Truss plates provide a fast, efficient way to connect timber members by embedding steel plates with sharpened teeth directly into the wood, offering a uniform load distribution and reduced installation time compared to bolted connections. Bolted connections require drilling holes and tightening bolts, which can create stress concentrations and may weaken the timber around the holes. Truss plates excel in applications needing high-speed assembly and consistent load transfer, while bolted connections offer more adjustability and are preferred where disassembly or on-site modifications are necessary.
Table of Comparison
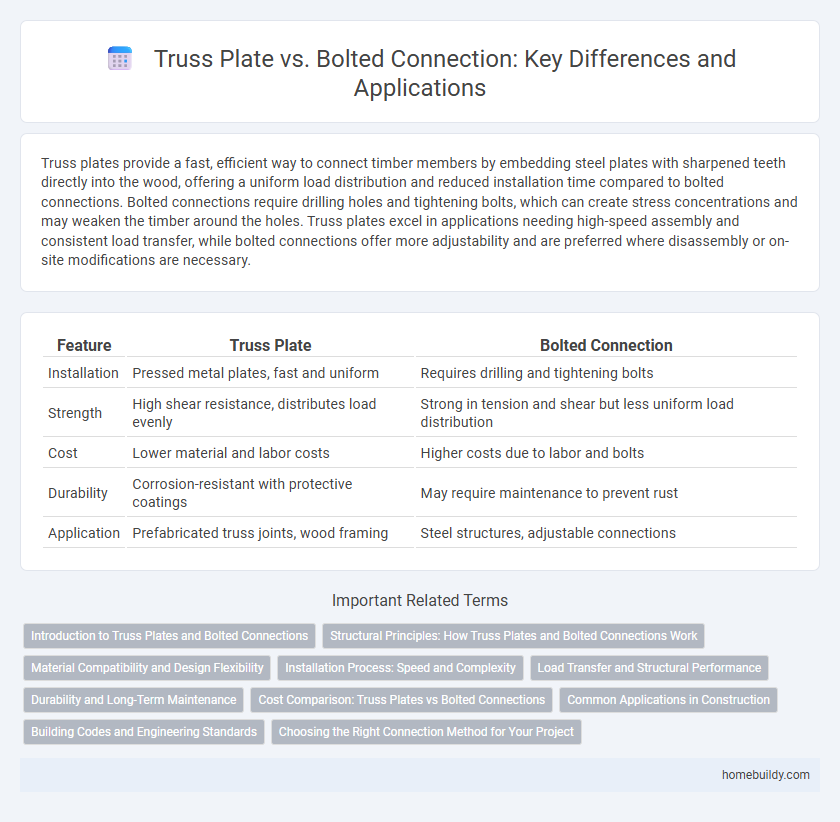
| Feature | Truss Plate | Bolted Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Pressed metal plates, fast and uniform | Requires drilling and tightening bolts |
| Strength | High shear resistance, distributes load evenly | Strong in tension and shear but less uniform load distribution |
| Cost | Lower material and labor costs | Higher costs due to labor and bolts |
| Durability | Corrosion-resistant with protective coatings | May require maintenance to prevent rust |
| Application | Prefabricated truss joints, wood framing | Steel structures, adjustable connections |
Introduction to Truss Plates and Bolted Connections
Truss plates are metal connectors used to join timber or steel elements in structural frameworks, offering precise alignment and efficient load transfer through their punched or stamped teeth embedded in the material. Bolted connections rely on bolts and nuts to fasten members together, providing adjustable and removable joints but potentially requiring larger surfaces for load distribution and careful torque application. Both systems are integral in construction, where truss plates ensure rapid assembly and consistent performance, while bolted connections offer flexibility and ease of maintenance.
Structural Principles: How Truss Plates and Bolted Connections Work
Truss plates transfer loads through numerous small teeth embedded into the connected members, enabling efficient distribution of tensile and compressive forces along the wood grain. Bolted connections rely on friction and shear resistance between clamped surfaces with bolts transmitting forces directly through the metal fasteners. The choice between truss plates and bolted connections depends on structural requirements, with truss plates ideal for load distribution in lightweight timber trusses and bolted connections suited for high-strength, removable joints.
Material Compatibility and Design Flexibility
Truss plates offer superior material compatibility by ensuring uniform stress distribution through embedded steel teeth, reducing localized stress concentrations common in bolted connections. Design flexibility is enhanced as truss plates accommodate various wood thicknesses and complex joint geometries without the need for precise hole alignment required by bolts. Unlike bolted connections, truss plates enable faster assembly and provide greater holding strength in timber structures.
Installation Process: Speed and Complexity
Truss plates offer significantly faster installation compared to bolted connections due to their simple press-fit design, eliminating the need for drilling or alignment of multiple bolts. The complexity of bolted connections increases installation time as precise hole alignment and torque specifications must be met to ensure structural integrity. Truss plates reduce labor costs and on-site fabrication, streamlining construction timelines in large-scale timber framing projects.
Load Transfer and Structural Performance
Truss plates provide efficient load transfer through uniform distribution and direct bearing on connected members, minimizing stress concentrations often seen in bolted connections. Bolted connections rely on discrete fasteners that may introduce localized stresses and potential slip, affecting overall structural performance under dynamic or cyclic loads. The continuous, rigid nature of truss plates generally results in enhanced stiffness and improved load-sharing capabilities compared to bolted assemblies.
Durability and Long-Term Maintenance
Truss plates offer superior durability compared to bolted connections due to their seamless integration with timber, reducing points of failure and minimizing corrosion risks. Unlike bolted connections that require periodic tightening and inspection, truss plates demand less long-term maintenance, ensuring stable structural integrity over time. This makes truss plates a cost-effective solution for reducing upkeep while enhancing the lifespan of timber frameworks.
Cost Comparison: Truss Plates vs Bolted Connections
Truss plates generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to bolted connections due to lower labor and installation expenses. The prefabricated nature of truss plates reduces onsite assembly time, resulting in significant savings on labor costs and minimizing potential errors. In contrast, bolted connections require more time-intensive alignment and tightening, increasing both labor costs and material expenses for fasteners.
Common Applications in Construction
Truss plates are commonly used in prefabricated wood truss systems due to their efficient load transfer and ease of installation, especially in residential roof framing and floor systems. Bolted connections are preferred in heavy timber and steel construction projects where strength, disassembly, and adjustability are critical, such as in bridges and large commercial buildings. The choice between truss plates and bolted connections depends on factors like load requirements, construction speed, and design flexibility.
Building Codes and Engineering Standards
Truss plates comply with stringent building codes such as ANSI/APA PRR 201 and ASTM D3052, ensuring reliable load transfer in wood frame structures by providing uniform stress distribution. Bolted connections adhere to standards like AISC Steel Construction Manual and ACI 318, requiring precise torque specifications for structural steel safety. Engineering standards emphasize truss plates for fast, efficient installation in prefabricated components, while bolted connections offer flexibility for on-site adjustments and maintenance.
Choosing the Right Connection Method for Your Project
Truss plates offer efficient load distribution and quicker installation by providing a large, continuous connection surface, ideal for lightweight and prefabricated structures. Bolted connections provide adjustable, high-strength joints suitable for heavy-duty frameworks and easy disassembly, favoring projects requiring maintenance or future modifications. Evaluating factors such as load requirements, installation time, cost, and future access needs helps determine the most effective connection method for your specific structural project.
Truss plate vs Bolted connection Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com