Radiator heating uses hot water or steam to warm metal units that radiate heat into a room, providing consistent and comfortable warmth. Baseboard heating relies on electric or hot water systems to distribute heat along the length of walls, offering precise temperature control and quiet operation. Both systems are energy-efficient options suited for different installation preferences and room layouts.
Table of Comparison
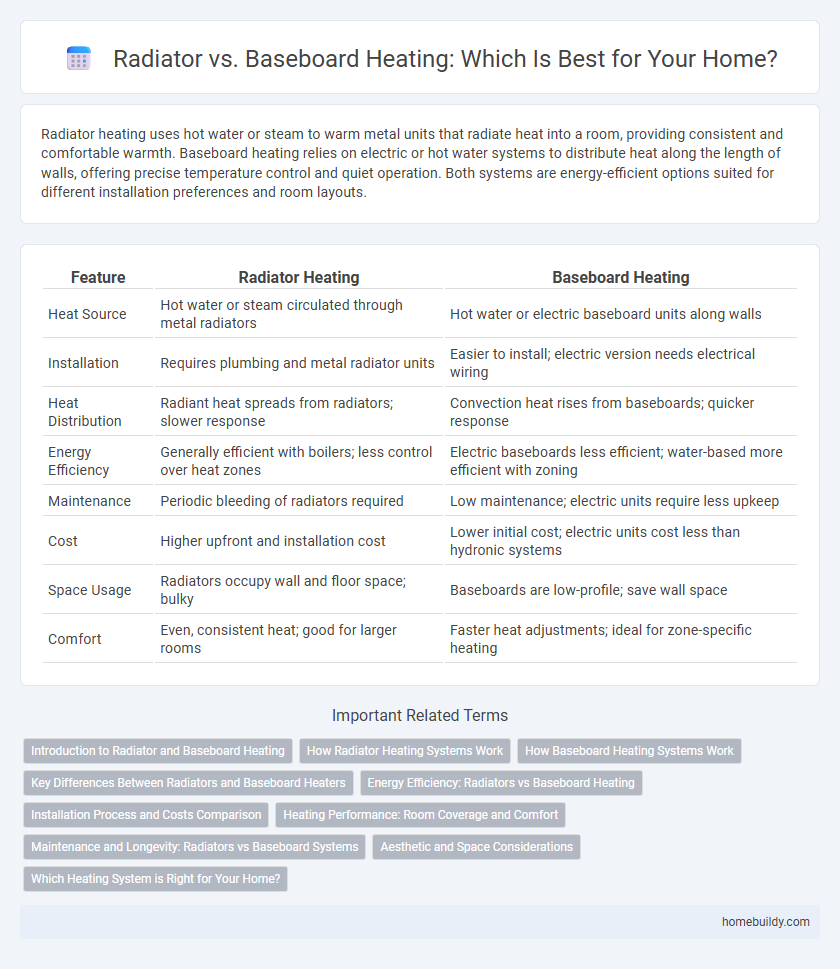
| Feature | Radiator Heating | Baseboard Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Hot water or steam circulated through metal radiators | Hot water or electric baseboard units along walls |
| Installation | Requires plumbing and metal radiator units | Easier to install; electric version needs electrical wiring |
| Heat Distribution | Radiant heat spreads from radiators; slower response | Convection heat rises from baseboards; quicker response |
| Energy Efficiency | Generally efficient with boilers; less control over heat zones | Electric baseboards less efficient; water-based more efficient with zoning |
| Maintenance | Periodic bleeding of radiators required | Low maintenance; electric units require less upkeep |
| Cost | Higher upfront and installation cost | Lower initial cost; electric units cost less than hydronic systems |
| Space Usage | Radiators occupy wall and floor space; bulky | Baseboards are low-profile; save wall space |
| Comfort | Even, consistent heat; good for larger rooms | Faster heat adjustments; ideal for zone-specific heating |
Introduction to Radiator and Baseboard Heating
Radiator heating utilizes hot water or steam circulated through metal radiators to emit heat via convection and radiation, offering consistent warmth and durability. Baseboard heating relies on electric or hydronic systems running along the floor's edge, providing efficient zonal temperature control and quieter operation. Both systems serve as effective home heating solutions, with radiators excelling in heat retention and baseboard units in space-saving design.
