Truss plates offer a faster and more cost-effective solution for reinforcing wooden structures compared to bolt reinforcement, as they can be easily nailed or pressed into place without requiring drilling or threading. Unlike bolts, truss plates distribute loads evenly across the joint, reducing stress concentrations and potential wood damage. This makes truss plates ideal for maintaining structural integrity in trusses and other timber connections.
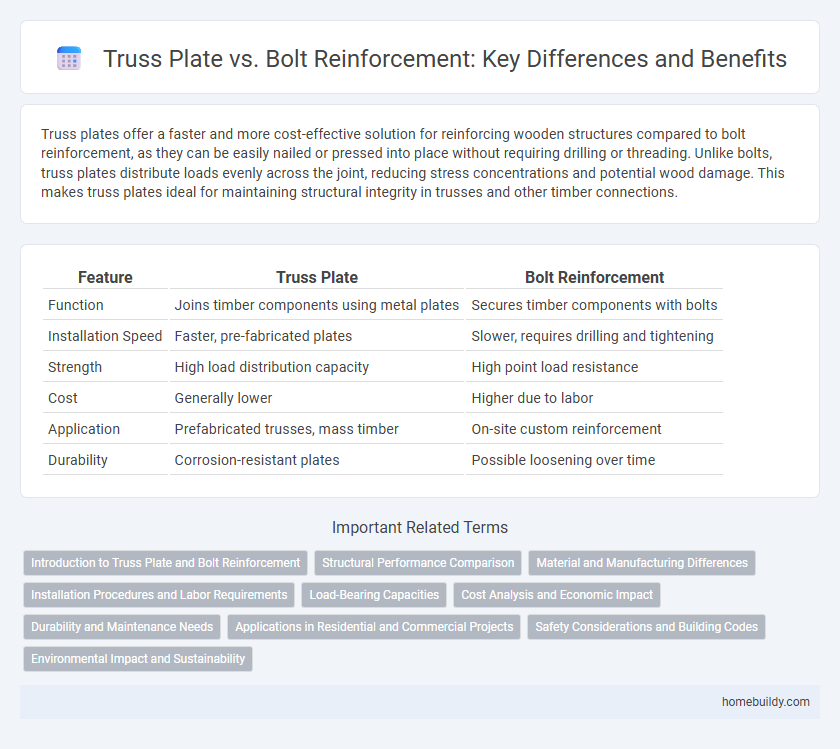
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Truss Plate | Bolt Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Joins timber components using metal plates | Secures timber components with bolts |
| Installation Speed | Faster, pre-fabricated plates | Slower, requires drilling and tightening |
| Strength | High load distribution capacity | High point load resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to labor |
| Application | Prefabricated trusses, mass timber | On-site custom reinforcement |
| Durability | Corrosion-resistant plates | Possible loosening over time |
Introduction to Truss Plate and Bolt Reinforcement
Truss plates are specialized steel connectors used to join timber members in truss construction, providing efficient load transfer through shear force distribution. Bolt reinforcement involves fastening structural elements with bolts to enhance joint stability and resist tension and shear forces. Comparing truss plates and bolt reinforcement reveals differences in application: truss plates offer rapid installation with uniform load distribution, while bolt reinforcement provides adjustable, high-strength connections suitable for retrofitting and heavy loads.
Structural Performance Comparison
Truss plates provide superior load distribution in timber connections compared to bolt reinforcement, enhancing joint stiffness and reducing stress concentrations. Bolt reinforcement often leads to localized stress around the fasteners, which can cause premature failure in high-load scenarios. The metal-to-wood contact of truss plates ensures consistent structural performance and improved durability in timber framing applications.
Material and Manufacturing Differences
Truss plates are typically made from galvanized steel with pointed teeth designed for secure wood-to-wood connections, produced through stamping or pressing processes to ensure precise tooth formation and consistent thickness. Bolt reinforcements use high-strength steel bolts and washers, requiring machining or forging techniques to achieve exact thread specifications and tensile strength for load-bearing applications. The stamped truss plates offer quicker installation due to their integrated teeth, while bolts provide adjustable and reusable fastening options tailored for heavy-duty structural demands.
Installation Procedures and Labor Requirements
Truss plate installation involves pressing metal plates with embedded teeth into timber joints using hydraulic presses, allowing for quick and precise connections with minimal labor. Bolt reinforcement requires drilling holes and securing steel bolts with nuts and washers, which is more time-consuming and demands skilled labor for accurate alignment and torque application. The streamlined process of truss plate installation significantly reduces labor requirements compared to the more labor-intensive bolt reinforcement method.
Load-Bearing Capacities
Truss plates offer superior load-bearing capacities due to their large surface area and multiple teeth that distribute forces evenly across timber joints, reducing localized stress. Bolt reinforcement provides high tensile strength but concentrates load on smaller areas, potentially causing stress points and requiring precise installation for optimal performance. For heavy structural applications, truss plates deliver more consistent load transfer and enhanced joint stability compared to bolt reinforcement.
Cost Analysis and Economic Impact
Truss plates generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to bolt reinforcement due to lower material and labor expenses, reducing overall project budget significantly. The installation time for truss plates is shorter, which translates into decreased labor costs and faster project completion, enhancing economic efficiency. Bolt reinforcement, while providing higher tensile strength, incurs higher upfront costs and maintenance expenses, making truss plates the preferred choice in budget-sensitive applications.
Durability and Maintenance Needs
Truss plates offer superior durability compared to bolt reinforcement due to their ability to distribute loads evenly across the joint, reducing stress concentrations that can lead to material fatigue. Maintenance needs for truss plates are minimal since they are embedded within the wood structure, preventing exposure to environmental factors that often cause corrosion or loosening in bolts. Bolt reinforcement requires regular inspections and tightening to maintain structural integrity, especially in harsh weather conditions where rust and wear are common.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Projects
Truss plates provide efficient load distribution and quick installation in both residential and commercial projects, making them ideal for roof trusses and floor systems. Bolt reinforcement offers superior tensile strength and is preferred in applications requiring adjustable connections or higher structural demands, such as commercial buildings with heavy load requirements. Choosing between truss plates and bolt reinforcement depends on project scale, load specifications, and design flexibility needs.
Safety Considerations and Building Codes
Truss plates offer superior load distribution and minimize stress concentrations compared to bolt reinforcement, enhancing structural safety by reducing the risk of joint failure under dynamic loads. Building codes such as the International Building Code (IBC) and Eurocode specify requirements favoring truss plates for timber connections due to their proven performance in stiffness and durability. Compliance with these codes ensures that truss plate installations meet safety margins and resist long-term wear, whereas bolted joints often require additional inspection and maintenance protocols.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Truss plates, typically made from galvanized steel, offer a more sustainable option compared to bolt reinforcement due to their efficient use of material and lower energy consumption during manufacturing. The lightweight nature of truss plates reduces transportation emissions and waste generation on-site, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. Bolt reinforcement, often involving larger quantities of steel and heavier components, can lead to increased resource extraction and longer processing times, negatively impacting environmental sustainability.
Truss plate vs Bolt reinforcement Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com