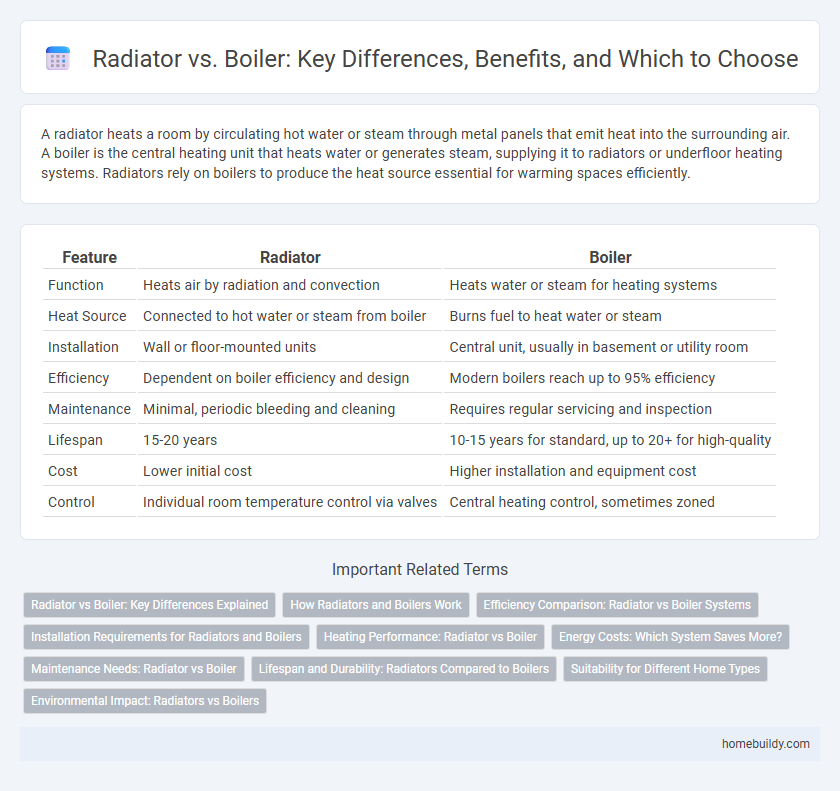
A radiator heats a room by circulating hot water or steam through metal panels that emit heat into the surrounding air. A boiler is the central heating unit that heats water or generates steam, supplying it to radiators or underfloor heating systems. Radiators rely on boilers to produce the heat source essential for warming spaces efficiently.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Radiator | Boiler |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Heats air by radiation and convection | Heats water or steam for heating systems |
| Heat Source | Connected to hot water or steam from boiler | Burns fuel to heat water or steam |
| Installation | Wall or floor-mounted units | Central unit, usually in basement or utility room |
| Efficiency | Dependent on boiler efficiency and design | Modern boilers reach up to 95% efficiency |
| Maintenance | Minimal, periodic bleeding and cleaning | Requires regular servicing and inspection |
| Lifespan | 15-20 years | 10-15 years for standard, up to 20+ for high-quality |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher installation and equipment cost |
| Control | Individual room temperature control via valves | Central heating control, sometimes zoned |
Radiator vs Boiler: Key Differences Explained
Radiators transfer heat directly to the air by convection, using hot water or steam from a boiler, while boilers generate the hot water or steam itself for heating systems. Radiators are individual units installed in rooms for localized heat distribution, whereas boilers serve as centralized heat sources supplying multiple radiators or heating elements through a piping network. Understanding the distinction between a radiator's heat emission and a boiler's heat generation is crucial for optimizing home heating efficiency.
How Radiators and Boilers Work
Radiators transfer heat by circulating hot water or steam produced by boilers through metal panels, which then emit warmth into the surrounding space through convection and radiation. Boilers generate this hot water or steam by heating water in a sealed vessel using fuel sources like gas, oil, or electricity, maintaining temperature through a thermostat and pressure-regulated system. The efficiency of a heating system relies on the synergy between the boiler's ability to produce consistent heat and the radiator's capacity to evenly distribute thermal energy.
Efficiency Comparison: Radiator vs Boiler Systems
Radiator systems offer efficient heat distribution by transferring heat directly through convection and radiation, minimizing energy loss compared to boiler systems that rely on centralized heat generation and water circulation. Boilers typically consume more energy due to heat loss in pipes and the need to maintain water temperature, whereas radiators provide localized heating with quicker room temperature adjustments. Optimizing radiator design and maintenance enhances overall system efficiency, making radiators a more energy-conserving option in many residential and commercial heating applications.
Installation Requirements for Radiators and Boilers
Radiators require connection to a central heating system with sufficient pipework for hot water circulation, typically involving wall-mounted brackets and space for units in each heated room. Boilers demand proper ventilation, a secure location compliant with safety standards, and connection to fuel sources like gas or oil, making their installation more complex and regulated. Both systems necessitate professional assessment for optimal placement, ensuring efficient heat distribution and adherence to building codes.
Heating Performance: Radiator vs Boiler
Radiators distribute heat by transferring hot water or steam from the boiler into metal panels, which then radiate warmth evenly throughout the room, ensuring consistent heating performance. Boilers serve as the heat source, efficiently generating hot water or steam, but their effectiveness depends on the quality and design of the connected radiators. Optimal heating performance is achieved when high-efficiency boilers are paired with modern, well-maintained radiators that maximize heat output and energy use.
Energy Costs: Which System Saves More?
Radiators typically offer better energy efficiency compared to boilers by delivering heat directly through hot water or steam, reducing energy waste and lowering heating bills. Boilers consume more fuel to heat water but can heat larger spaces more uniformly, often leading to higher operational energy costs. Choosing between a radiator and boiler system largely depends on the specific heating requirements and local energy prices, with radiators generally favored for cost-effective energy use in smaller or well-insulated settings.
Maintenance Needs: Radiator vs Boiler
Radiators require regular bleeding to remove trapped air and ensure efficient heat distribution, while boilers demand routine inspection of pressure levels, safety valves, and combustion efficiency for optimal performance. Radiator maintenance is generally simpler and less frequent compared to boilers, which involve more complex components such as pumps, heat exchangers, and fuel systems that need periodic servicing. Effective upkeep of both systems extends their lifespan and improves energy efficiency in heating applications.
Lifespan and Durability: Radiators Compared to Boilers
Radiators typically have a longer lifespan than boilers, often lasting 20 to 30 years with proper maintenance, whereas boilers generally require replacement within 10 to 15 years due to wear on components like heat exchangers. The durability of radiators is enhanced by their simple, robust design made from cast iron or steel, which withstands corrosion and pressure fluctuations better than boiler elements. Boilers face more frequent repairs and efficiency declines because of their mechanical complexity and continuous exposure to high temperatures and moisture.
Suitability for Different Home Types
Radiators are ideal for older homes with existing pipework and thick walls that retain heat, providing consistent and efficient warmth. Boilers offer versatile installation options suitable for both large modern houses and compact apartments, allowing for centralized heat distribution and hot water supply. Choosing between radiator and boiler systems depends on the home's size, insulation quality, and heating requirements.
Environmental Impact: Radiators vs Boilers
Radiators and boilers differ significantly in environmental impact, with radiators serving as heat distribution devices that rely on the boiler's efficiency and fuel source. Boilers fueled by natural gas or oil emit higher levels of greenhouse gases compared to modern electric or condensing boilers, which reduce carbon footprints through improved combustion efficiency. Choosing energy-efficient boilers paired with radiators designed for optimal heat transfer minimizes overall environmental impact and energy consumption.
Radiator vs Boiler Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com