Radiators use hot water or steam to heat a room efficiently and provide consistent warmth over time, making them ideal for larger spaces. Electric heaters generate heat quickly through electrical resistance, offering portable and instant warmth suitable for smaller areas or temporary use. Choosing between a radiator and an electric heater depends on factors like room size, energy efficiency, and heating speed needs.
Table of Comparison
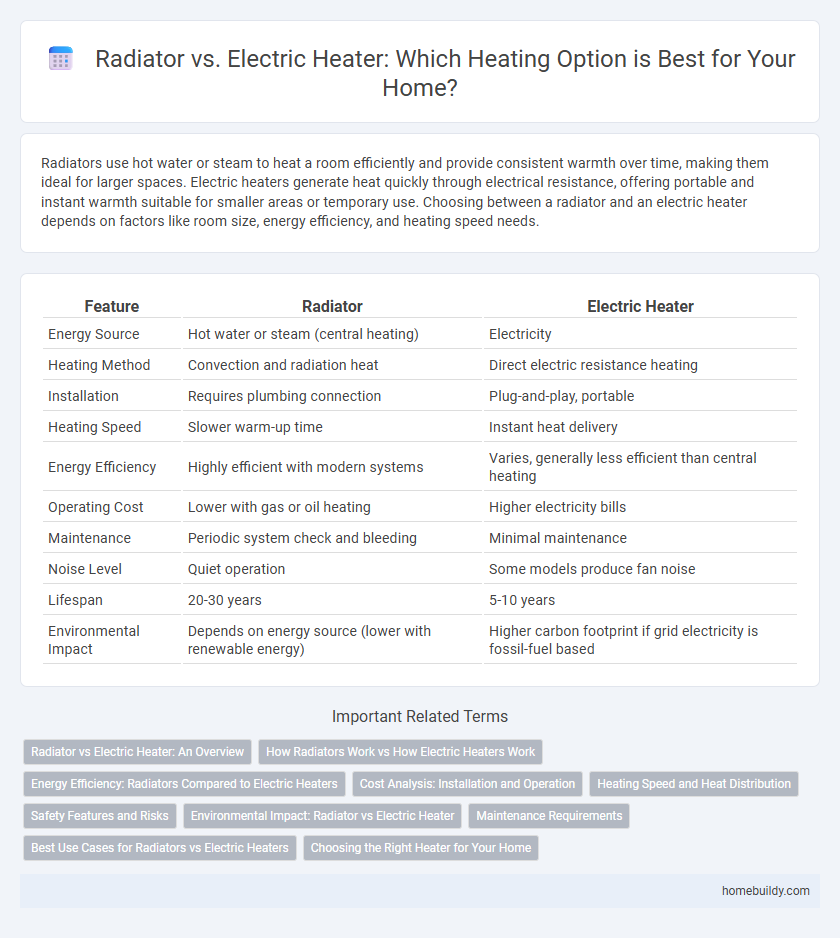
| Feature | Radiator | Electric Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Hot water or steam (central heating) | Electricity |
| Heating Method | Convection and radiation heat | Direct electric resistance heating |
| Installation | Requires plumbing connection | Plug-and-play, portable |
| Heating Speed | Slower warm-up time | Instant heat delivery |
| Energy Efficiency | Highly efficient with modern systems | Varies, generally less efficient than central heating |
| Operating Cost | Lower with gas or oil heating | Higher electricity bills |
| Maintenance | Periodic system check and bleeding | Minimal maintenance |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | Some models produce fan noise |
| Lifespan | 20-30 years | 5-10 years |
| Environmental Impact | Depends on energy source (lower with renewable energy) | Higher carbon footprint if grid electricity is fossil-fuel based |
Radiator vs Electric Heater: An Overview
Radiators provide consistent, energy-efficient heat by circulating hot water or steam through metal panels, making them ideal for prolonged warmth in larger spaces. Electric heaters convert electricity directly into heat, offering quick, portable solutions but often at higher operating costs and less uniform heat distribution. Choosing between a radiator and an electric heater depends on factors such as room size, energy efficiency preferences, and heating duration requirements.