How Radiator Heating Systems Work
Radiator heating systems work by circulating hot water or steam through metal radiators, which then emit heat through convection and radiation to warm a room efficiently. These systems rely on a boiler to heat the water or generate steam, distributing it via pipes connected to the radiators in each space. The gradual heat release from radiators maintains consistent warmth and enhances indoor comfort compared to the surface heat of baseboard systems.
How Baseboard Heating Systems Work
Baseboard heating systems operate by distributing heat through convection, where warm air rises from the heated baseboard units along the walls, gradually warming the room. These systems often use hot water or electric resistance coils within the baseboard enclosure to generate heat efficiently. Baseboard heaters provide consistent, zoned heating control, making them a popular choice for energy-efficient home heating solutions.
Key Differences Between Radiators and Baseboard Heaters
Radiators use hot water or steam to transfer heat through metal panels, providing rapid and consistent warmth, while baseboard heaters rely on electric resistance or hot water convection to distribute heat along the base of walls. Radiators typically offer higher heat output and enhanced durability, whereas baseboard heaters allow for more flexible installation and zonal temperature control. Energy efficiency varies depending on the heat source, with hot water radiators often delivering lower operating costs compared to electric baseboard units.
Energy Efficiency: Radiators vs Baseboard Heating
Radiators typically provide superior energy efficiency compared to baseboard heating due to their ability to retain and distribute heat more evenly through water-based systems. Radiator systems use less energy by maintaining consistent room temperatures with lower thermostat settings, while baseboard heaters often rely on electric resistance heating, which can be more costly and less efficient. The thermal mass of radiators ensures longer heat retention, reducing the frequency of heating cycles and ultimately lowering energy consumption.
Installation Process and Costs Comparison
Radiator heating systems typically require more extensive installation involving piping and wall mounting, which can increase labor costs compared to baseboard heating units that are easier to install along base walls with minimal modifications. Radiators often demand a boiler or hot water system integration, raising initial setup expenses, while baseboard heaters can function with simpler, less expensive electrical or hydronic systems. Overall, radiator installation usually incurs higher upfront costs, but both options vary significantly based on home layout and existing infrastructure.
Heating Performance: Room Coverage and Comfort
Radiators provide efficient heating by radiating warmth evenly across a room, ensuring consistent temperature distribution and improved comfort compared to baseboard heating, which primarily relies on convection and may result in uneven heat spread. Radiators typically cover larger room areas more effectively due to their ability to emit radiant heat, which penetrates objects and occupants directly, enhancing overall room comfort. Baseboard systems often struggle with colder zones near windows or corners, whereas radiators maintain stable warmth, offering superior room coverage and comfort levels.
Maintenance and Longevity: Radiators vs Baseboard Systems
Radiator heating systems typically require less frequent maintenance due to their durable cast iron or steel construction, which resists corrosion and wear over time. Baseboard heating systems, often reliant on electric or hydronic components, may need regular cleaning to prevent dust buildup and periodic inspection of electrical or piping elements to ensure efficiency. Radiators generally offer longer longevity, often lasting 30-50 years, while baseboard systems may have a shorter lifespan of around 20-30 years depending on usage and maintenance quality.
Aesthetic and Space Considerations
Radiators typically offer a classic, bulkier design that can become a focal point in a room, while baseboard heating provides a sleek, low-profile appearance that blends seamlessly with walls, saving valuable floor space. Radiators often require more clearance and can limit furniture placement, whereas baseboard systems allow for greater flexibility in room layout and decor choices. The choice between the two depends largely on the desired aesthetic and the importance of maximizing usable living space.
Which Heating System is Right for Your Home?
Radiators provide efficient and consistent heat by circulating hot water or steam through metal panels, making them ideal for homes with high ceilings and older architecture. Baseboard heating offers a quieter, low-profile solution with electric or hydronic options, suitable for rooms where space and aesthetics are priorities. Choosing between radiator and baseboard heating depends on your home's design, energy source availability, and desired heating efficiency.
Radiator vs Baseboard Heating Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com