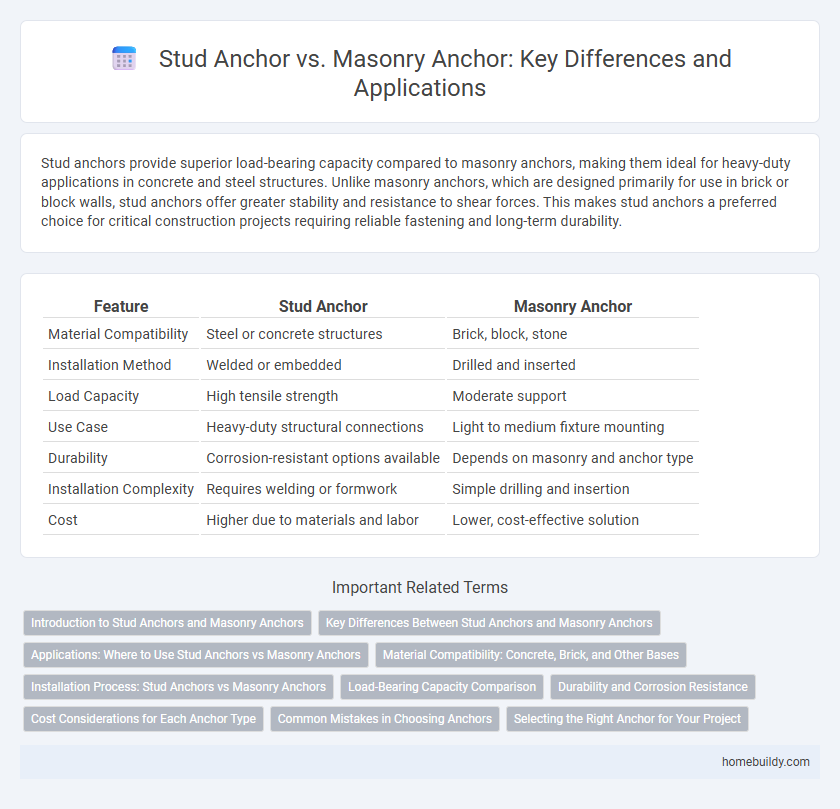
Stud anchors provide superior load-bearing capacity compared to masonry anchors, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications in concrete and steel structures. Unlike masonry anchors, which are designed primarily for use in brick or block walls, stud anchors offer greater stability and resistance to shear forces. This makes stud anchors a preferred choice for critical construction projects requiring reliable fastening and long-term durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stud Anchor | Masonry Anchor |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | Steel or concrete structures | Brick, block, stone |
| Installation Method | Welded or embedded | Drilled and inserted |
| Load Capacity | High tensile strength | Moderate support |
| Use Case | Heavy-duty structural connections | Light to medium fixture mounting |
| Durability | Corrosion-resistant options available | Depends on masonry and anchor type |
| Installation Complexity | Requires welding or formwork | Simple drilling and insertion |
| Cost | Higher due to materials and labor | Lower, cost-effective solution |
Introduction to Stud Anchors and Masonry Anchors
Stud anchors are mechanical fasteners designed to secure heavy loads to concrete, steel, or other solid substrates by embedding directly into the base material with high shear and tensile strength. Masonry anchors, typically made for brick, block, or stone, rely on expansion or chemical bonding to grip porous surfaces and provide stability in lighter load applications. Understanding the load capacity and substrate compatibility of stud anchors versus masonry anchors is essential for selecting the appropriate fastening solution in construction and structural applications.
Key Differences Between Stud Anchors and Masonry Anchors
Stud anchors provide superior load-bearing capacity by embedding directly into concrete or steel, offering high shear and tensile strength ideal for structural applications. Masonry anchors are designed specifically for brick, block, or stone substrates, optimizing grip through expansion or chemical bonding to prevent loosening in porous materials. The key difference lies in their installation method and substrate compatibility, with stud anchors requiring solid base materials while masonry anchors accommodate brittle, uneven surfaces.
Applications: Where to Use Stud Anchors vs Masonry Anchors
Stud anchors are ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring high load capacity in concrete and steel structures, such as securing steel columns, beams, and heavy machinery. Masonry anchors are better suited for lighter duties, anchoring fixtures into brick, block, or stone where minimal structural stress is involved. Use stud anchors in industrial and commercial construction demanding superior strength and durability, while masonry anchors fit residential repairs and non-structural attachments.
Material Compatibility: Concrete, Brick, and Other Bases
Stud anchors offer superior material compatibility by providing strong, reliable anchoring in concrete, brick, and other masonry bases due to their robust steel construction and design that minimizes stress on the substrate. Masonry anchors, while effective in softer materials like brick, often lack the tensile strength and durability for high-load applications in dense concrete or mixed base materials. Selecting stud anchors for concrete and brick ensures enhanced load distribution and long-term performance in structural and heavy-duty installations.
Installation Process: Stud Anchors vs Masonry Anchors
Stud anchors require drilling a precise hole into concrete or steel followed by inserting and tightening the anchor stud, ensuring strong mechanical interlock with the base material. Masonry anchors, often installed by drilling into brick, block, or stone, rely on expansion or chemical bonding to secure fasteners, with installation varying based on anchor type such as sleeve, wedge, or adhesive anchors. The stud anchor installation demands careful alignment and torque control for optimal load-bearing capacity, whereas masonry anchors necessitate consideration of substrate integrity and anchor expansion to prevent material cracking.
Load-Bearing Capacity Comparison
Stud anchors provide superior load-bearing capacity compared to masonry anchors due to their deeper embedment and direct engagement with the structural substrate. The mechanical interlock and higher tensile strength of stud anchors enable them to withstand heavier static and dynamic loads in concrete and steel applications. In contrast, masonry anchors rely on surface friction and weaker substrate materials, resulting in lower load limits and reduced overall performance.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Stud anchors exhibit superior durability compared to masonry anchors due to their robust design and heavy-duty steel construction. Their corrosion resistance is often enhanced by protective coatings such as galvanization or stainless steel materials, ensuring longer lifespan in harsh environments. Masonry anchors, while effective for lighter loads, generally offer less resistance to corrosion and wear, making stud anchors the preferred choice for heavy-duty applications requiring sustained durability.
Cost Considerations for Each Anchor Type
Stud anchors generally have higher upfront costs compared to masonry anchors due to their more complex installation requirements and superior load-bearing capacity. Masonry anchors offer a cost-effective solution for lighter applications and easier installation in brick or concrete block structures. Evaluating the total project budget should include both material prices and labor intensity, where stud anchors may incur higher labor costs but provide long-term durability savings.
Common Mistakes in Choosing Anchors
Choosing the wrong type of anchor, such as selecting a masonry anchor instead of a stud anchor, often leads to insufficient load-bearing capacity and structural failure. Common mistakes include neglecting the wall material, misjudging the weight the anchor must support, and ignoring installation guidelines specific to stud anchors. Understanding the differences in design and application between stud anchors and masonry anchors is crucial for secure and durable mounting.
Selecting the Right Anchor for Your Project
Stud anchors provide superior load-bearing capacity and are ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring high shear and tensile strength, outperforming typical masonry anchors which are better suited for lighter loads in concrete or brick. When selecting the right anchor for your project, evaluate the substrate type, load requirements, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance and safety. Proper installation techniques and compatibility with structural elements also influence the effectiveness of stud versus masonry anchors in construction tasks.
Stud anchor vs masonry anchor Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com