
Rafter ties provide strong lateral restraint by connecting opposite rafters, preventing outward wall spread and enhancing roof stability, but require careful installation and sufficient attic space, which can limit headroom. Rafter brackets offer a simpler, less invasive solution by reinforcing individual rafter connections to the top plate, allowing easier retrofit and minimal attic interference but may not provide as comprehensive lateral support as rafter ties. Choosing between rafter ties and rafter brackets depends on structural requirements, space availability, and ease of installation, with ties favored for robust load distribution and brackets for straightforward reinforcement.
Common Applications in Roof Construction
Rafter ties are commonly used in traditional roof construction to prevent outward wall thrust by connecting opposite rafters across the building's width, enhancing structural stability. Rafter brackets provide localized support by securing rafters to beams or wall plates, ideal for reinforcing roof joints where additional load transfer is required. Both components contribute to roof integrity, with rafter ties effectively maintaining roof shape under tension and brackets offering targeted reinforcement in complex roofing designs.
Choosing Between Rafter Ties and Rafter Brackets
Choosing between rafter ties and rafter brackets depends on the specific structural requirements and load conditions of a roof. Rafter ties provide horizontal support by connecting opposing rafters, preventing outward wall spread, while rafter brackets offer localized reinforcement at rafter-to-beam connections for enhanced stability. Evaluating factors such as roof design, span length, and load distribution ensures the optimal use of rafter ties versus rafter brackets for durable roof framing.
Rafter tie vs Rafter bracket Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com