Radiators and convectors both serve to heat indoor spaces by transferring heat to the surrounding air, but they operate differently. Radiators heat through radiant heat transfer, warming objects and people directly, while convectors primarily use convection currents by heating the air that circulates around the room. Choosing between a radiator and a convector depends on factors like heating efficiency, room size, and desired warmth distribution patterns.
Table of Comparison
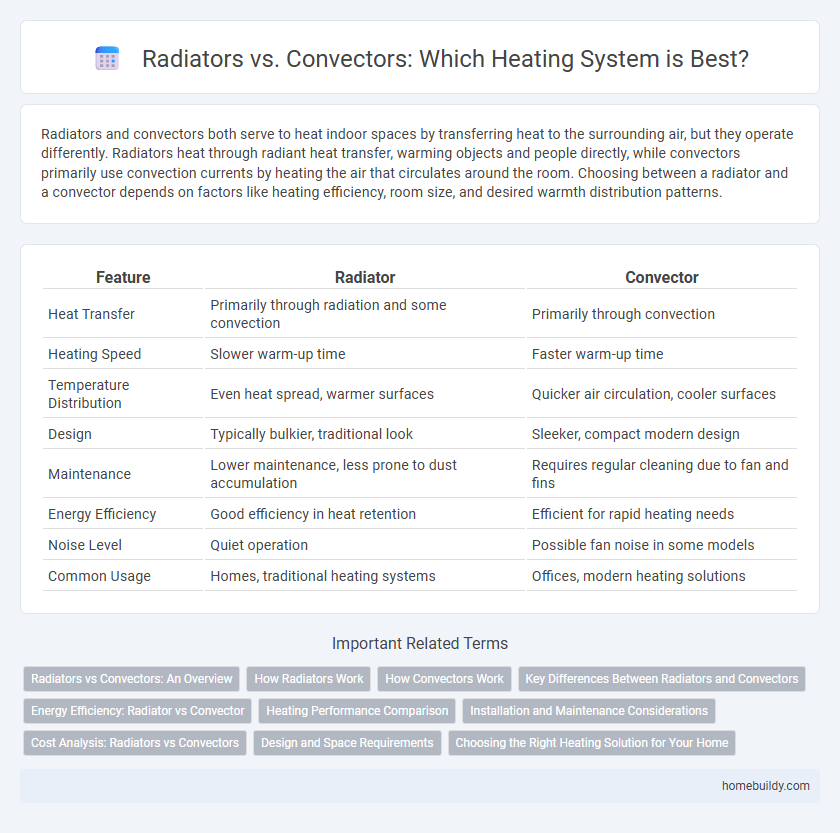
| Feature | Radiator | Convector |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer | Primarily through radiation and some convection | Primarily through convection |
| Heating Speed | Slower warm-up time | Faster warm-up time |
| Temperature Distribution | Even heat spread, warmer surfaces | Quicker air circulation, cooler surfaces |
| Design | Typically bulkier, traditional look | Sleeker, compact modern design |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance, less prone to dust accumulation | Requires regular cleaning due to fan and fins |
| Energy Efficiency | Good efficiency in heat retention | Efficient for rapid heating needs |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | Possible fan noise in some models |
| Common Usage | Homes, traditional heating systems | Offices, modern heating solutions |
Radiators vs Convectors: An Overview
Radiators and convectors are both heating devices that transfer heat through convection, but radiators primarily rely on natural convection and radiation to warm a room, while convectors enhance heat transfer through forced convection using fins or fans. Radiators typically have a larger surface area to emit infrared radiation, providing a consistent and gentle heat, whereas convectors offer faster room heating due to increased airflow. The choice between radiators and convectors depends on heating efficiency, installation space, and desired comfort levels.
How Radiators Work
Radiators work by heating water or steam inside metal panels, which then transfer heat through convection and radiation to warm a room efficiently. Unlike convectors that primarily rely on air movement to distribute heat, radiators emit infrared energy that directly warms objects and people in their vicinity. This dual heating method provides consistent and comfortable warmth while reducing energy consumption in central heating systems.
How Convectors Work
Convectors operate by heating air through metal fins or plates that absorb heat from a hot water or steam source, causing the warmed air to rise and circulate naturally within a room. Unlike radiators that radiate heat directly through a broad surface, convectors rely primarily on forced or natural air convection to distribute warmth efficiently. This design allows convectors to heat spaces quickly by promoting air flow over heated elements.
Key Differences Between Radiators and Convectors
Radiators use hot water or steam to transfer heat primarily through radiation, creating a warm air layer that circulates slowly, whereas convectors rely on heating air directly via metal fins, promoting faster air circulation through convection. Radiators tend to provide a more even and comfortable heat distribution, while convectors heat a room more quickly but can cause temperature fluctuations. The choice between radiators and convectors depends on the desired heating speed, efficiency, and comfort level for the space.
Energy Efficiency: Radiator vs Convector
Radiators typically offer higher energy efficiency by using natural convection and radiation heat transfer to evenly distribute warmth, reducing energy waste. Convectors rely primarily on forced convection, which can lead to faster heat loss and less consistent room temperatures, increasing overall energy consumption. Choosing a radiator often results in lower heating bills and improved thermal comfort due to its ability to maintain steady heat output with less power usage.
Heating Performance Comparison
Radiators provide consistent and efficient heat distribution by warming the air through convection and radiation, creating a comfortable indoor environment. Convectors primarily rely on convection to circulate warm air quickly but may cause uneven temperature distribution in larger spaces. Radiators generally offer better heat retention and longer-lasting warmth compared to convectors.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Radiators typically require more space for installation compared to convectors, as they are bulkier and mounted on walls, whereas convectors are compact and can be installed discreetly under windows or in floor ducts. Maintenance for radiators involves periodic bleeding to remove trapped air and ensure efficient heating, while convectors demand regular cleaning to prevent dust buildup within their fins, which can impair heat transfer. Choosing between the two depends on available space, ease of access for maintenance, and the desired heating efficiency within the room.
Cost Analysis: Radiators vs Convectors
Radiators typically have higher upfront installation costs compared to convectors, due to their bulkier design and more extensive plumbing requirements. Convectors offer lower initial expenses and faster heat-up times, making them more cost-effective for short-term heating needs. However, radiators provide better long-term efficiency and durability, potentially reducing overall energy costs and maintenance expenses over time.
Design and Space Requirements
Radiators typically feature a bulkier design due to their large metal panels and fins, which require more wall space and can limit room layout options. Convectors have a slimmer profile with a compact design that fits easily under windows or along baseboards, optimizing limited space in smaller rooms. The choice between radiator and convector depends on balancing heat output efficiency with the available space and desired interior aesthetics.
Choosing the Right Heating Solution for Your Home
Radiators provide consistent, long-lasting heat by warming large surface areas, making them ideal for maintaining steady room temperatures in larger spaces. Convectors heat air quickly by circulating warm air through fins, offering faster room warming but sometimes less even heat distribution. Selecting between radiators and convectors depends on your home's insulation, room size, heating speed preference, and energy efficiency requirements.
Radiator vs Convectors Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com