Radiator heating systems distribute warmth by heating the air surrounding the radiators, leading to quicker heat-up times but potentially uneven temperature distribution in a room. Underfloor heating provides consistent and energy-efficient heat by warming the entire floor surface, creating a comfortable environment with lower operating temperatures. Choosing between radiator and underfloor heating depends on factors such as installation costs, space constraints, and heating preferences.
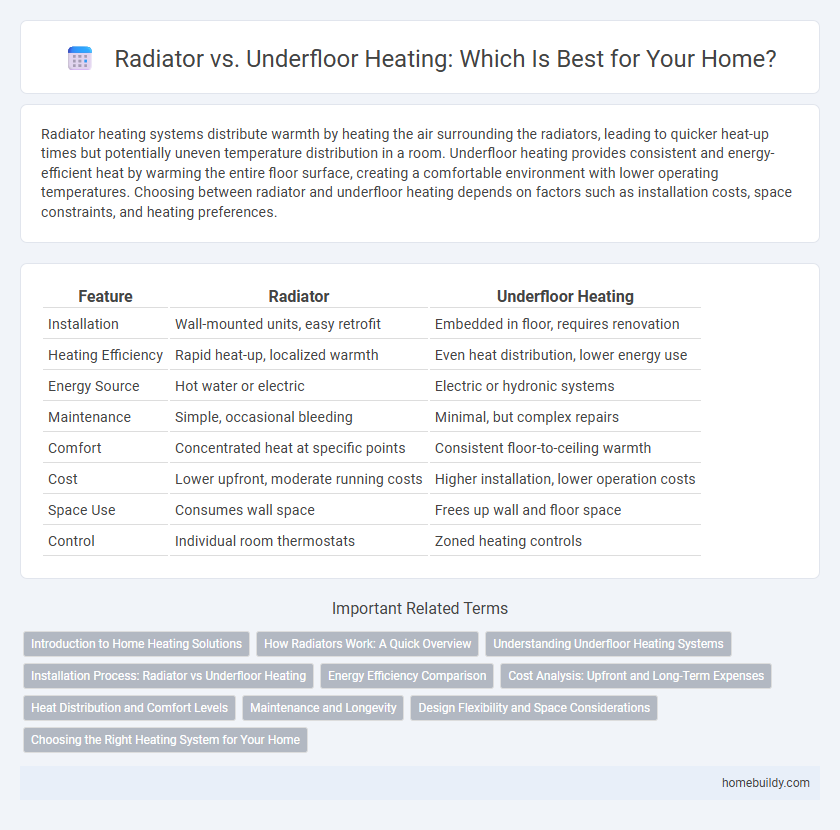
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Radiator | Underfloor Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Wall-mounted units, easy retrofit | Embedded in floor, requires renovation |
| Heating Efficiency | Rapid heat-up, localized warmth | Even heat distribution, lower energy use |
| Energy Source | Hot water or electric | Electric or hydronic systems |
| Maintenance | Simple, occasional bleeding | Minimal, but complex repairs |
| Comfort | Concentrated heat at specific points | Consistent floor-to-ceiling warmth |
| Cost | Lower upfront, moderate running costs | Higher installation, lower operation costs |
| Space Use | Consumes wall space | Frees up wall and floor space |
| Control | Individual room thermostats | Zoned heating controls |
Introduction to Home Heating Solutions
Radiators provide efficient, direct heat through hot water or steam circulated within metal panels, ideal for fast room warming. Underfloor heating emits gentle, consistent warmth by heating the floor surface, promoting energy efficiency and uniform temperature distribution. Choosing between these systems depends on space, installation complexity, and desired heating comfort.
How Radiators Work: A Quick Overview
Radiators work by circulating hot water or steam through metal panels, which then radiate heat into the surrounding air, effectively warming a room. These heating units rely on convection and radiation to distribute warmth quickly and evenly, providing consistent temperature control. Compared to underfloor heating, radiators heat the air directly above them, resulting in faster room heating but less overall heat distribution.
Understanding Underfloor Heating Systems
Underfloor heating systems distribute heat evenly through embedded pipes or electric mats beneath the floor, offering superior energy efficiency compared to traditional radiators. Unlike radiators that heat from a single point, underfloor heating provides consistent warmth across the entire floor surface, enhancing comfort and reducing heating costs. This system is compatible with various floor types and integrates seamlessly with modern energy-efficient boilers or heat pumps.
Installation Process: Radiator vs Underfloor Heating
Radiator installation typically involves mounting panels on walls and connecting them to existing pipework, allowing for quicker setup and easier access for maintenance. Underfloor heating requires a more extensive installation process including laying heating elements or water pipes beneath the flooring, which often involves lifting or replacing floor surfaces. While radiators suit retrofit projects due to minimal disruption, underfloor heating is ideal for new builds or major renovations given its complexity and installation time.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Radiators typically heat a room faster by warming the air directly but tend to operate at higher water temperatures, resulting in lower energy efficiency compared to underfloor heating systems that use lower temperature water and provide more uniform heat distribution. Underfloor heating can reduce energy consumption by up to 15-20% due to its ability to maintain consistent warmth and minimize heat loss, especially in well-insulated homes. Energy efficiency varies based on insulation quality, thermostat control, and system design, but underfloor heating generally offers superior efficiency in modern energy-efficient buildings.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Radiators typically have lower upfront installation costs compared to underfloor heating systems, which require extensive floor modifications and higher material expenses. Long-term, underfloor heating offers better energy efficiency, potentially reducing heating bills and maintenance costs over time. The choice depends on balancing initial budget constraints with anticipated savings from improved thermal performance.
Heat Distribution and Comfort Levels
Radiators typically deliver heat through convection, creating warmer air near the unit but can result in uneven temperature distribution across a room, potentially causing cold spots. Underfloor heating provides more consistent and uniform heat distribution by warming the entire floor surface, leading to higher comfort levels through radiant heat that evenly warms occupants and objects. This even heat spread from underfloor systems often enhances comfort compared to radiators that may cause localized warming near the heat source.
Maintenance and Longevity
Radiators require periodic bleeding and occasional valve replacements to maintain optimum performance, with a typical lifespan of 15-20 years when properly maintained. Underfloor heating systems demand less frequent maintenance but can be costly to repair if issues arise, commonly lasting 30-50 years due to their protected installation beneath the floor. Choosing between radiator and underfloor heating involves weighing short-term maintenance efforts against long-term durability and potential repair complexities.
Design Flexibility and Space Considerations
Radiators offer limited design flexibility due to their fixed wall-mounted positions, which can restrict furniture placement and room layout options. Underfloor heating provides a significant advantage by being completely concealed, freeing up wall space and allowing maximum use of interior design elements. This space-saving feature makes underfloor heating ideal for small rooms or modern aesthetics that prioritize minimalism and open floor plans.
Choosing the Right Heating System for Your Home
Radiators provide efficient, rapid heat distribution ideal for homes requiring quick temperature adjustments, while underfloor heating offers consistent warmth and energy efficiency by evenly heating room surfaces. Choosing the right heating system depends on factors like room size, insulation quality, installation costs, and maintenance preferences. Evaluating energy consumption data and comfort requirements ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness for your home's heating needs.
Radiator vs Underfloor Heating Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com