How Radiators Work vs How Electric Heaters Work
Radiators operate by heating water or steam within metal panels, which then radiate warmth through convection and thermal radiation to the surrounding space, providing consistent and energy-efficient heating. Electric heaters use electrical resistance to generate heat directly, converting electricity into thermal energy through metal coils or ceramic elements, resulting in quicker heat output but often higher energy consumption. Radiators typically maintain ambient temperature longer due to water's heat retention properties, while electric heaters offer rapid warmth but cool down faster once turned off.
Energy Efficiency: Radiators Compared to Electric Heaters
Radiators typically operate by circulating hot water or steam, providing consistent and efficient heat distribution with lower energy consumption compared to electric heaters that convert electricity directly into heat. Hydronic radiators are often more energy-efficient due to their ability to retain and evenly spread heat over time, reducing the need for continuous energy use. Electric heaters, while offering quick heat, usually consume more electricity, leading to higher operating costs and less sustainable energy use in the long term.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Operation
Radiators generally have a higher initial installation cost due to plumbing and integration with central heating systems, while electric heaters offer lower upfront expenses and simpler setup. Operating costs for radiators tend to be lower, especially when connected to efficient boilers or renewable energy sources, making them more economical over time compared to electric heaters, which rely solely on electricity and can incur higher energy bills. Maintenance expenses for radiators are typically minimal but depend on system complexity, whereas electric heaters require virtually no maintenance, impacting long-term cost considerations.
Heating Speed and Heat Distribution
Radiators typically provide slower heating speed as they rely on convection and radiation to warm the surrounding air gradually, while electric heaters generate heat almost instantly through electric resistance elements. Radiators offer more even and consistent heat distribution across a room due to their larger surface area and natural circulation of warm air. Electric heaters may create localized heat spots, leading to less uniform warmth compared to the steady and widespread heat emitted by radiators.
Safety Features and Risks
Radiators typically operate using hot water or steam, minimizing the risk of burns and fire hazards compared to electric heaters that rely on exposed heating elements prone to overheating and ignition. Many radiators include built-in safety valves and overheat protection, which reduce the likelihood of accidents, whereas electric heaters often require additional safety features like tip-over switches and automatic shutoff. Understanding the inherent safety differences helps consumers choose heating solutions that align with household safety priorities.
Environmental Impact: Radiator vs Electric Heater
Radiators typically use hot water or steam heated by a boiler, which can be powered by renewable energy sources, resulting in lower carbon emissions compared to many electric heaters that rely on electricity from fossil fuels. Electric heaters often have a higher environmental impact due to electricity generation's reliance on coal or natural gas, producing more greenhouse gases. Choosing a radiator connected to an efficient boiler or renewable energy system significantly reduces overall environmental footprint compared to conventional electric heaters.
Maintenance Requirements
Radiators typically require minimal maintenance, mainly periodic bleeding to remove trapped air and occasional inspection for leaks or corrosion to ensure efficient heat transfer. Electric heaters demand less upkeep, with most maintenance involving cleaning dust from heating elements and checking electrical connections for safety. Both systems benefit from regular inspections, but radiators generally have more mechanical components needing attention compared to the simpler electric heater design.
Best Use Cases for Radiators vs Electric Heaters
Radiators excel in providing consistent, long-lasting heat, making them ideal for larger rooms and homes with existing central heating systems. Electric heaters are better suited for quick, portable warmth in small spaces or temporary heating needs. Choosing radiators benefits energy efficiency and comfort in well-insulated environments, while electric heaters offer convenience and flexibility for spot heating.
Choosing the Right Heater for Your Home
Radiators provide efficient, consistent heat by warming the surrounding air through convection and radiation, making them ideal for larger, well-insulated spaces. Electric heaters offer rapid, localized warmth and are often portable, suitable for smaller rooms or temporary heating needs. Selecting the right heater depends on factors such as room size, insulation quality, energy costs, and desired heating speed.
Radiator vs Electric Heater Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com