Radiator heaters provide consistent, long-lasting warmth by using heated oil or water to radiate heat evenly throughout a room, making them ideal for prolonged heating. Convector heaters heat air quickly by drawing it over a heating element and releasing warm air through vents, offering rapid but less uniform heat distribution. Choosing between the two depends on whether you prioritize sustained warmth with energy efficiency or fast, targeted heating for immediate comfort.
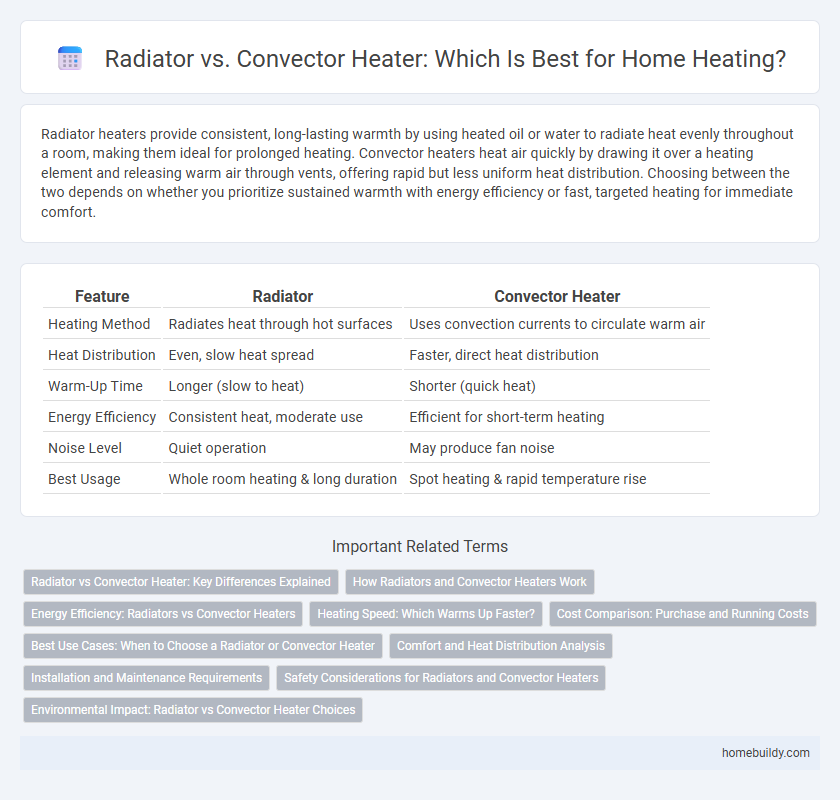
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Radiator | Convector Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Radiates heat through hot surfaces | Uses convection currents to circulate warm air |
| Heat Distribution | Even, slow heat spread | Faster, direct heat distribution |
| Warm-Up Time | Longer (slow to heat) | Shorter (quick heat) |
| Energy Efficiency | Consistent heat, moderate use | Efficient for short-term heating |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | May produce fan noise |
| Best Usage | Whole room heating & long duration | Spot heating & rapid temperature rise |
Radiator vs Convector Heater: Key Differences Explained
Radiators and convector heaters differ primarily in their heat distribution methods; radiators emit infrared heat that warms objects and people directly, while convector heaters circulate warm air through convection currents. Radiators typically provide more consistent, long-lasting warmth, making them ideal for sustained heating, whereas convector heaters heat up rooms quickly but may cool down faster. Energy efficiency varies based on usage, with radiators often preferred for central heating systems, and convector heaters suited for spot or temporary heating solutions.
How Radiators and Convector Heaters Work
Radiators work by circulating hot water or steam through metal panels, which then radiate heat directly to surrounding surfaces and air, providing consistent warmth. Convector heaters heat air by passing it over a heated element, causing the warm air to rise and create convection currents that distribute heat throughout the room. Radiators deliver steady, long-lasting heat, while convector heaters offer quicker room temperature increases through enhanced airflow.
Energy Efficiency: Radiators vs Convector Heaters
Radiators convert water heat into warm air through natural convection, providing steady and long-lasting heat with minimal energy loss, making them highly energy-efficient for continuous heating. Convector heaters rapidly circulate warm air using a fan, which heats a room faster but can consume more electricity and may lead to uneven temperature distribution. Energy efficiency between radiator and convector heaters depends on usage patterns; radiators excel in sustained, low-energy heating, while convector heaters suit quick, short-term heat needs but at potentially higher energy costs.
Heating Speed: Which Warms Up Faster?
Radiators use hot water or steam to transfer heat slowly through convection and radiation, resulting in a gradual but steady warming of the room. Convector heaters rely on electric elements to heat air directly, producing faster heat distribution and quicker room temperature increase. For rapid heating, convector heaters generally outperform radiators due to their ability to warm air immediately.
Cost Comparison: Purchase and Running Costs
Radiators typically have a higher initial purchase cost compared to convector heaters due to their durable metal construction and built-in thermal mass, which allows for longer heat retention. Convector heaters generally consume less energy in short bursts, resulting in lower running costs for quick, targeted heating, while radiators are more efficient for sustained room warming but may incur higher electricity or fuel expenses over time. Evaluating long-term usage patterns is crucial to determine total cost efficiency between the two heating options.
Best Use Cases: When to Choose a Radiator or Convector Heater
Radiators excel in heating large rooms slowly and maintaining consistent warmth, making them ideal for living rooms and bedrooms during prolonged use. Convector heaters provide rapid heat and better air circulation, suited for small spaces or quick heating needs like bathrooms and offices. Choosing between the two depends on room size, heating duration, and required heat distribution efficiency.
Comfort and Heat Distribution Analysis
Radiators provide steady, radiant heat that warms objects and people directly, offering consistent comfort throughout the room. Convector heaters heat the air quickly through convection, creating rapid warmth but often resulting in uneven temperature distribution and cooler zones. Radiators excel in maintaining stable, comfortable heat levels, while convector heaters may cause fluctuating warmth due to air movement.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Radiators typically require professional installation involving wall mounting and connection to a central heating system, which can be time-consuming but ensures efficient heat distribution. Convector heaters are often easier to install, usually requiring only plug-in options or simple wall mounting without plumbing work, reducing setup time and cost. Maintenance for radiators involves periodic bleeding and checking for leaks, whereas convector heaters demand regular dusting and occasional fan servicing to maintain optimal performance.
Safety Considerations for Radiators and Convector Heaters
Radiators typically operate with hot water or steam, reducing surface temperatures and minimizing burn risks compared to convector heaters, which use exposed heating elements that can reach higher temperatures and pose a greater fire hazard. Radiators' enclosed design limits direct contact with heat sources, enhancing safety, especially in households with children or pets. Proper maintenance of both systems is crucial to prevent leaks or electrical faults, but radiators generally offer safer heat distribution with less risk of accidental burns or ignition.
Environmental Impact: Radiator vs Convector Heater Choices
Radiators typically use hot water or steam from a central boiler, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced carbon emissions when paired with efficient heating systems. Convector heaters often rely on electric resistance heating, which can increase environmental impact depending on the electricity source, especially if not renewable. Choosing radiators connected to energy-efficient boilers or renewable heat sources minimizes overall environmental footprint compared to standalone electric convector heaters.
Radiator vs Convector Heater Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com