Stud anchors provide superior mechanical strength and are ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring direct load transfer, while epoxy anchors rely on adhesive bonding within drilled holes for enhanced corrosion resistance and ease of installation. Unlike epoxy anchors, stud anchors offer immediate load-bearing capacity without curing time, making them suitable for fast-paced construction environments. Epoxy anchors, however, are preferred in environments with irregular or damaged concrete where drilling precision is compromised.
Table of Comparison
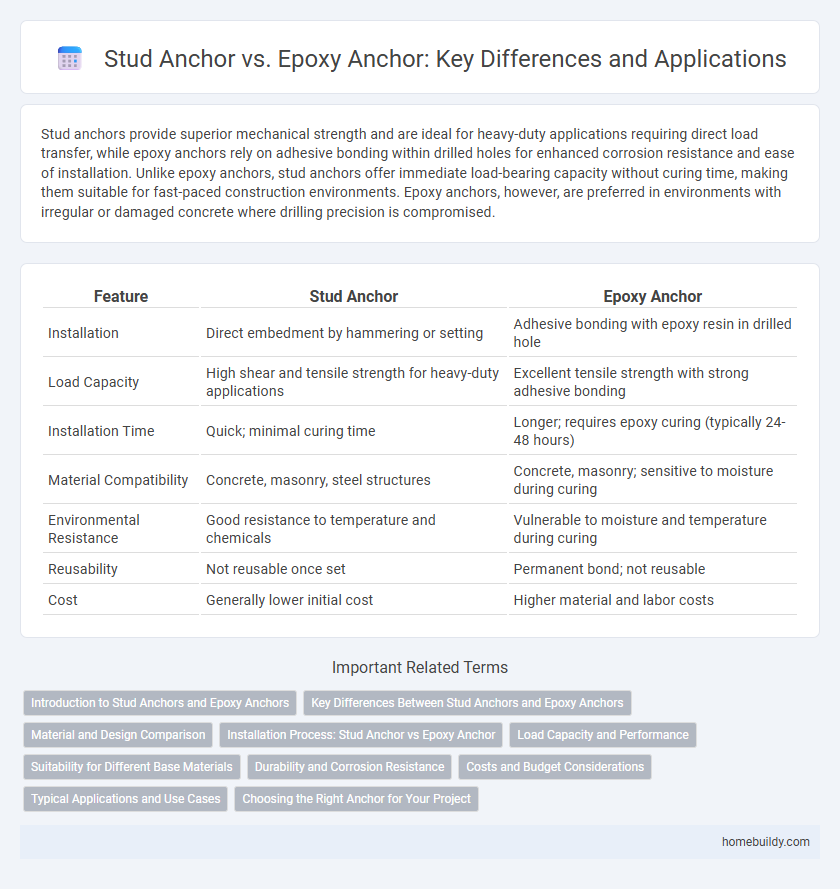
| Feature | Stud Anchor | Epoxy Anchor |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Direct embedment by hammering or setting | Adhesive bonding with epoxy resin in drilled hole |
| Load Capacity | High shear and tensile strength for heavy-duty applications | Excellent tensile strength with strong adhesive bonding |
| Installation Time | Quick; minimal curing time | Longer; requires epoxy curing (typically 24-48 hours) |
| Material Compatibility | Concrete, masonry, steel structures | Concrete, masonry; sensitive to moisture during curing |
| Environmental Resistance | Good resistance to temperature and chemicals | Vulnerable to moisture and temperature during curing |
| Reusability | Not reusable once set | Permanent bond; not reusable |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher material and labor costs |
Introduction to Stud Anchors and Epoxy Anchors
Stud anchors provide reliable mechanical fastening by embedding threaded rods or bolts directly into concrete, ensuring high load-bearing capacity and ease of installation. Epoxy anchors use chemical adhesives to bond the anchor to the substrate, offering superior resistance to vibration and corrosion in challenging environments. Both anchoring methods are essential in construction, with stud anchors favored for quick setup and epoxy anchors preferred for enhanced durability in structural applications.
