Truss plates are metal connectors specifically designed to join timber members in roof trusses, providing strong, rigid connections through embedded teeth that grip the wood securely. Unlike general timber connectors such as bolts or brackets, truss plates distribute loads evenly across multiple points, enhancing structural stability and reducing stress concentrations. This makes truss plates ideal for prefabricated trusses where precise, reliable joints are essential for overall performance.
Table of Comparison
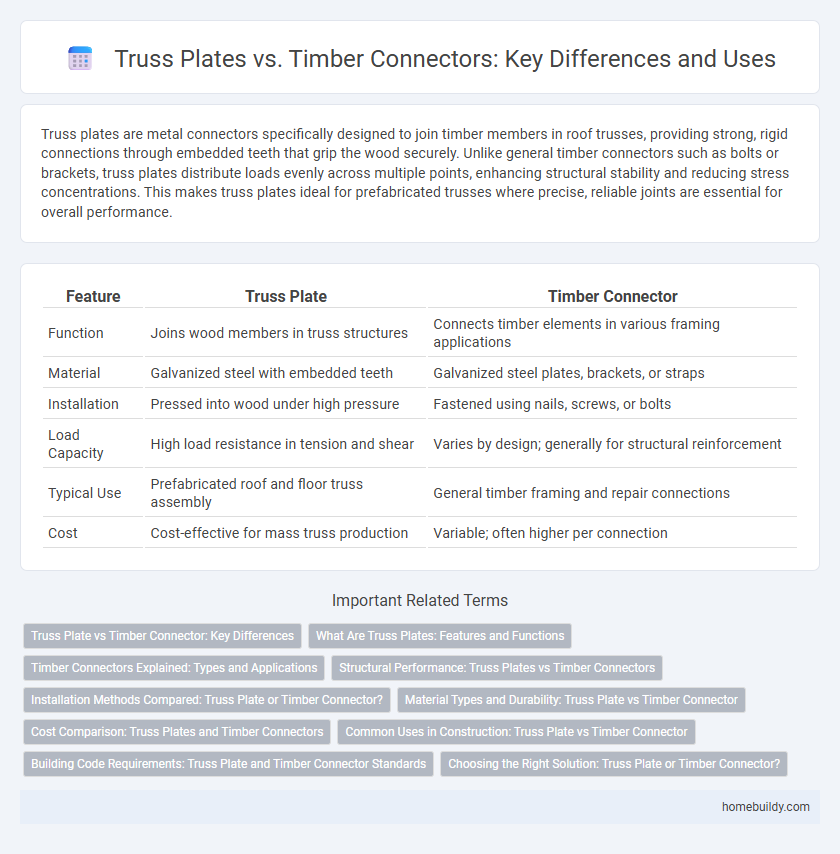
| Feature | Truss Plate | Timber Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Joins wood members in truss structures | Connects timber elements in various framing applications |
| Material | Galvanized steel with embedded teeth | Galvanized steel plates, brackets, or straps |
| Installation | Pressed into wood under high pressure | Fastened using nails, screws, or bolts |
| Load Capacity | High load resistance in tension and shear | Varies by design; generally for structural reinforcement |
| Typical Use | Prefabricated roof and floor truss assembly | General timber framing and repair connections |
| Cost | Cost-effective for mass truss production | Variable; often higher per connection |
Truss Plate vs Timber Connector: Key Differences
Truss plates and timber connectors serve distinct roles in wood construction, with truss plates primarily designed for joining truss members through metal stamping, offering high load capacity and enhancing structural integrity. Timber connectors, on the other hand, encompass a broader range of fastening solutions like bolts, screws, and metal straps, providing versatile attachment points for beams and other timber elements. Understanding these key differences ensures the selection of proper hardware based on load requirements and connection type, optimizing the performance and safety of timber frameworks.
What Are Truss Plates: Features and Functions
Truss plates are metal connectors designed with multiple teeth that embed into timber to securely join structural wood components, providing high load-bearing capacity and efficient force distribution. Unlike general timber connectors, truss plates offer precise alignment and enhanced stability for prefabricated roof trusses and heavy timber frameworks. Their steel composition ensures corrosion resistance and long-term durability in various construction environments.
Timber Connectors Explained: Types and Applications
Timber connectors serve as critical components in wood construction, offering various types such as metal brackets, joist hangers, and angle connectors to ensure structural integrity. Unlike truss plates, which are primarily used to fasten truss joints, timber connectors provide versatile applications in framing, deck building, and cabinetry. Their selection depends on load requirements, wood type, and connection angles, making them essential for both residential and commercial timber projects.
Structural Performance: Truss Plates vs Timber Connectors
Truss plates provide superior load distribution and enhanced shear strength compared to traditional timber connectors, ensuring greater structural integrity in wood frame construction. Their precision-engineered steel plates offer consistent performance under dynamic loads, reducing the risk of joint failure and improving overall durability. Timber connectors, while easier to install, often lack the uniform strength and may be prone to deformation or loosening over time.
Installation Methods Compared: Truss Plate or Timber Connector?
Truss plates install by pressing or nailing them into pre-cut timber joints, creating strong, rigid connections with minimal labor and specialized tools. Timber connectors require screws or bolts and often pre-drilling, resulting in longer installation times but providing greater adjustability and disassembly options. Choosing between truss plates and timber connectors depends on project scale, desired joint strength, and installation speed.
Material Types and Durability: Truss Plate vs Timber Connector
Truss plates are typically made from galvanized steel, offering high resistance to corrosion and substantial load-bearing capacity, making them durable for long-term structural applications. Timber connectors, often manufactured from stainless steel, aluminum, or galvanized steel, vary in durability depending on the material and protective coatings used. The choice between truss plates and timber connectors often hinges on material strength and environmental resistance, with galvanized steel truss plates excelling in heavy-duty durability.
Cost Comparison: Truss Plates and Timber Connectors
Truss plates generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to timber connectors due to their lower material and installation expenses. Timber connectors often require additional labor and precision, increasing overall project costs. Choosing truss plates can reduce both direct costs and time invested in assembly for wood framing projects.
Common Uses in Construction: Truss Plate vs Timber Connector
Truss plates are primarily used for connecting metal components in prefabricated roof trusses, providing high-strength joints in engineered wood frameworks. Timber connectors, such as metal brackets, bolts, and straps, are commonly employed for securing solid wood beams in traditional carpentry and framing applications. Both serve critical roles in construction, with truss plates favored for consistent, mass-produced connections and timber connectors offering flexibility for various structural adjustments and repairs.
Building Code Requirements: Truss Plate and Timber Connector Standards
Truss plates and timber connectors must comply with strict building code requirements including standards set by the American Institute of Timber Construction (AITC) and the International Building Code (IBC). Truss plates, governed primarily by ASTM standards such as ASTM A653 for steel quality and AITC 117 for installation, ensure structural integrity through precision-engineered metal connectors, while timber connectors follow ANSI/AITC A190 standards tailored for fastening timber elements. Adhering to these codes guarantees appropriate load transfer, corrosion resistance, and safety in wood frame construction.
Choosing the Right Solution: Truss Plate or Timber Connector?
Selecting between a truss plate and a timber connector depends on structural requirements, load capacity, and installation conditions. Truss plates provide efficient load distribution and are ideal for prefabricated wood trusses, while timber connectors offer versatility for on-site adjustments and complex joint configurations. Evaluating factors such as strength, ease of assembly, and project scope ensures the optimal choice for durable, stable timber framing.
Truss plate vs Timber connector Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com