Key Differences Between Stud Anchors and Epoxy Anchors
Stud anchors provide mechanical fastening by embedding a threaded rod into pre-drilled holes, ensuring immediate load-bearing capacity and easy removal or adjustment. Epoxy anchors utilize strong adhesive resins to bond threaded rods or rebar within drilled holes, offering superior chemical resistance and increased load strength, especially in cracked concrete. Stud anchors typically allow faster installation and reuse, while epoxy anchors require precise curing time and provide enhanced durability in corrosive environments.
Material and Design Comparison
Stud anchors, typically made from high-strength steel or stainless steel, offer superior mechanical performance and corrosion resistance compared to epoxy anchors, which rely on adhesive resins for bonding. The design of stud anchors includes a threaded body for secure embedment and load transfer in concrete, whereas epoxy anchors depend on chemical adhesion and often require longer curing times. Material durability in stud anchors ensures consistent load capacity and reliability, making them preferable for heavy-duty structural applications over epoxy-based systems.
Installation Process: Stud Anchor vs Epoxy Anchor
Stud anchors require drilling a precise hole to accommodate the anchor size, followed by tapping the anchor into the hole and tightening the nut to secure it, ensuring immediate load-bearing capacity. Epoxy anchors involve injecting a chemical adhesive into the drilled hole before inserting a threaded rod or rebar, which then cures to create a strong bond, but require curing time before load application. The installation process for stud anchors is faster and less dependent on environmental conditions compared to epoxy anchors, which demand clean holes and controlled temperatures for optimal curing and strength.
Load Capacity and Performance
Stud anchors provide superior load capacity compared to epoxy anchors, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring reliable performance under high stress. Unlike epoxy anchors that rely on chemical bonding, stud anchors achieve mechanical interlock with concrete for enhanced shear and tensile strength. Their consistent performance in wet or cracked concrete conditions ensures greater durability and safety in structural installations.
Suitability for Different Base Materials
Stud anchors offer superior performance in concrete and solid masonry due to their mechanical interlock, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications and high-load environments. Epoxy anchors provide greater versatility across various base materials, including hollow or cracked brick and weaker substrates, by chemically bonding to the material's pores. When selecting between stud and epoxy anchors, consider the base material's strength and integrity to ensure optimal load distribution and long-term stability.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Stud anchors exhibit superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to epoxy anchors, thanks to their robust metal construction and resistance to chemical degradation. Unlike epoxy anchors, which can deteriorate under prolonged exposure to moisture and fluctuating temperatures, stud anchors maintain structural integrity in harsh environments. Their galvanized or stainless steel variants offer enhanced protection against rust, making them ideal for long-term applications in construction and infrastructure projects.
Costs and Budget Considerations
Stud anchors generally offer lower upfront costs compared to epoxy anchors, making them more budget-friendly for projects with tight financial constraints. Unlike epoxy anchors, which require specialized adhesives and longer curing times, stud anchors reduce labor expenses and installation time. However, project-specific requirements and load demands should be evaluated to determine the most cost-effective anchoring solution.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Stud anchors are commonly used in heavy-duty applications such as securing structural steel, machinery, and concrete formwork where high load capacity and immediate tensioning are required. Epoxy anchors are preferred for retrofitting and repair work, especially in situations involving irregular concrete conditions or where drilling precision is critical. Stud anchors offer faster installation with superior shear strength, making them ideal for dynamic loads in industrial and construction projects.
Choosing the Right Anchor for Your Project
Stud anchors provide superior load-bearing capacity and immediate strength compared to epoxy anchors, making them ideal for heavy-duty structural applications. Epoxy anchors excel in situations requiring corrosion resistance and versatility in various substrate conditions but demand longer curing times before achieving full strength. Selecting between stud and epoxy anchors hinges on factors such as load requirements, installation environment, and project timelines to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Stud anchor vs epoxy anchor Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com